java学习(二):反射
系列文章目录
https://editor.csdn.net/md/?articleId=131757340
文章目录
- 系列文章目录
- 参考
- 【1】注解
-
- 1. 什么是注解
- 2. 内置注解
- 3. 元注解
- 4.自定义注解
- 【2】反射--基本概念
- 一、反射的基本概念
-
- 1. 为什么要用反射?
- 2. 什么是反射?
- 3. 用和不用反射的区别?
- 4.开发中什么场景下用反射?
- 5.反射优点和缺点:
- 二、反射的使用
-
- 1. 获取反射对象的4种方式
- 2.哪些类型哟class对象?
- 三、类加载过程
-
- 1.加载过程
- 2. 补充:java 内存分析
- 3. 类加载器 + 类的双亲委派机制
- 4. 怎么获取类运行过程中的各种对象(方法、参数、构造器等)
- 5. 用class对象能怎么用?
- 6.应用:反射的动态性:
参考
可以参考的笔记: https://blog.csdn.net/ProGram_Java521/article/details/127733167
学习视频:
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1PY411e7J6?p=192&vd_source=585eef59d366645f5bf03840b1010547
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1p4411P7V3/?spm_id_from=333.337.search-card.all.click
【1】注解
1. 什么是注解
–对程序作出解释。@注释名”在代码中存在的,还可以添加一些参数值
注解在哪里使用?–可以附加在package,class,method,field等上面,相当于给他们添加了额外的辅助信息,我们可以通过反射机制实现对这些元数据的访问
2. 内置注解
@Override @Deprecated等
3. 元注解
负责注解其他的注解。通过4个元注解说明其他注解的作用域、作用方式等。
@Target :描述作用范围
@Retention :描述注解的生命周期(源码、类、runtime运行时)
@Document :包含再javadoc中
@Ingerited :自雷可以继承父类中的注解
4.自定义注解
设置作用域、返回类型等可以借助元注解
【2】反射–基本概念
一、反射的基本概念
1. 为什么要用反射?
1)java程序中的两种对象类型,编译时类型 和 运行时类型。如果出现编译时类型和运行时类型不一致,要怎么解决?
2)如果已知运行时类型,可以用instanceof 直接判断。
3)无法预知运行时类型,只能依靠运行时的信息获取对象和类的真实信息 --由此引入反射机制。
2. 什么是反射?
在代码运行过程中,允许程序借助Reflection API取得类的任何内部信息、操作类的属性和方法。
作用:操作字节码
正常方式: 引入包类 --》new 实例化对象 --》 取得实例化对象
反射方式: 实例化对象 --》getClass()方法 --》得到完整的“包类”名称
3. 用和不用反射的区别?
不用反射,出了类之后,private属性和方法不能使用–类的封装性
使用反射:可以访问私有方法属性
4.开发中什么场景下用反射?
1)一般业务开发,对使用对象已知和确定,基本可以不用反射
2)对于框架的开发,体现动态性,考虑使用反射。
5.反射优点和缺点:
优点:自适应 灵活 动态获取
缺点:性能较差。
二、反射的使用
1. 获取反射对象的4种方式
CLass.forName(“完整包名”)
对象.getClass()
任何类型.class
ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader().loadClass(“完整包名”)
基本数据类型 Integer.TYPE
2.哪些类型哟class对象?
class
interface
数组
enum
annotation 注解
基本数据类型
void
三、类加载过程
1.加载过程
·过程1:类的装载(Loading)
把class文件读入内存,并创建一个java.lamg.Class对象,由类加载器完成
·过程2:链接(linking)
验证(verify):确保类加载嘻嘻符合JVM规范。比如,cafebabe
准备(prepare):给static变量分配内存并且设置初始值。这里的内存都在方法区中分配
解析(Resolve):虚拟机常量池内的符号引用(常量名)替换为直接引用(引用地址)
·过程3:初始化(initialization)
执行类构造器方法。
2. 补充:java 内存分析
堆:存new的对象和数组,可以被所有线程共享
栈:存基本变量类型、引用类型的变量(存引用在堆里的具体地址)
方法区:所有class和static变量,被所有线程共享
3. 类加载器 + 类的双亲委派机制
4. 怎么获取类运行过程中的各种对象(方法、参数、构造器等)
常用的API 接口
5. 用class对象能怎么用?
