POI和esayExcel
目前比较流行的就是Apache PoI和阿里巴巴的easyExcel!
PIO
Apache POI 是用Java编写的免费开源的跨平台的 Java API,Apache POI提供API给Java程序对Microsoft Office格式档案读和写的功能。POI为“Poor Obfuscation Implementation”的首字母缩写,意为“简洁版的模糊实现”。

1 POI-Excel写操作
注意:xsl是03版本的,xlsx是07版本的,他们的区别有:
1.1 依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.poigroupId>
<artifactId>poiartifactId>
<version>3.9version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.poigroupId>
<artifactId>poi-ooxmlartifactId>
<version>3.9version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>joda-timegroupId>
<artifactId>joda-timeartifactId>
<version>2.10.1version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junitgroupId>
<artifactId>junitartifactId>
<version>3.8.1version>
dependency>
1.2 写操作
(1)03版本
@Test
public void testWrite03() throws IOException {
// 创建工作簿 07是HSSFWorkbook
Workbook workbook = new HSSFWorkbook();
// 创建工作表
Sheet sheet = workbook.createSheet("学生统计表");
// 创建一行
Row row1 = sheet.createRow(0);
// 创建单元格
// 第一行第一个
Cell cell11 = row1.createCell(0);
cell11.setCellValue("姓名");
// 第一行第二个
Cell cell12 = row1.createCell(1);
cell12.setCellValue("年龄");
Cell cell13 = row1.createCell(2);
cell13.setCellValue("性别");
Row row2 = sheet.createRow(1);
Cell cell21 = row2.createCell(0);
cell21.setCellValue("王五");
// 第一行第二个
Cell cell22 = row2.createCell(1);
cell22.setCellValue("20");
Cell cell23 = row2.createCell(2);
cell23.setCellValue("男");
// 生成表(IO流)
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(path + "student03.xls");
workbook.write(fileOutputStream);
if(fileOutputStream != null) {
fileOutputStream.close();
}
}
(2)07版本
- 07 版本是XSSFWorkbook, 03版本是HSSFWorkbook
- 07版本后缀是.xlsx, 03版本是xls
1 POI-Excel批量写操作
(1)03版本HSSF
缺点:最多只能处理65536行,否则会抛出异常。
优点:过程中写入缓存,不操作磁盘,最后一次性写入磁盘,速度快。
@Test
public void testWriteBatch() throws IOException {
Workbook workbook = new HSSFWorkbook();
Sheet sheet = workbook.createSheet("统计表");
for (int rowNum = 0; rowNum < 65536; rowNum++) {
Row row = sheet.createRow(rowNum);
for (int cellNum = 0; cellNum < 10; cellNum++) {
Cell cell = row.createCell(cellNum);
cell.setCellValue(rowNum + "," + cellNum);
}
}
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(path + "03batch.xls");
workbook.write(fileOutputStream);
if (fileOutputStream != null) {
fileOutputStream.close();
}
}
(2)07版本XSSF
XSSFWorkbook
- 缺点:写数据时速度非常慢,非常耗内存,也会发生内存溢出,如100万条。
- 优点:可以写较大的数据量,如20万条。
(3)07版本升级版 SXSSFWorkbook
优点:可以写非常大的数据量,如100万条甚至更多条,数据速度快,占用更少的内存
注意:
- 过程中产生临时文件,需要清理临时文件。((SXSSFWorkbook) workbook).dispose();
- 默认由100条记录被保存在内存中,如果超过这数量,则最前面的数据被写入临时件。
- 如果想自定义内存中数据的数量,可以使用new SXSSFWorkbook(数量)
@Test
public void testWriteBatch07() throws IOException {
Workbook workbook = new SXSSFWorkbook();
Sheet sheet = workbook.createSheet("统计表");
for (int rowNum = 0; rowNum < 655551; rowNum++) {
Row row = sheet.createRow(rowNum);
for (int cellNum = 0; cellNum < 10; cellNum++) {
Cell cell = row.createCell(cellNum);
cell.setCellValue(rowNum + "," + cellNum);
}
}
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(path + "07batch.xlsx");
workbook.write(fileOutputStream);
if (fileOutputStream != null) {
fileOutputStream.close();
}
((SXSSFWorkbook) workbook).dispose();
}
2 POI-Excel读操作
(1)03版本
@Test
public void read03() throws IOException {
// 获取流
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(path + "student03.xls");
Workbook workbook = new HSSFWorkbook(fileInputStream);
// 得到表和行
Sheet sheet = workbook.getSheetAt(0);
Row row = sheet.getRow(0);
Cell cell = row.getCell(0);
