tensorRT搭建mlp网络教程(C++)
提示:写完文章后,目录可以自动生成,如何生成可参考右边的帮助文档
文章目录
- 前言
- 一、简单介绍tensoorrt
- 二、环境搭建-visual studio
-
- 1.环境搭建前提
- 1.环境搭建步骤
- 三、tensorrt搭建MLP网络步骤
-
- 构建引擎engine步骤
- 推理部署步骤
- 四、权重转换wts
-
- 保存权重wts格式介绍
- 权重wts加载代码
- 五、MLP代码实现
- 总结
前言
本文属于tensorrt入门篇,采用C++ API搭建MLP网络,并实现推理,帮助与我类似的小白更快上手python版本的方法。另外,本文将使用visual studio编译器。
同篇基于python搭建mlp文章链接
提示:以下是本篇文章正文内容,下面案例可供参考
一、简单介绍tensoorrt
TensorRT是英伟达针对自家平台做的一个加速包,可以认为 TensorRT 是一个只有前向传播的深度学习框架,这个框架可以将 Caffe,TensorFlow 的网络模型解析,然后与 TensorRT 中对应的层进行一一映射,把其他框架的模型统一全部转换到 TensorRT 中,然后在 TensorRT 中可以针对 NVIDIA 自家 GPU 实施优化策略,并进行部署加速。根据官方文档,使用TensorRT,在CPU或者GPU模式下其可提供10X乃至100X的加速。本人的实际经验中,TensorRT提供了20X的加速
TensorRT主要做了这么两件事情,来提升模型的运行速度:
1.TensorRT支持INT8和FP16的计算。深度学习网络在训练时,通常使用 32 位或 16 位数据。TensorRT则在网络的推理时选用不这么高的精度,达到加速推断的目的。
2.TensorRT对于网络结构进行了重构,把一些能够合并的运算合并在了一起,针对GPU的特性做了优化。
二、环境搭建-visual studio
1.环境搭建前提
简单介绍visual studio的环境配置,前提条件你已经将tensorrt库相应放在cuda文件夹下了。我将以本人环境作为说明。
前提条件:
将 C:\bag-tangjunjun\TensorRT-8.2.5.1.Windows10.x86_64.cuda-11.4.cudnn8.2\TensorRT-8.2.5.1\include中头文件 复制到C:\Program Files\NVIDIA GPU Computing Toolkit\CUDA\v11.4\include
将C:\bag-tangjunjun\TensorRT-8.2.5.1.Windows10.x86_64.cuda-11.4.cudnn8.2\TensorRT-8.2.5.1\lib 中所有lib文件 复制到C:\Program Files\NVIDIA GPU Computing Toolkit\CUDA\v11.4\lib\x64
将C:\bag-tangjunjun\TensorRT-8.2.5.1.Windows10.x86_64.cuda-11.4.cudnn8.2\TensorRT-8.2.5.1\lib 中所有dll文件复制到C:\Program Files\NVIDIA GPU Computing Toolkit\CUDA\v11.4\bin
1.环境搭建步骤
①选择项目——>xxxx(你的项目名称)属性——>VC++目录——>包含目录,添加库文件路径;
如:C:\Program Files\NVIDIA GPU Computing Toolkit\CUDA\v11.1\include

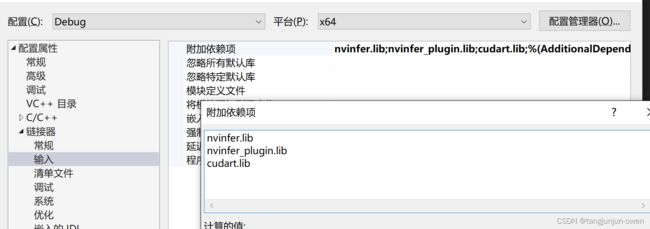
②选择项目——>xxxx(你的项目名称)属性——>VC++目录——>库目录,添加库文件路径;
如:C:\Program Files\NVIDIA GPU Computing Toolkit\CUDA\v11.1\lib\x64
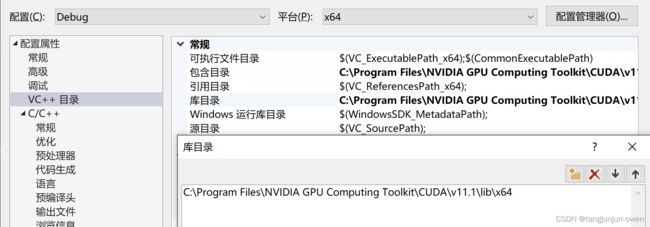
③选择项目——>xxxx(你的项目名称)属性——>链接器——>输入——>附加依赖项,添加以下文件;
nvinfer.lib
nvinfer_plugin.lib
cudart.lib
注:也可将Tensorrt中bin文件夹下的所有.lib后缀添加进来。
三、tensorrt搭建MLP网络步骤
需引用头文件如下:
#include "NvInferRuntimeCommon.h"
#include
using namespace nvinfer1;
构建引擎engine步骤
①构建glogging,为创建builder做准备,简单创建代码如下:
class Logger : public nvinfer1::ILogger
{
void log(Severity severity, const char* msg) noexcept override
{
// suppress info-level messages
if (severity != Severity::kINFO)
std::cout << msg << std::endl;
}
} gLogger;
②创建builder,使用gLogger
IBuilder* builder = createInferBuilder(gLogger); // Create builder with the help of logger 构建builder
③构建网络
INetworkDefinition* network = builder->createNetworkV2(0U); //创造网络
网络构建完毕后,需为网络添加结构,可以使用onnx/caffe/uft解析添加网络,但本篇博客使用C++ API 构建网络,如下:
ITensor* data = network->addInput("data", DataType::kFLOAT, Dims3{ 1, 1, 1 });// Create an input with proper *name 创建输入,参数:名称 类型 维度
IFullyConnectedLayer* fc1 = network->addFullyConnected(*data, 1, weightMap["linear.weight"], weightMap["linear.bias"]); // Add layer for MLP 参数:输入 输出 w权重 b权重
fc1->getOutput(0)->setName("out"); // set output with *name 设置fc1层的输出,(对特殊的网络层通过ITensor->setName()方法设定名称,方便后面的操作);指定网络的output节点,tensorrt必须指定输出节点,否则有可能会在优化过程中将该节点优化掉
network->markOutput(*fc1->getOutput(0)); //设为网络的输出,防止被优化掉
其中weightMap为权重保存变量,类似一个字典
④设置网络参数
调用TensorRT的builder来创建优化的runtime。 builder的其中一个功能是搜索其CUDA内核目录以获得最快的实现,因此用来构建优化的engine的GPU设备和实际跑的GPU设备一定要是相同的才行,这也是为什么无法适应其它环境原因。
