SkyWalking8.7源码解析(五):链路基本知识、链路ID生成、TraceSegment、Span基本概念、Span完整模型、StackBasedTracingSpan
21、链路基本知识
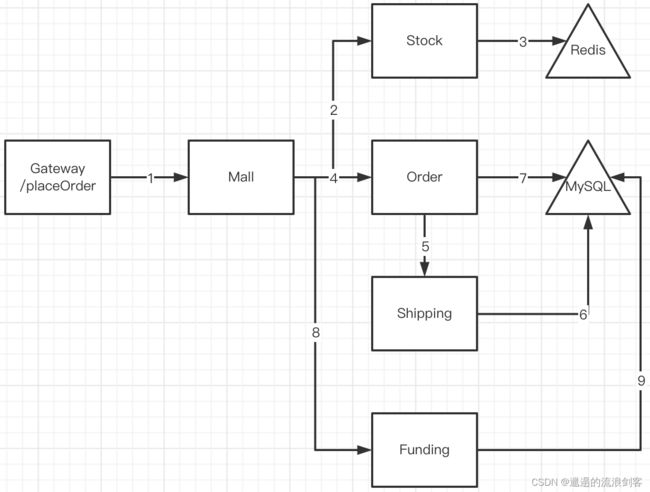
上图是一个下单接口的链路,在链路中首先要理解的概念是Segment,Segment表示一个JVM进程内的所有操作,上图中有6个Segment。Gateway Segment是Mall Segment的parent,通过parent关系就可以把多个Segment按顺序拼起来组装成一个链路
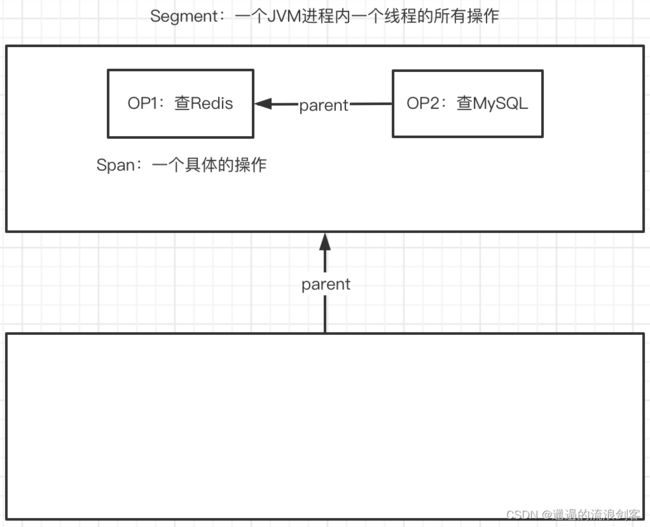
一个Segment里可能发生多个操作,如上图Segment中操作1是查Redis,操作2是查MySQL,这就是两个Span,Span表示一个具体的操作。Span之间也是基于parent的关系构建起来的,而Segment是Span的容器

多个Segment连接起来就组成了一个Trace,每个Trace都有一个全局唯一的ID
推荐阅读:
OpenTracing语义规范
OpenTracing语义规范译文
谷歌Dapper论文
谷歌Dapper论文译文
小结:

22、链路ID生成
定义了traceId的抽象类DistributedTraceId,代码如下:
/**
* The DistributedTraceId presents a distributed call chain.
*
* This call chain has a unique (service) entrance,
*
* such as: Service : http://www.skywalking.com/cust/query, all the remote, called behind this service, rest remote, db
* executions, are using the same DistributedTraceId even in different JVM.
* 在一条链路中(Trace),无论请求分布于多少不同的进程中,这个TraceId都不会改变
*
* The DistributedTraceId contains only one string, and can NOT be reset, creating a new instance is the
* only option.
