手写神经网络实现mnist分类
手写神经网络,实现mnist数据集分类。本过程使用numpy实现,没有使用机器学习和深度学习框架。
1. 数据读取及处理
import numpy as np
import struct
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import os
from PIL import Image
from sklearn.utils import gen_batches
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report, confusion_matrix
from typing import *
from numpy.linalg import *
train_image_file = './mnist/train-images-idx3-ubyte'
train_label_file = './mnist/train-labels-idx1-ubyte'
test_image_file = './mnist/t10k-images-idx3-ubyte'
test_label_file = './mnist/t10k-labels-idx1-ubyte'
def decode_image(path):
with open(path, 'rb') as f:
magic, num, rows, cols = struct.unpack('>IIII', f.read(16))
images = np.fromfile(f, dtype=np.uint8).reshape(-1, 784)
images = np.array(images, dtype = float)
return images
def decode_label(path):
with open(path, 'rb') as f:
magic, n = struct.unpack('>II',f.read(8))
labels = np.fromfile(f, dtype=np.uint8)
labels = np.array(labels, dtype = float)
return labels
def load_data():
train_X = decode_image(train_image_file)
train_Y = decode_label(train_label_file)
test_X = decode_image(test_image_file)
test_Y = decode_label(test_label_file)
return (train_X, train_Y, test_X, test_Y)2. 数据随机显示
trainX, trainY, testX, testY = load_data()
num_train, num_feature = trainX.shape
plt.figure(1, figsize=(20,10))
for i in range(8):
idx = np.random.choice(range(num_train))
plt.subplot(int('24'+str(i+1)))
plt.imshow(trainX[idx,:].reshape((28,28)))
plt.title('label is %d'%trainY[idx])
plt.show()3. 标签one-hot化
# normalize the input value to make it between 0 and 1.
trainX, testX = trainX/255, testX/255
# convert labels to one-hot vector.
def to_onehot(y):
y = y.astype(int)
num_class = len(set(y))
Y = np.eye((num_class))
return Y[y]
trainY = to_onehot(trainY)
testY = to_onehot(testY)
num_train, num_feature = trainX.shape
num_test, _ = testX.shape
_, num_class = trainY.shape
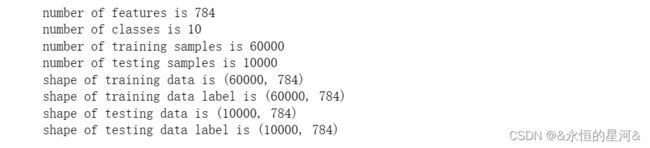
print('number of features is %d'%num_feature)
print('number of classes is %d'%num_class)
print('number of training samples is %d'%num_train)
print('number of testing samples is %d'%num_test)
print('shape of training data is ' + str(trainX.shape))
print('shape of training data label is ' + str(trainX.shape))
print('shape of testing data is ' + str(testX.shape))
print('shape of testing data label is ' + str(testX.shape) )4. 激活函数实现
from abc import ABC, abstractmethod, abstractproperty
class Activation(ABC):
'''
An abstract class that implements an activation function
'''
@abstractmethod
def value(self, x: np.ndarray) -> np.ndarray:
'''
Value of the activation function when input is x.
Parameters:
x is an input to the activation function.
Returns:
Value of the activation function. The shape of the return is the same as that of x.
'''
return x
@abstractmethod
def derivative(self, x: np.ndarray) -> np.ndarray:
'''
Derivative of the activation function with input x.
Parameters:
x is the input to activation function
Returns:
Derivative of the activation function w.r.t x.
'''
return x
class Identity(Activation):
'''
Identity activation function. Input and output are identical.
'''
def __init__(self):
super(Identity, self).__init__()
def value(self, x: np.ndarray) -> np.ndarray:
return x
def derivative(self, x: np.ndarray) -> np.ndarray:
n, m = x.shape
return np.ones((n, m))
class Sigmoid(Activation):
'''
Sigmoid activation function y = 1/(1 + e^(x*k)), where k is the parameter of the sigmoid function
'''
def __init__(self):
'''
Parameters:
there are no parameters.