builder具有许多属性,可以通过设置这些属性来控制网络运行的精度,以及自动调整参数。还可以查询builder以找出硬件本身支持的降低的精度类型。
有个特别重要的属性,最大batch size :大batch size指定TensorRT将要优化的batch大小。在运行时,只能选择比这个值小的batch。
config有个workspace size:各种layer算法通常需要临时工作空间。这个参数限制了网络中所有的层可以使用的最大的workspace空间大小。 如果分配的空间不足,TensorRT可能无法找到给定层的实现。
IBuilderConfig* config = builder->createBuilderConfig(); // Create hardware configs为builder分配内存,默认全部分配builder->setMaxBatchSize(1); // Set configurations
config->setMaxWorkspaceSize(1 << 20); // Set workspace size
⑤创建引擎engine
ICudaEngine* engine = builder->buildEngineWithConfig(*network, *config);// Build CUDA Engine using network and configurations
network->destroy();//顺带销毁网络,释放内存
⑥引擎engine序列化
IHostMemory** modelStream;//引擎变量声明,并保存序列化结果
(*modelStream) = engine->serialize(); //调用序列化方法
⑦释放内存
engine->destroy(); //释放engine结构
builder->destroy();//释放builder结构
⑧保存序列化引擎
// Open the file and write the contents there in binary format
std::ofstream p(file_engine, std::ios::binary);
if (!p) {
std::cerr << "could not open plan output file" << std::endl;
return;
}
p.write(reinterpret_cast<const char*>(modelStream->data()), modelStream->size());
其中modelStream为序列化的变量,file_engine为保存engine的地址,如:“C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\code\tensorrt-code\mlp\mlp.wts”
⑨释放序列化内存
modelStream->destroy();
以上为tensorrt C++ API 将网络编译成engine,并保存的全部流程,若后续更改不同网络,主要更改步骤③构建网络模块。
推理部署步骤
①读取引擎engine
char* trtModelStream{ nullptr }; //指针函数,创建保存engine序列化文件结果
size_t size{ 0 };
// read model from the engine file
std::ifstream file(file_engine, std::ios::binary);
if (file.good()) {
file.seekg(0, file.end);
size = file.tellg();
file.seekg(0, file.beg);
trtModelStream = new char[size];
assert(trtModelStream);
file.read(trtModelStream, size);
file.close();
}
其中file_engine为:file_engine = “C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\code\tensorrt-code\mlp\mlp.engine”
②反序列化
// create a runtime (required for deserialization of model) with NVIDIA's logger
IRuntime* runtime = createInferRuntime(gLogger); //反序列化方法
assert(runtime != nullptr);
// deserialize engine for using the char-stream
ICudaEngine* engine = runtime->deserializeCudaEngine(trtModelStream, size, nullptr);
assert(engine != nullptr);
/*
一个engine可以有多个execution context,并允许将同一套weights用于多个推理任务。可以在并行的CUDA streams流中按每个stream流一个engine和一个context来处理图像。每个context在engine相同的GPU上创建。
*/
runtime->destroy(); //顺道销毁runtime,释放内存
其中gLogger来源创建引擎构建的glogging
以上为初始化过程,从以下为实施推理过程
③构建可执行方法
IExecutionContext* context = engine->createExecutionContext(); // create execution context -- required for inference executions
④设置输入输出
float out[1]; // array for output
float data[1]; // array for input
for (float& i : data)
i = 12.0; // put any value for input
⑤调用推理
// do inference using the parameters
doInference(*context, data, out, 1);
doInference推理代码如下:
void doInference(IExecutionContext& context, float* input, float* output, int batchSize) {
const ICudaEngine& engine = context.getEngine(); // Get engine from the context
// Pointers to input and output device buffers to pass to engine.
void* buffers[2]; // Engine requires exactly IEngine::getNbBindings() number of buffers.
