Centos7:Flask-Apache部署
系列文章目录
RHCE第0章:RHCE开始前的准备
RHCE第1章:Web服务器(上)
RHCE第1章:Web服务器(下)
RHCE第2章:DNS服务
RHCE第3章:DHCP服务器
RHCE第4章:Firewall服务、
RHCE第5章:SELinux
RHCE第6章:nfs网络文件系统
RHCE第7章:samba文件共享
RHCE第8章:链路聚合和桥接
RHCE第9章:KVM虚拟化技术
RHCE第10章:时间服务器
RHCE第11章:Mariadb数据库(上)
RHCE第11章:Mariadb数据库(中)
RHCE第11章:Mariadb数据库(下)
RHCE第11章:Mariadb数据库(后)
RHCE第12章:FTP服务
RHCE第13章:ISCSI存储网络
RHCE第14章:邮件服务器
RHCE第15章:Kickstart
Centos7:http/PhP升级
Centos7:Flask-Apache部署
文章目录
- 系列文章目录
- 前言
- 一、安装Python虚拟环境
-
- 1.编译安装
- 2.虚拟环境创建
- 二、安装mod_wsgi
- 三、编写配置文件
-
- 1.flask文件
- 2.虚拟环境文件
- 3.httpd文件
- 总结
前言
之前写过几个Flask网页来完成一些操作,一直使用的都是Screen+uwsgi所以在并发上边支持的不太好(反正就我自己用),但最近完成的一个项目,对并发要求稍微高一点,前几天也在升级软件,就顺便把Flask的安装部署也记录一下。
一、安装Python虚拟环境
1.编译安装
我使用的是Flask==2.1.2官方的最新稳定版。官方建议Python环境使用3.7以上,所以我选择了3.8.5版本编译安装。
官方下载地址

下载完成后上传服务器,解压-编译-安装
tar -xvf Python-3.8.5.tar.xz
cd Python-3.8.5
./configure --enable-shared
make
make install
2.虚拟环境创建
自己选择一个合适的地方创建虚拟环境。
python3 -m venv flask
source flask/bin/activate
二、安装mod_wsgi
官方教程中,可以使用yum命令安装,但实际操作不行,所以还是选择编译安装。
mod_wsgi 4.9.4下载

编译的时候要指定之前安装好的apache和python
tar -xvf mod_wsgi-4.9.4.tar.gz
cd mod_wsgi-4.9.4
./configure --with-apxs=/usr/local/apache2/bin/apxs --with-python=/opt/env/flask/bin/python3
make
make install
三、编写配置文件
1.flask文件
activate_this = '/opt/env/flask/bin/activate_this.py'
with open(activate_this) as file_:
exec(file_.read(), dict(__file__=activate_this))
import sys
sys.path.insert(0, "/var/www/web")
from app import app as application
这时固定写发只有这里面只有两个参数需要改变,一个是第一行的虚拟环境路径,一个是第五行的自己的项目目录路径。
2.虚拟环境文件
第一个文件在虚拟环境中是不存在的,需要我们自己创建
具体内容也是固定写法
vim /opt/env/flask/bin/activate_this.py
"""By using execfile(this_file, dict(__file__=this_file)) you will
activate this virtualenv environment.
This can be used when you must use an existing Python interpreter, not
the virtualenv bin/python
"""
try:
__file__
except NameError:
raise AssertionError(
"You must run this like execfile('path/to/activate_this.py', dict(__file__='path/to/activate_this.py'))")
import sys
import os
old_os_path = os.environ['PATH']
os.environ['PATH'] = os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__)) + os.pathsep + old_os_path
base = os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__)))
if sys.platform == 'win32':
site_packages = os.path.join(base, 'Lib', 'site-packages')
else:
site_packages = os.path.join(base, 'lib', 'python%s' % sys.version[:3], 'site-packages')
prev_sys_path = list(sys.path)
import site
site.addsitedir(site_packages)
sys.real_prefix = sys.prefix
sys.prefix = base
# Move the added items to the front of the path:
new_sys_path = []
for item in list(sys.path):
if item not in prev_sys_path:
new_sys_path.append(item)
sys.path.remove(item)
sys.path[:0] = new_sys_path
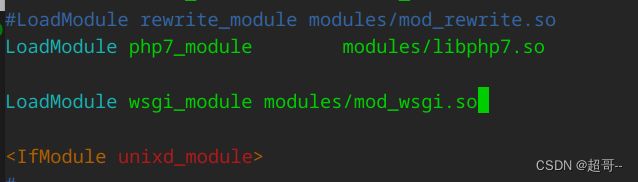
3.httpd文件
编写apache的conf文件
最底下添加一行,意思是将这个目录下的.conf文件都导入
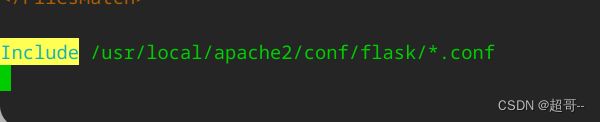
编写.conf文件(前缀随意)
Listen 5000(可以自己设定端口)
<VirtualHost *:5000>
ServerName 你的域名
WSGIDaemonProcess web user=www group=www threads=5
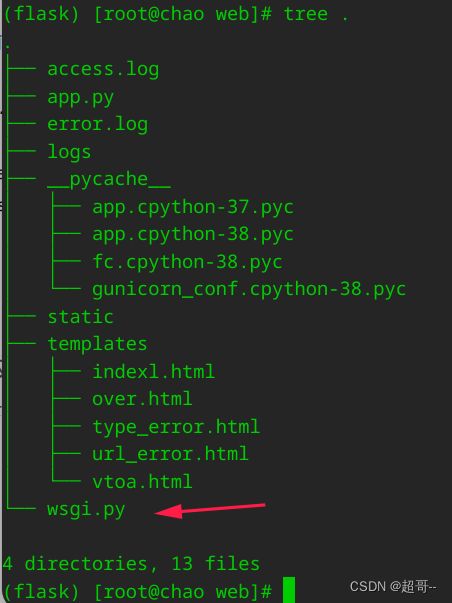
WSGIScriptAlias / /var/www/web/wsgi.py(你的配置文件)
ErrorLog /var/www/web/error.log(日志目录)
CustomLog /var/www/web/access.log combined
DocumentRoot /var/www/web(项目目录)
<Directory /var/www/web>
WSGIProcessGroup web(项目名称)
WSGIApplicationGroup %{GLOBAL}
Require all granted
</Directory>
</VirtualHost>
注意 一些常用的运维知识,比如服务器开放端口之类,请自行学习,也可以看我的RHCE系列专栏。
总结
至此Flask-Apache的部署完成