*/
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@ToString
@EqualsAndHashCode
public abstract class DistributedTraceId {
@Getter
private final String id;
}

DistributedTraceId有两个实现PropagatedTraceId和NewDistributedTraceId
PropagatedTraceId构造函数需要传入traceId并赋值
public class PropagatedTraceId extends DistributedTraceId {
public PropagatedTraceId(String id) {
super(id);
}
}
NewDistributedTraceId会通过GlobalIdGenerator的generate()方法生成traceId并赋值
public class NewDistributedTraceId extends DistributedTraceId {
public NewDistributedTraceId() {
super(GlobalIdGenerator.generate());
}
}
GlobalIdGenerator的generate()方法,该方法用于生成TraceId和SegmentId,代码如下:
/**
* 生成唯一ID
* TraceId SegmentId
*/
public final class GlobalIdGenerator {
private static final String PROCESS_ID = UUID.randomUUID().toString().replaceAll("-", "");
private static final ThreadLocal<IDContext> THREAD_ID_SEQUENCE = ThreadLocal.withInitial(
() -> new IDContext(System.currentTimeMillis(), (short) 0));
private GlobalIdGenerator() {
}
/**
* 生成一个新的id由三部分组成
* Generate a new id, combined by three parts.
*
* 第一部分表示应用实例的id
* The first one represents application instance id.
*
* 第二部分表示线程id
* The second one represents thread id.
*
* 第三部分包含两部分,一个毫秒级的时间戳+一个当前线程里的序号(0-9999不断循环)
* The third one also has two parts, 1) a timestamp, measured in milliseconds 2) a seq, in current thread, between
* 0(included) and 9999(included)
*
* @return unique id to represent a trace or segment
*/
public static String generate() {
return StringUtil.join(
'.',
PROCESS_ID,
String.valueOf(Thread.currentThread().getId()),
String.valueOf(THREAD_ID_SEQUENCE.get().nextSeq())
);
}
生成的traceId由三部分组成,第一部分表示应用实例的Id,是一个UUID;第二部分表示线程Id;第三部分是一个毫秒级的时间戳+一个当前线程里的序号,该序号的范围是0-9999
第三部分调用ThreadLocal中IDContext的nextSeq()方法生成,代码如下:
public final class GlobalIdGenerator {
private static final ThreadLocal<IDContext> THREAD_ID_SEQUENCE = ThreadLocal.withInitial(
() -> new IDContext(System.currentTimeMillis(), (short) 0));
private static class IDContext {
// 上次生成sequence的时间戳
private long lastTimestamp;
// 线程的序列号
private short threadSeq;
// Just for considering time-shift-back only.
// 时钟回拨
private long lastShiftTimestamp;
private int lastShiftValue;
private IDContext(long lastTimestamp, short threadSeq) {
this.lastTimestamp = lastTimestamp;
this.threadSeq = threadSeq;
}
private long nextSeq() {
// 时间戳 * 10000 + 线程的序列号
return timestamp() * 10000 + nextThreadSeq();
}
private long timestamp() {
long currentTimeMillis = System.currentTimeMillis();
if (currentTimeMillis < lastTimestamp) { // 发生了时钟回拨
// Just for considering time-shift-back by Ops or OS. @hanahmily 's suggestion.
if (lastShiftTimestamp != currentTimeMillis) {
lastShiftValue++;
lastShiftTimestamp = currentTimeMillis;
}
return lastShiftValue;
} else { // 时钟正常
lastTimestamp = currentTimeMillis;
return lastTimestamp;
}
}
private short nextThreadSeq() {
if (threadSeq == 10000) {
threadSeq = 0;
}
return threadSeq++;
}
}
23、TraceSegment
先来看下TraceSegment中定义的属性:
/**
* {@link TraceSegment} is a segment or fragment of the distributed trace. See https://github.com/opentracing/specification/blob/master/specification.md#the-opentracing-data-model
* A {@link TraceSegment} means the segment, which exists in current {@link Thread}. And the distributed trace is formed
* by multi {@link TraceSegment}s, because the distributed trace crosses multi-processes, multi-threads.