'''
super(Sigmoid, self).__init__()
def value(self, x: np.ndarray) -> np.ndarray:
'''
Parameters:
x is a two dimensional numpy array.
Returns:
a two dimensioal array representing the element-wise sigmoid of x.
'''
#### write your code below ####
v = 1 / (1+np.exp(-x))
return v
def derivative(self, x: np.ndarray) -> np.ndarray:
'''
Parameters:
x is a two dimensional array.
Returns:
a two dimensional array whose shape is the same as that of x. The returned value is the elementwise
derivative of the sigmoid function w.r.t. x.
'''
#### write your code below ####
d_v = self.value(x) * (1-self.value(x))
return d_v
class ReLU(Activation):
'''
Rectified linear unit activation function
'''
def __init__(self):
super(ReLU, self).__init__()
def value(self, x: np.ndarray) -> np.ndarray:
#### write your code below ####
v = np.maximum(0, x)
return v
def derivative(self, x: np.ndarray) -> np.ndarray:
'''
The derivative of the ReLU function w.r.t. x. Set the derivative to 0 at x=0.
Parameters:
x is a two dimensional array.
Returns:
elementwise derivative of ReLU. The shape of the returned value is the same as that of x.
'''
#### write your code below ####
d_v = np.where(x>0, 1, 0)
return d_v
class Softmax(Activation):
'''
softmax nonlinear function.
'''
def __init__(self):
'''
There are no parameters in softmax function.
'''
super(Softmax, self).__init__()
def value(self, x: np.ndarray) -> np.ndarray:
'''
Parameters:
x is the input to the softmax function. x is a two dimensional numpy array. Each row is the input to the softmax function
Returns:
output of the softmax function. The returned value is with the same shape as that of x.
'''
#### write your code below ####
x = x - x.max(axis=1, keepdims=True)
y = np.exp(x)
return y / y.sum(axis=1, keepdims=True)
def derivative(self, x: np.ndarray) -> np.ndarray:
'''
Parameters:
x is the input to the softmax function. x is a two dimensional numpy array.
Returns:
a two dimensional array representing the derivative of softmax function w.r.t. x.
'''
#### write your code below ####
d_v = self.value(x) * (1-self.value(x))
return d_v4. 损失函数实现
##################################################################################################################
# LOSS FUNCTIONS
##################################################################################################################
class Loss(ABC):
'''
Abstract class for a loss function
'''
@abstractmethod
def value(self, yhat: np.ndarray, y: np.ndarray) -> float:
'''
Value of the empirical loss function.
Parameters:
y_hat is the output of a neural network. The shape of y_hat is (n, k). Each row represents the one sample output.
y contains true labels with shape (n, k).
Returns:
value of the empirical loss function.
'''
return 0
@abstractmethod
def derivative(self, yhat: np.ndarray, y: np.ndarray) -> np.ndarray:
'''
Derivative of the empirical loss function with respect to the predictions.
Parameters:
Returns:
The derivative of the loss function w.r.t. y_hat. The returned value is a two dimensional array with
shape (n, k)
'''
return yhat
class CrossEntropy(Loss):
'''
Cross entropy loss function
'''
def value(self, yhat: np.ndarray, y: np.ndarray) -> float:
#### write your code below ####
delta = 1e-7
return -np.sum(y * np.log(yhat + delta))
def derivative(self, yhat: np.ndarray, y: np.ndarray) -> np.ndarray:
#### write your code below ####
return yhat - y
class CEwithLogit(Loss):
'''
Cross entropy loss function with logits (input of softmax activation function) and true labels as inputs.
'''
def value(self, logits: np.ndarray, y: np.ndarray) -> float:
#### write your code below ####
n, k = y.shape
beta = logits.max(axis = 1).reshape((n, 1))
tmp = np.log(np.sum(np.exp(logits - beta), axis=1)+1e-7)
los = -np.sum(y*logits) + np.sum(beta) + np.sum(tmp)
los = los / n
return los
def derivative(self, logits: np.ndarray, y: np.ndarray) -> np.ndarray:
#### write your code below ####
n, k = y.shape
beta = logits.max(axis = 1).reshape((n, 1))
tmp = logits - beta
tmp = np.exp(tmp)
numer = np.sum(tmp, axis = 1, keepdims = True)
yhat = tmp/numer
der = (yhat - y) / n
return der5. 评估指标实现
##################################################################################################################
# METRICS
##################################################################################################################
def accuracy(y_hat: np.ndarray, y: np.ndarray) -> float:
'''
Accuracy of predictions, given the true labels.