动态创建对象:
1)newInstance 对无参构造函数创建对象
2)getDeclaredConstructor 先获取构造器,在用构造器创建对象。
3)执行方法 getMethod,用invoke进行调用的激活
4)私有属性 方法可以用setAccessible(true); // 关掉权限检测
6.应用:反射的动态性:
package com.common.inject;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
class ReflectTest {
// 举例1:反射的动态性--类
public <T> T getInstance(String className) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException {
Class c1 = Class.forName(className);
Constructor con = c1.getDeclaredConstructor();
con.setAccessible(true);
return (T) con.newInstance();
}
// 举例2:反射的动态性--方法
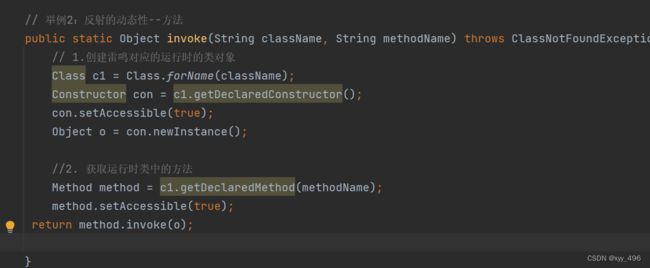
public static Object invoke(String className, String methodName) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException {
// 1.创建雷鸣对应的运行时的类对象
Class c1 = Class.forName(className);
Constructor con = c1.getDeclaredConstructor();
con.setAccessible(true);
Object o = con.newInstance();
//2. 获取运行时类中的方法
Method method = c1.getDeclaredMethod(methodName);
method.setAccessible(true);
return method.invoke(o);
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, InvocationTargetException, NoSuchMethodException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException {
String className ="com.common.inject.LearnInject";
String methodName = "del";
System.out.println(invoke(className, methodName));
}
}
public class LearnInject {
private int id;
public LearnInject() {
}
public LearnInject(int id, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
public int add(int a, int b) {
return a + b;
}
private String del() {
return "This is del method";
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchFieldException, NoSuchMethodException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException {
Class c1 = Class.forName("com.common.inject.LearnInject");
Class c0 = ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader()
.loadClass("com.common.inject.LearnInject");
System.out.println(c1 == c0);
// 创建实例对象:构造器
// LearnInject l1 = (LearnInject)c1.newInstance();
// System.out.println(l1);
Constructor constructor = c1.getDeclaredConstructor(int.class, String.class);
LearnInject l2 = (LearnInject)constructor.newInstance(1, "one");
System.out.println(l2.toString());
System.out.println(l2.add(1, 2));
// 通过反射调用方法
LearnInject l3 = (LearnInject) c1.newInstance();
Method add = c1.getDeclaredMethod("add",int.class,int.class);
int invoke = (int) add.invoke(l3, 1, 2);
System.out.println(invoke);
Field id = c1.getDeclaredField("id");
id.setAccessible(true); // 关掉权限检测
id.set(l3, 10);
System.out.println(l3.id);
// Class c1 = Class.forName("com.common.inject.LearnInject");
// System.out.println(c1);
// System.out.println(c1.hashCode());
//
// System.out.println(c1);
// // 获取类运行过程中的对象
// System.out.println(c1.getName());
// System.out.println(c1.getClassLoader());
// System.out.println(c1.getField("name")); // getField获取public
// System.out.println(c1.getDeclaredField("id")); // getDeclaredField获取所有的变量
//
//
// Method[] methods = c1.getMethods(); // getMethods 获取本类和父类的所有public方法
// for (Method method : methods) {
// System.out.println("getMethods:" + method);
// }
//
//
// methods = c1.getDeclaredMethods(); // getDeclaredMethods 获取本类的所有方法
// for (Method method : methods) {
// System.out.println("getDeclaredMethods:" + method);
// }
//
// System.out.println(c1.getMethod("add", int.class, int.class));
//
// LearnInject learnInject = new LearnInject();
// Class c2 = learnInject.getClass();
// System.out.println(c2);
//
// System.out.println(c2.hashCode());
//
// Class c3 = LearnInject.class;
// System.out.println(c3);
// System.out.println(c3.hashCode());
//
// // 内置基本类型可以用类名.Type
// Class type = Integer.TYPE;
// System.out.println(type.hashCode());
//
// Integer val = new Integer(1);
// System.out.println(val.getClass().hashCode());
}
}