*
* Trace不是一个具体的数据模型,而是多个Segment串起来表示的逻辑对象
*/
public class TraceSegment {
/**
* 每个segment都有一个全局唯一的id
* The id of this trace segment. Every segment has its unique-global-id.
*/
private String traceSegmentId;
/**
* 指向当前segment的parent segment的指针
* 对于大部分RPC调用,ref只会包含一个元素.但如果是批处理或者是消息队列,就会有多个parents,这里时候只会保存第一个引用
* The refs of parent trace segments, except the primary one. For most RPC call, {@link #ref} contains only one
* element, but if this segment is a start span of batch process, the segment faces multi parents, at this moment,
* we only cache the first parent segment reference.
*
* 这个字段不会被序列化.为了快速访问整条链路保存了parent的引用
* This field will not be serialized. Keeping this field is only for quick accessing.
*/
private TraceSegmentRef ref;
- traceSegmentId:每个Segment都有一个全局唯一的Id
- ref:指向当前Segment的Parent Segment的指针
TraceSegmentRef的代码如下:
@Getter
public class TraceSegmentRef {
private SegmentRefType type; // segment类型:跨进程或跨线程
private String traceId;
private String traceSegmentId; // parent segmentId
private int spanId; // parent segment spanId
private String parentService; // Mall -> Order 对于Order服务来讲,parentService就是Mall
private String parentServiceInstance; // parentService的具体一个实例
private String parentEndpoint; // 进入parentService的那个请求
private String addressUsedAtClient;
public enum SegmentRefType {
CROSS_PROCESS, CROSS_THREAD
}
public class TraceSegment {
/**
* The spans belong to this trace segment. They all have finished. All active spans are hold and controlled by
* "skywalking-api" module.
* 保存segment中所有的span
*/
private List<AbstractTracingSpan> spans;
/**
* The relatedGlobalTraceId represent the related trace. Most time it related only one
* element, because only one parent {@link TraceSegment} exists, but, in batch scenario, the num becomes greater
* than 1, also meaning multi-parents {@link TraceSegment}. But we only related the first parent TraceSegment.
* 当前segment所在trace的id
*/
private DistributedTraceId relatedGlobalTraceId;
- spans:保存Segment中所有的Span
- relatedGlobalTraceId:当前Segment所在Trace的Id
TraceSegment中的定义方法如下:
public class TraceSegment {
/**
* 创建一个空的trace segment,生成一个新的segment id
* Create a default/empty trace segment, with current time as start time, and generate a new segment id.
*/
public TraceSegment() {
this.traceSegmentId = GlobalIdGenerator.generate();
this.spans = new LinkedList<>();
this.relatedGlobalTraceId = new NewDistributedTraceId();
this.createTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
}
/**
* 设置当前segment的parent segment
* Establish the link between this segment and its parents.
*
* @param refSegment {@link TraceSegmentRef}
*/
public void ref(TraceSegmentRef refSegment) {
if (null == ref) {
this.ref = refSegment;
}
}
/**
* 将当前segment关联到某一条trace上
* Establish the line between this segment and the relative global trace id.
*/
public void relatedGlobalTrace(DistributedTraceId distributedTraceId) {
if (relatedGlobalTraceId instanceof NewDistributedTraceId) {
this.relatedGlobalTraceId = distributedTraceId;
}
}
/**
* 添加span
* After {@link AbstractSpan} is finished, as be controller by "skywalking-api" module, notify the {@link
* TraceSegment} to archive it.
*/
public void archive(AbstractTracingSpan finishedSpan) {
spans.add(finishedSpan);
}
/**
* Finish this {@link TraceSegment}. return this, for chaining
*/
public TraceSegment finish(boolean isSizeLimited) {
this.isSizeLimited = isSizeLimited;
return this;
}
finish()需要传入isSizeLimited,SkyWalking中限制了Segment中Span的数量,默认是最大是300,上层调用finish()方法时会判断此时该Segment中的Span是否到达上限
public class Config {
public static class Agent {
/**
* The max number of spans in a single segment. Through this config item, SkyWalking keep your application
* memory cost estimated.