// In order to bind the buffers, we need to know the names of the input and output tensors.
// Note that indices are guaranteed to be less than IEngine::getNbBindings()
const int inputIndex = engine.getBindingIndex("data");
const int outputIndex = engine.getBindingIndex("out");
// Create GPU buffers on device -- allocate memory for input and output
cudaMalloc(&buffers[inputIndex], batchSize * INPUT_SIZE * sizeof(float));
cudaMalloc(&buffers[outputIndex], batchSize * OUTPUT_SIZE * sizeof(float));
// create CUDA stream for simultaneous CUDA operations
cudaStream_t stream;
cudaStreamCreate(&stream);
// copy input from host (CPU) to device (GPU) in stream
cudaMemcpyAsync(buffers[inputIndex], input, batchSize * INPUT_SIZE * sizeof(float), cudaMemcpyHostToDevice, stream);
// execute inference using context provided by engine
context.enqueue(batchSize, buffers, stream, nullptr);//*******************************************************************************************************************重点推理****************
// copy output back from device (GPU) to host (CPU)
cudaMemcpyAsync(output, buffers[outputIndex], batchSize * OUTPUT_SIZE * sizeof(float), cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost,
stream);
// synchronize the stream to prevent issues (block CUDA and wait for CUDA operations to be completed)
cudaStreamSynchronize(stream);
// Release stream and buffers (memory)
cudaStreamDestroy(stream);
cudaFree(buffers[inputIndex]);
cudaFree(buffers[outputIndex]);
}
以上为tensorrt实现推理过程
四、权重转换wts
Tensorrt对权重的使用–>如何保存tensorrt的权重文件wts,如何使用C++加载权重wts文件
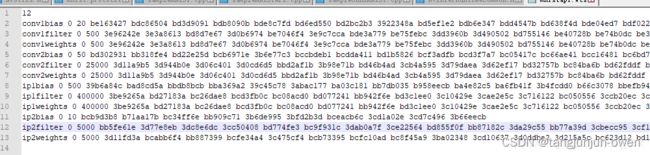
保存权重wts格式介绍
conv1bias就是第一个卷积层的偏置系数,后面的0指的是 kFLOAT 类型,也就是float 32;后面的20是系数的个数,因为输出是20,所以偏置是20个;
convlfiter是卷积核的系数,因为是20个5 x 5的卷积核,所以有20 x 5 x 5=500个参数。
你用相应工具解析解析模型将层名和权值参数键值对存到这个文件中就可以了。
权重wts加载代码
使用C++加载权重方法如下:
/*
Weights是类别类型
class Weights
{
public:
DataType type; //!< The type of the weights.
const void* values; //!< The weight values, in a contiguous array.
int64_t count; //!< The number of weights in the array.
};
*/
//file为文件路径
std::map<std::string, Weights> loadWeights(const std::string file) {
/**
* Parse the .wts file and store weights in dict format.
*
* @param file path to .wts file
* @return weight_map: dictionary containing weights and their values
*/
std::cout << "[INFO]: Loading weights..." << file << std::endl;
std::map<std::string, Weights> weightMap; //定义声明
// Open Weight file
std::ifstream input(file);
assert(input.is_open() && "[ERROR]: Unable to load weight file...");
// Read number of weights
int32_t count;
input >> count;
assert(count > 0 && "Invalid weight map file.");
// Loop through number of line, actually the number of weights & biases
while (count--) {
// TensorRT weights
Weights wt{DataType::kFLOAT, nullptr, 0};
uint32_t size;
// Read name and type of weights
std::string w_name;
input >> w_name >> std::dec >> size;
wt.type = DataType::kFLOAT;
uint32_t *val = reinterpret_cast<uint32_t *>(malloc(sizeof(val) * size));
for (uint32_t x = 0, y = size; x < y; ++x) {
// Change hex values to uint32 (for higher values)
input >> std::hex >> val[x]; //hex为16进制
}
wt.values = val;
wt.count = size;
// Add weight values against its name (key)
weightMap[w_name] = wt; //将权重结果保存此处
}
return weightMap;
}
五、MLP代码实现
本节将给出实现mlp的完整代码,该代码已被修改过,我将logger、构建engine与推理infer整理到一个cpp文件,如下:
旧代码路径可参考我的博客园
#include "NvInfer.h" // TensorRT library
#include "iostream" // Standard input/output library
//#include "logging.h" // logging file -- by NVIDIA
#include // for weight maps
#include 总结
本文使用tensorrt的C++ API方式,通过手动构建network部分,实现mlp网络搭建,可供读者初步学习。