Parameters:
y_hat is the outputs of softmax function. y_hat is with the shape (n, k).
y is the true targets. y is with the shape (n, k).
Returns:
accuracy which is a float number.
'''
#### write your code below ####
n = y.shape[0]
return np.sum(np.argmax(y_hat, axis = 1) == np.argmax(y, axis = 1)) / n6. 神经网络实现
# The following is the python class for neural network.
# Using this class, users can design a neural network with any number of layers within which there could be any number of neuros
class NeuralNetwork():
'''
Fully connected neural network.
Attributes:
n_layers is the number of layers.
activation is a list of Activation objects corresponding to each layer's activation function.
loss is a Loss object corresponding to the loss function used to train the network.
learning_rate is the learning rate.
W is a list of weight matrix used in each layer.
b is a list of biases used in each layer.
'''
def __init__(self, layer_size: List[int], activation: List[Activation], loss: Loss, learning_rate: float = 0.01) -> None:
'''
Initializes a NeuralNetwork object
'''
assert len(activation) == len(layer_size), \
"Number of sizes for layers provided does not equal the number of activation"
self.layer_size = layer_size
self.num_layer = len(layer_size)
self.activation = activation
self.loss = loss
self.learning_rate = learning_rate
self.W = []
self.b = []
for i in range(self.num_layer-1):
W = np.random.randn(layer_size[i], layer_size[i+1]) #/ np.sqrt(layer_size[i])
b = np.random.randn(1, layer_size[i+1])
self.W.append(W)
self.b.append(b)
self.A = []
self.Z = []
def forward(self, X: np.ndarray) -> (List[np.ndarray], List[np.ndarray]):
'''
Forward pass of the network on a dataset of n examples with m features. Except the first layer, each layer
computes linear transformation plus a bias followed by a nonlinear transformation.
Parameters:
X is the training data with shape (n, m).
Returns:
A is a list of numpy data, representing the output of each layer after the first layer. There are
self.num_layer numpy arrays in the list and each array is of shape (n, self.layer_size[i]).
Z is a list of numpy data, representing the input of each layer after the first layer. There are
self.num_layer numpy arrays in the list and each array is of shape (n, self.layer_size[i]).
'''
num_sample = X.shape[0]
A, Z = [], []
T_X = X
#### write your code below ####
for i in range(self.num_layer):
if i == 0:
a = X.copy()
z = X.copy()
else:
a = A[-1]
z = a.dot(self.W[i-1]) + self.b[i-1]
a = self.activation[i].value(z)
Z.append(z)
A.append(a)
self.A = A
self.Z = Z
return Z, A
def backward(self, dLdyhat) -> List[np.ndarray]:
'''
Backward pass of the network on a dataset of n examples with m features. The derivatives are computed from
the end of the network to the front.
Parameters:
dLdyhat is the derivative of the empirical loss w.r.t. yhat which is the output of the neural network.
dLdyhat is with shape (n, self.layer_size[-1])
Returns:
dZ is a list of numpy array. Each numpy array in dZ represents the derivative of the emipirical loss function
w.r.t. the input of that specific layer. There are self.n_layer arrays in the list and each array is of
shape (n, self.layer_size[i])
'''
dZ = []
#### write your code below ####
for i in range(self.num_layer-1, -1, -1):
if i == self.num_layer - 1:
dLdz = dLdyhat
else:
dLda = np.dot(dLdz, self.W[i].T)
dLdz = self.activation[i].derivative(self.Z[i]) * dLda
dZ.append(dLdz)
dZ = list(reversed(dZ))
self.dZ = dZ
return dZ
def update_weights(self) -> List[np.ndarray]:
'''
Having computed the delta values from the backward pass, update each weight with the sum over the training
examples of the gradient of the loss with respect to the weight.