*/
public static int SPAN_LIMIT_PER_SEGMENT = 300;
小结:
24、Span基本概念
Span的最顶层实现为AsyncSpan,代码如下:
/**
* Span能够使用这些API来激活并扩展它的生命周期跨线程
* Span could use these APIs to active and extend its lift cycle across thread.
*
* 这个典型的使用是在异步插件,尤其是RPC插件
* This is typical used in async plugin, especially RPC plugins.
*/
public interface AsyncSpan {
/**
* The span finish at current tracing context, but the current span is still alive, until {@link #asyncFinish}
* called.
*
* This method must be called
*
* 1. In original thread(tracing context). 2. Current span is active span.
*
* During alive, tags, logs and attributes of the span could be changed, in any thread.
*
* The execution times of {@link #prepareForAsync} and {@link #asyncFinish()} must match.
*
* @return the current span
*/
AbstractSpan prepareForAsync();
/**
* Notify the span, it could be finished.
*
* The execution times of {@link #prepareForAsync} and {@link #asyncFinish()} must match.
*
* @return the current span
*/
AbstractSpan asyncFinish();
}
AbstractSpan继承了AsyncSpan,代码如下:
/**
* AbstractSpan定义了Span的骨架
* The AbstractSpan represents the span's skeleton, which contains all open methods.
*/
public interface AbstractSpan extends AsyncSpan {
/**
* Set the component id, which defines in {@link ComponentsDefine}
* 指定当前span表示的操作发生在哪个插件上
*
* @return the span for chaining.
*/
AbstractSpan setComponent(Component component);
/**
* 指定当前span表示的操作所在的插件属于哪一种skywalking划分的类型
*
* @param layer
* @return
*/
AbstractSpan setLayer(SpanLayer layer);
setLayer()用于指定当前Span表示的操作所在的插件属于哪一种SkyWalking划分的类型,在SpanLayer中定义了五种类型:
public enum SpanLayer {
DB(1), RPC_FRAMEWORK(2), HTTP(3), MQ(4), CACHE(5);
public AbstractSpan extends AsyncSpan {
/**
* span上打标签
*/
AbstractSpan tag(AbstractTag<?> tag, String value);
/**
* 记录异常,时间使用当前本地时间
* Record an exception event of the current walltime timestamp.
* wallTime:挂钟时间,本地时间
* serverTime:服务器时间
*
* @param t any subclass of {@link Throwable}, which occurs in this span.
* @return the Span, for chaining
*/
AbstractSpan log(Throwable t);
/**
* 是否是entry span
* @return true if the actual span is an entry span.
*/
boolean isEntry();
/**
* 是否是exit span
* @return true if the actual span is an exit span.
*/
boolean isExit();
/**
* 记录指定时间发生的事件
* Record an event at a specific timestamp.
*
* @param timestamp The explicit timestamp for the log record.
* @param event the events
* @return the Span, for chaining
*/
AbstractSpan log(long timestamp, Map<String, ?> event);
/**
* Sets the string name for the logical operation this span represents.
* 如果当前span的操作是:
* 一个http请求,那么operationName就是请求的url
* 一条sql语句,那么operationName就是sql
* 一个redis操作,那么operationName就是redis命令
*
* @return this Span instance, for chaining
*/
AbstractSpan setOperationName(String operationName);
/**
* Start a span.
*
* @return this Span instance, for chaining
*/
AbstractSpan start();
/**
* Get the id of span
*
* @return id value.
*/
int getSpanId();
String getOperationName();
/**
* Reference other trace segment.
*
* @param ref segment ref
*/
void ref(TraceSegmentRef ref);
AbstractSpan start(long startTime);
/**
* 什么叫peer,就是对端地址
* 一个请求可能跨多个进程,操作多种中间件,那么每一次RPC,对面的服务的地址就是remotePeer
* 每一次中间件的操作,中间件的地址就是remotePeer
*
* @param remotePeer
* @return
*/
AbstractSpan setPeer(String remotePeer);
小结:

25、Span完整模型
抽象类AbstractTracingSpan实现了AbstractSpan接口,代码如下:
/**
* The AbstractTracingSpan represents a group of {@link AbstractSpan} implementations, which belongs a real
* distributed trace.