// 一定要判断类型
System.out.println(cell.getStringCellValue());
fileInputStream.close();
}
(2)07版本同写操作
(3)读取不同的数据类型
@Test
public void readTypeTest03() throws IOException {
// 获取流
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(path + "student03.xls");
Workbook workbook = new HSSFWorkbook(fileInputStream);
// 得到表和行
Sheet sheet = workbook.getSheetAt(0);
// 获取标题内容。
Row rowTitle = sheet.getRow(0);
if(rowTitle != null) {
for (int cellNum = 0; cellNum < rowTitle.getPhysicalNumberOfCells(); cellNum++) {
Cell cell = rowTitle.getCell(cellNum);
if (cell != null) {
String value = cell.getStringCellValue();
System.out.print(value + " | ");;
}
}
System.out.println();
}
for (int rowNum = 1; rowNum < sheet.getPhysicalNumberOfRows() ; rowNum++) {
Row row = sheet.getRow(rowNum);
if(row != null) {
for (int cellNum = 0; cellNum < row.getPhysicalNumberOfCells(); cellNum++) {
Cell cell = row.getCell(cellNum);
if(cell != null) {
int cellType = cell.getCellType();
String cellValue = "";
switch (cellType){
case XSSFCell.CELL_TYPE_STRING:
cellValue = cell.getStringCellValue();
break;
case XSSFCell.CELL_TYPE_BOOLEAN:
cellValue = String.valueOf(cell.getBooleanCellValue());
break;
case XSSFCell.CELL_TYPE_BLANK:
break;
case XSSFCell.CELL_TYPE_NUMERIC:
if (DateUtil.isCellDateFormatted(cell)){
Date dateCellValue = cell.getDateCellValue();
cellValue = new DateTime(dateCellValue).toString("yyyy-MM-dd");
}else{
// 不是日期格式,防止数字过长
cell.setCellType(XSSFCell.CELL_TYPE_STRING);
cellValue = cell.getStringCellValue();
}
break;
case XSSFCell.CELL_TYPE_ERROR:
System.out.print("【数据类型错误】");
break;
}
System.out.print(cellValue + " | ");
}
}
}
System.out.println();
}
fileInputStream.close();
}
esayExcel
1 依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibabagroupId>
<artifactId>easyexcelartifactId>
<version>3.1.0version>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<artifactId>poi-ooxml-schemasartifactId>
<groupId>org.apache.poigroupId>
exclusion>
exclusions>
dependency>
2 写操作
首先建实体类
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class Student implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1602341773222025686L;
@ExcelProperty(index = 0, value = {"姓名"})
private String name;
@ExcelProperty(index = 1, value = {"年龄"})
private Integer age;
@ExcelProperty(index = 2, value = {"性别"})
private String gender;
}
测试
@Test
public void writeExcelTest() {
String file = path + "student001.xls";
List<Student> students = Arrays.asList(new Student("张三", 22, "男"),
new Student("李四", 20, "女"));
EasyExcel.write(file, Student.class).sheet("学生信息").doWrite(students);
}
3 读操作
监听方法
public class StudentListener extends AnalysisEventListener<Student> {
//一行一行读取excel内容
@Override
public void invoke(Student data, AnalysisContext analysisContext) {
System.out.println("*****" + data);
}
//读取表头内容
@Override
public void invokeHeadMap(Map<Integer, String> headMap, AnalysisContext context) {
System.out.println("表头: " + headMap);
}
//读取完成之后
@Override
public void doAfterAllAnalysed(AnalysisContext analysisContext) {
System.out.println("数据读完了");
}
}
测试
@Test
public void readExcelTest() {
String file = path + "student001.xls";
// 这里 需要指定读用哪个class去读,然后读取第一个sheet 文件流会自动关闭
List<Student> students = EasyExcel.read(file, Student.class, new StudentListener()).sheet().doReadSync();
students.forEach(System.out::println);
}
注意:如果想要忽略某一列可以 @ExcelIgnore注解排除
esayExcel 高级用法
1 复杂表头
例如:下面的表头
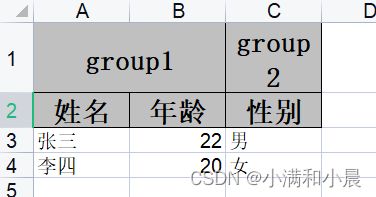
@ExcelProperty注解的value属性是一个数组类型, 设置多个head时会自动合并.