Parameters:
there is no input parameters
Returns:
W is the newly updated weights (i.e. self.W)
'''
#### write your code below ####
for i in range(self.num_layer-1):
a = self.A[i]
dW = np.dot(a.T, self.dZ[i+1])
db = np.sum(self.dZ[i+1], axis = 0, keepdims = True)
self.W[i] -= self.learning_rate*dW
self.b[i] -= self.learning_rate*db
return
def one_epoch(self, X: np.ndarray, Y: np.ndarray, batch_size: int, train: bool = True)-> (float, float):
'''
One epoch of either training or testing procedure.
Parameters:
X is the data input. X is a two dimensional numpy array.
Y is the data label. Y is a one dimensional numpy array.
batch_size is the number of samples in each batch.
train is a boolean value indicating training or testing procedure.
Returns:
loss_value is the average loss function value.
acc_value is the prediction accuracy.
'''
n = X.shape[0]
slices = list(gen_batches(n, batch_size))
num_batch = len(slices)
idx = list(range(n))
np.random.shuffle(idx)
loss_value, acc_value = 0, 0
for i, index in enumerate(slices):
index = idx[slices[i]]
x, y = X[index,:], Y[index]
Z, A = model.forward(x) # Execute forward pass
yhat = A[-1]
z = Z[-1]
if train:
dLdz = self.loss.derivative(z, y) # Calculate derivative of the loss with respect to out
self.backward(dLdz) # Execute the backward pass to compute the deltas
self.update_weights() # Calculate the gradients and update the weights
loss_value += self.loss.value(yhat, y)*x.shape[0]
acc_value += accuracy(yhat, y)*x.shape[0]
loss_value = loss_value/n
acc_value = acc_value/n
return loss_value, acc_value7. 模型训练
def train(model : NeuralNetwork, X: np.ndarray, Y: np.ndarray, batch_size: int, epoches: int) -> (List[np.ndarray], List[float]):
'''
trains the neural network.
Parameters:
model is a NeuralNetwork object.
X is the data input. X is a two dimensional numpy array.
Y is the data label. Y is a one dimensional numpy array.
batch_size is the number of samples in each batch.
epoches is an integer, representing the number of epoches.
Returns:
epoch_loss is a list of float numbers, representing loss function value in all epoches.
epoch_acc is a list of float numbers, representing the accuracies in all epoches.
'''
loss_value, acc = model.one_epoch(X, Y, batch_size, train = False)
epoch_loss, epoch_acc = [loss_value], [acc]
print('Initialization: ', 'loss %.4f '%loss_value, 'accuracy %.2f'%acc)
for epoch in range(epoches):
if epoch%100 == 0 and epoch > 0: # decrease the learning rate
model.learning_rate = min(model.learning_rate/10, 1.0e-5)
loss_value, acc = model.one_epoch(X, Y, batch_size, train = True)
if epoch%1 == 0:
print("Epoch {}/{}: Loss={}, Accuracy={}".format(epoch, epoches, loss_value, acc))
epoch_loss.append(loss_value)
epoch_acc.append(acc)
return epoch_loss, epoch_acc
# training procedure
num_sample, num_feature = trainX.shape
epoches = 200
batch_size = 512
Loss = []
Acc = []
learning_rate = 1/num_sample*batch_size
np.random.seed(2023)
model = NeuralNetwork([784, 256, 64, 10], [Identity(), ReLU(), ReLU(), Softmax()], CEwithLogit(), learning_rate = learning_rate)
epoch_loss, epoch_acc = train(model, trainX, trainY, batch_size, epoches)
# testing procedure
test_loss, test_acc = model.one_epoch(testX, testY, batch_size, train = False)
z, yhat = model.forward(testX)
yhat = np.argmax(yhat, axis = 1)
y = np.argmax(testY, axis = 1)
print(confusion_matrix(yhat, y))
print(classification_report(yhat, y))上面都神经网络原理的基础,希望各位能够手动推导各个公式并实现。