*/
public abstract class AbstractTracingSpan implements AbstractSpan {
/**
* span id从0开始
* Span id starts from 0.
*/
protected int spanId;
/**
* parent span id从0开始.-1代表没有parent span
* Parent span id starts from 0. -1 means no parent span.
*/
protected int parentSpanId;
/**
* span上的tag
*/
protected List<TagValuePair> tags;
protected String operationName;
protected SpanLayer layer;
/**
* The span has been tagged in async mode, required async stop to finish.
* 表示当前异步操作是否已经开始
*/
protected volatile boolean isInAsyncMode = false;
/**
* The flag represents whether the span has been async stopped
* 表示当前异步操作是否已经结束
*/
private volatile boolean isAsyncStopped = false;
/**
* The context to which the span belongs
* TracingContext用于管理一条链路上的segment和span
*/
protected final TracingContext owner;
/**
* The start time of this Span.
*/
protected long startTime;
/**
* The end time of this Span.
*/
protected long endTime;
/**
* Error has occurred in the scope of span.
*/
protected boolean errorOccurred = false;
protected int componentId = 0;
/**
* Log is a concept from OpenTracing spec. https://github.com/opentracing/specification/blob/master/specification.md#log-structured-data
*/
protected List<LogDataEntity> logs;
/**
* The refs of parent trace segments, except the primary one. For most RPC call, {@link #refs} contains only one
* element, but if this segment is a start span of batch process, the segment faces multi parents, at this moment,
* we use this {@link #refs} to link them.
* 用于当前span指定自己所在的segment的前一个segment,除非这个span所在的segment是整条链路上的第一个segment
*/
protected List<TraceSegmentRef> refs;
/**
* Finish the active Span. When it is finished, it will be archived by the given {@link TraceSegment}, which owners
* it.
* span结束的时候,添加到TraceSegment的spans中
* @param owner of the Span.
*/
public boolean finish(TraceSegment owner) {
this.endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
owner.archive(this);
return true;
}
SkyWalking中Trace数据模型的实现如下图:
一个Trace由多个TraceSegment组成,TraceSegment使用TraceSegmentRef指向它的上一个TraceSegment。每个TraceSegment中有多个Span,每个Span都有spanId和parentSpanId,spanId从0开始,parentSpanId指向上一个span的Id。一个TraceSegment中第一个创建的Span叫EntrySpan,调用的本地方法对应LocalSpan,离开当前Segment对应ExitSpan。每个Span都有一个refs,每个TraceSegment的第一个Span的refs会指向它所在TraceSegment的上一个TraceSegment
小结:

26、StackBasedTracingSpan
StackBasedTracingSpan是一个内部具有栈结构的Span,它可以启动和关闭多次在一个类似栈的执行流程中
在看StackBasedTracingSpan源码之前,我们先来看下StackBasedTracingSpan的工作原理:
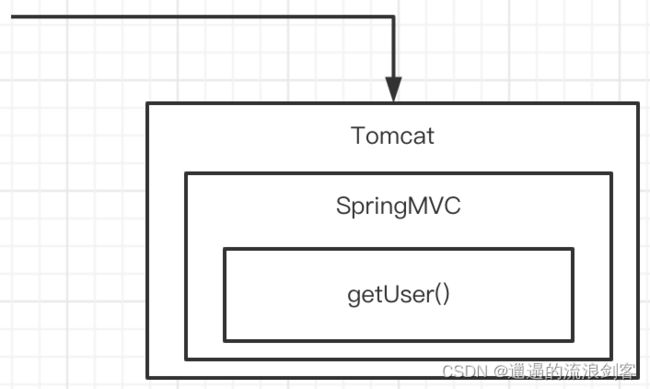
如上图,假设有一个应用部署在Tomcat上,使用SpringMVC提供一个getUser()的Controller方法,getUser()方法直接返回不会调用其他的第三方

在这样一个单体结构中,只会有一个TraceSegment,TraceSegment中会有一个EntrySpan
请求进来后,走到Tomcat,SkyWalking的Tomcat插件会尝试创建EntrySpan,如果发现自己是这个请求到达后第一个工作的插件就会创建EntrySpan,如果不是第一个就会复用之前插件创建的EntrySpan。Tomcat插件创建EntrySpan,并会在Span上记录tags、logs、component、layer等信息,代码如下:
public class TomcatInvokeInterceptor implements InstanceMethodsAroundInterceptor {
@Override
public void beforeMethod(EnhancedInstance objInst, Method method, Object[] allArguments, Class<?>[] argumentsTypes,
MethodInterceptResult result) throws Throwable {
Request request = (Request) allArguments[0];
ContextCarrier contextCarrier = new ContextCarrier();
CarrierItem next = contextCarrier.items();
while (next.hasNext()) {
next = next.next();
next.setHeadValue(request.getHeader(next.getHeadKey()));
}
// 创建EntrySpan
AbstractSpan span = ContextManager.createEntrySpan(request.getRequestURI(), contextCarrier);
Tags.URL.set(span, request.getRequestURL().toString());
Tags.HTTP.METHOD.set(span, request.getMethod());
span.setComponent(ComponentsDefine.TOMCAT);
SpanLayer.asHttp(span);
if (TomcatPluginConfig.Plugin.Tomcat.COLLECT_HTTP_PARAMS) {
collectHttpParam(request, span);
}
}
请求经过Tomcat后交给SpringMVC,SpringMVC插件也会创建EntrySpan,代码如下:
public abstract class AbstractMethodInterceptor implements InstanceMethodsAroundInterceptor {
@Override
public void beforeMethod(EnhancedInstance objInst, Method method, Object[] allArguments, Class<?>[] argumentsTypes,
MethodInterceptResult result) throws Throwable {
Boolean forwardRequestFlag = (Boolean) ContextManager.getRuntimeContext().get(FORWARD_REQUEST_FLAG);
/**
* Spring MVC plugin do nothing if current request is forward request.
* Ref: https://github.com/apache/skywalking/pull/1325
*/
if (forwardRequestFlag != null && forwardRequestFlag) {
return;
}
String operationName;
if (SpringMVCPluginConfig.Plugin.SpringMVC.USE_QUALIFIED_NAME_AS_ENDPOINT_NAME) {
operationName = MethodUtil.generateOperationName(method);
} else {
EnhanceRequireObjectCache pathMappingCache = (EnhanceRequireObjectCache) objInst.getSkyWalkingDynamicField();
String requestURL = pathMappingCache.findPathMapping(method);
if (requestURL == null) {
requestURL = getRequestURL(method);
pathMappingCache.addPathMapping(method, requestURL);
requestURL = pathMappingCache.findPathMapping(method);
}
operationName = getAcceptedMethodTypes(method) + requestURL;
}
Object request = ContextManager.getRuntimeContext().get(REQUEST_KEY_IN_RUNTIME_CONTEXT);
if (request != null) {
StackDepth stackDepth = (StackDepth) ContextManager.getRuntimeContext().get(CONTROLLER_METHOD_STACK_DEPTH);
if (stackDepth == null) {
final ContextCarrier contextCarrier = new ContextCarrier();
if (IN_SERVLET_CONTAINER && HttpServletRequest.class.isAssignableFrom(request.getClass())) {
final HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest = (HttpServletRequest) request;
CarrierItem next = contextCarrier.items();
while (next.hasNext()) {
next = next.next();
next.setHeadValue(httpServletRequest.getHeader(next.getHeadKey()));
}
// 创建EntrySpan
AbstractSpan span = ContextManager.createEntrySpan(operationName, contextCarrier);