1.1 写操作
和之前类似,只是实体类注解需要修改
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class Student implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1602341773222025686L;
@ExcelProperty(value = {"group1", "姓名"}, index = 0)
private String name;
@ExcelProperty(value = {"group1", "年龄"}, index = 1)
private Integer age;
@ExcelProperty(value = {"group2", "性别"}, index = 2)
private String gender;
}
1.2 读操作
List<Student> students = EasyExcel.read(file, Student.class, new StudentListener()).sheet().doReadSync();
public class StudentListener extends AnalysisEventListener<Student> {
/**
* 创建list集合封装最终的数据
*/
private List<Object> list = new ArrayList<>();
/**
* sheet页索引
*/
private int sheetIndex = 0;
/**
* 一行一行读取, 只读取数据,不读取表头
* @param student
* @param analysisContext
*/
@Override
public void invoke(Student student, AnalysisContext analysisContext) {
System.out.println(student);
}
/**
* 读取表头
* @param headMap
* @param context
*/
@Override
public void invokeHeadMap(Map<Integer, String> headMap, AnalysisContext context) {
System.out.println("表头" + headMap);
}
/**
* 读取之后
* @param analysisContext
*/
@Override
public void doAfterAllAnalysed(AnalysisContext analysisContext) {
}
}
2 日期数字格式化
对于日期和数字,有时候需要对其展示的样式进行格式化, EasyExcel提供了以下注解
@DateTimeFormat 日期格式化
@NumberFormat 数字格式化(小数或百分数)
@DateTimeFormat(value = "yyyy年MM月dd日 HH时mm分ss秒") // 日期格式化
@NumberFormat(value = "###.#") // 数字格式化,保留1位小数
3 写的数据转换器
在实际应用场景中, 我们系统db存储的数据可以是枚举, 在界面或导出到Excel文件需要展示为对于的枚举值形式.
比如: 性别, 状态等. EasyExcel提供了转换器接口Converter供我们使用, 我们只需要自定义转换器实现接口, 并将自定义转换器类型传入要转换的属性字段中. 以下面的性别gender字段为例:
// 性别添加了转换器, db中存入的是integer类型的枚举 0 , 1 ,2
@ExcelProperty(value = “性别”, index = 2, converter = GenderConverter.class)
public class GenderConverter implements Converter<Integer> {
private static final String MALE = "男";
private static final String FEMALE = "女";
@Override
public Class supportJavaTypeKey() {
return Integer.class;
}
@Override
public CellDataTypeEnum supportExcelTypeKey() {
return CellDataTypeEnum.STRING;
}
@Override
public Integer convertToJavaData(CellData cellData, ExcelContentProperty excelContentProperty, GlobalConfiguration globalConfiguration) throws Exception {
String value = cellData.getStringValue();
if (Objects.equals(FEMALE, value)) {
return 0;
} else {
return 1;
}
}
@Override
public CellData convertToExcelData(Integer integer, ExcelContentProperty excelContentProperty, GlobalConfiguration globalConfiguration) throws Exception {
if (integer == 1) {
return new CellData(MALE);
} else {
return new CellData(FEMALE);
}
}
}