Tags.URL.set(span, httpServletRequest.getRequestURL().toString());
Tags.HTTP.METHOD.set(span, httpServletRequest.getMethod());
span.setComponent(ComponentsDefine.SPRING_MVC_ANNOTATION);
SpanLayer.asHttp(span);
if (SpringMVCPluginConfig.Plugin.SpringMVC.COLLECT_HTTP_PARAMS) {
RequestUtil.collectHttpParam(httpServletRequest, span);
}
if (!CollectionUtil.isEmpty(SpringMVCPluginConfig.Plugin.Http.INCLUDE_HTTP_HEADERS)) {
RequestUtil.collectHttpHeaders(httpServletRequest, span);
}
} else if (ServerHttpRequest.class.isAssignableFrom(request.getClass())) {
final ServerHttpRequest serverHttpRequest = (ServerHttpRequest) request;
CarrierItem next = contextCarrier.items();
while (next.hasNext()) {
next = next.next();
next.setHeadValue(serverHttpRequest.getHeaders().getFirst(next.getHeadKey()));
}
// 创建EntrySpan
AbstractSpan span = ContextManager.createEntrySpan(operationName, contextCarrier);
Tags.URL.set(span, serverHttpRequest.getURI().toString());
Tags.HTTP.METHOD.set(span, serverHttpRequest.getMethodValue());
span.setComponent(ComponentsDefine.SPRING_MVC_ANNOTATION);
SpanLayer.asHttp(span);
if (SpringMVCPluginConfig.Plugin.SpringMVC.COLLECT_HTTP_PARAMS) {
RequestUtil.collectHttpParam(serverHttpRequest, span);
}
if (!CollectionUtil.isEmpty(SpringMVCPluginConfig.Plugin.Http.INCLUDE_HTTP_HEADERS)) {
RequestUtil.collectHttpHeaders(serverHttpRequest, span);
}
} else {
throw new IllegalStateException("this line should not be reached");
}
stackDepth = new StackDepth();
ContextManager.getRuntimeContext().put(CONTROLLER_METHOD_STACK_DEPTH, stackDepth);
} else {
AbstractSpan span = ContextManager.createLocalSpan(buildOperationName(objInst, method));
span.setComponent(ComponentsDefine.SPRING_MVC_ANNOTATION);
}
stackDepth.increment();
}
}
Tomcat已经创建了EntrySpan,SpringMVC就不能再创建EntrySpan了,SpringMVC会复用Tomcat创建的EntrySpan。Tomcat已经在Span上记录tags、logs、component、layer等信息,SpringMVC这里会覆盖掉之前Tomcat在Span上记录的信息
EntrySpan就是使用StackBasedTracingSpan这种基于栈的Span来实现的,EntrySpan中有两个属性:当前栈深stackDepth和当前最大栈深currentMaxDepth

Tomcat创建EntrySpan,EntrySpan中当前栈深=1,当前最大栈深=1

SpringMVC复用Tomcat创建的EntrySpan,会把当前栈深和当前最大栈深都+1,此时当前栈深=2,当前最大栈深=2

当getUser()方法执行完后,首先返回到SpringMVC,会把当前栈深-1,当前最大栈深是只增不减的,此时当前栈深=1,当前最大栈深=2

当返回到Tomcat时,当前栈深-1,此时当前栈深=0,当前最大栈深=2,当前栈深=0时,就代表EntrySpan出栈了

如何判断当前EntrySpan是复用前面的呢?只需要判断currentMaxDepth不等于1就是复用前面的EntrySpan,如果等于1就是当前插件创建的EntrySpan。记录Span信息的时候都是请求进来EntrySpan入栈的流程,只要stackDepth=currentMaxDepth时就是请求进来的流程,所以只有stackDepth=currentMaxDepth时才允许记录Span的信息
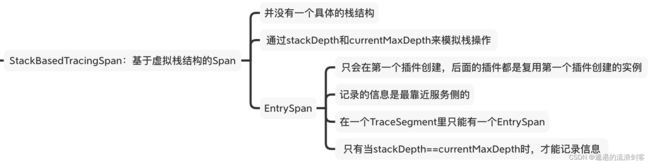
EntrySpan有如下几个特性:
- 在一个TraceSegment里面只能存在一个EntrySpan
- 后面的插件复用前面插件创建的EntrySpan时会覆盖掉前面插件设置的Span信息
- EntrySpan记录的信息永远是最靠近服务提供侧的信息
EntrySpan和ExitSpan都是通过StackBasedTracingSpan来实现的,继承关系如下:

StackBasedTracingSpan中包含stackDepth属性,代码如下:
/**
* StackBasedTracingSpan是一个内部具有栈结构的Span
* The StackBasedTracingSpan represents a span with an inside stack construction.
*
* 这种类型的Span可以启动和关闭多次在一个类似栈的执行流程中
* This kind of span can start and finish multi times in a stack-like invoke line.
*/
public abstract class StackBasedTracingSpan extends AbstractTracingSpan {
protected int stackDepth;
@Override
public boolean finish(TraceSegment owner) {
if (--stackDepth == 0) {
return super.finish(owner);
} else {
return false;
}
}
finish()方法中,当stackDepth等于0时,栈就空了,就代表EntrySpan结束了
EntrySpan中包含currentMaxDepth属性,代码如下:
/**
* The EntrySpan represents a service provider point, such as Tomcat server entrance.
*
* It is a start point of {@link TraceSegment}, even in a complex application, there maybe have multi-layer entry point,
* the EntrySpan only represents the first one.
*
* But with the last EntrySpan's tags and logs, which have more details about a service provider.
*
* Such as: Tomcat Embed - Dubbox The EntrySpan represents the Dubbox span.
*/
public class EntrySpan extends StackBasedTracingSpan {
private int currentMaxDepth;
public EntrySpan(int spanId, int parentSpanId, String operationName, TracingContext owner) {
super(spanId, parentSpanId, operationName, owner);
this.currentMaxDepth = 0;
}
/**
* Set the {@link #startTime}, when the first start, which means the first service provided.
* EntrySpan只会由第一个插件创建,但是后面的插件复用EntrySpan时都要来调用一次start方法
* 因为每一个插件都认为自己是第一个创建这个EntrySpan的
*/
@Override
public EntrySpan start() {
// currentMaxDepth = stackDepth = 1时,才调用start方法记录启动时间
if ((currentMaxDepth = ++stackDepth) == 1) {
super.start();
}
// 复用span时清空之前插件记录的span信息
clearWhenRestart();
return this;
}
@Override
public EntrySpan tag(String key, String value) {
// stackDepth = currentMaxDepth时,才记录span信息
if (stackDepth == currentMaxDepth || isInAsyncMode) {
super.tag(key, value);
}
return this;
}
@Override
public AbstractTracingSpan setLayer(SpanLayer layer) {
if (stackDepth == currentMaxDepth || isInAsyncMode) {
return super.setLayer(layer);
} else {
return this;
}
}
@Override
public AbstractTracingSpan setComponent(Component component) {
if (stackDepth == currentMaxDepth || isInAsyncMode) {
return super.setComponent(component);
} else {
return this;
}
}
@Override
public AbstractTracingSpan setOperationName(String operationName) {
if (stackDepth == currentMaxDepth || isInAsyncMode) {
return super.setOperationName(operationName);
} else {
return this;
}
}
@Override
public EntrySpan log(Throwable t) {
super.log(t);
return this;
}
@Override
public boolean isEntry() {
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean isExit() {
return false;
}
private void clearWhenRestart() {
this.componentId = DictionaryUtil.nullValue();
this.layer = null;
this.logs = null;
this.tags = null;
}
}
小结:
参考:
SkyWalking8.7.0源码分析(如果你对SkyWalking Agent源码感兴趣的话,强烈建议看下该教程)

