图像处理之hough圆形检测
hough检测原理
点击图像处理之Hough变换检测直线查看
下面直接描述检测圆形的方法
基于Hough变换的圆形检测方法
对于一个半径为 r r r,圆心为 ( a , b ) (a,b) (a,b)的圆,我们将其表示为:
( x − a ) 2 + ( y − b ) 2 = r 2 (x-a)^2+(y-b)^2=r^2 (x−a)2+(y−b)2=r2
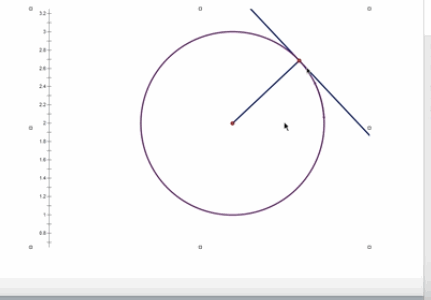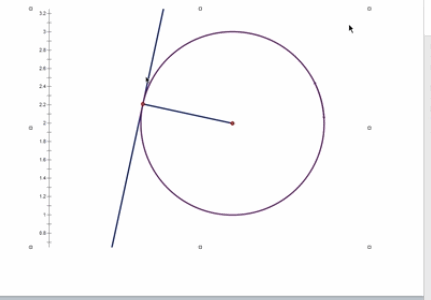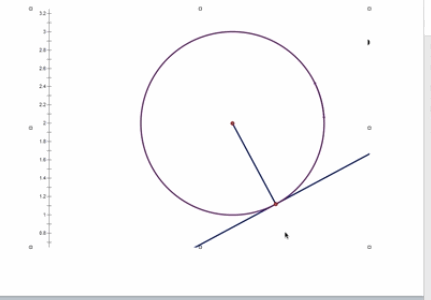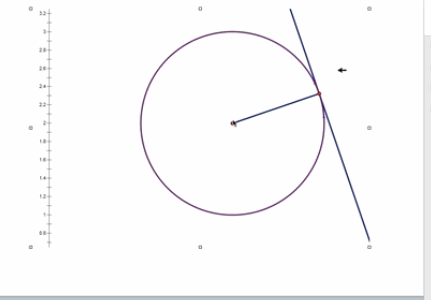
此时 x = [ x , y ] T , a = [ a , b , r ] T x=[x,y]^T,a=[a,b,r]^T x=[x,y]T,a=[a,b,r]T,其参数空间为三维。显然,图像空间上的一点 ( x , y ) (x,y) (x,y),在参数空间中对应着一个圆锥,如下图所示。
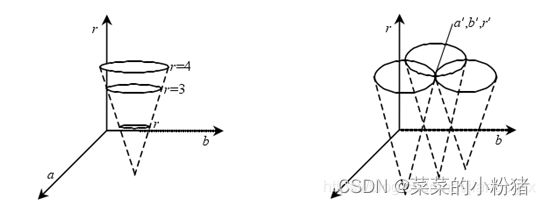
而图像空间的一个圆就对应着这一簇圆锥相交的一个点,这个特定点在参数空间的三维参数一定,就表示一定半径一定圆心坐标的图像空间的那个圆。
上述方法是经典的Hough圆检测方法的原理,它具有精度高,抗干扰能力强等优点,但由于该方法的参数空间为三维,要在三维空间上进行证据累计的话,需要的时间和空间都是庞大的,在实际应用中不适用。为加快Hough变换检测圆的速度,学者们进行了大量研究,也出现了很多改进的Hough变换检测圆的方法。如利用图像梯度信息的Hough变换,对圆的标准方程对x求导得到下式:
2 ( x − a ) + 2 ( y − b ) d y d x = 0 2(x-a)+2(y-b)\frac{dy}{dx}=0 2(x−a)+2(y−b)dxdy=0
从上式看出,此时的参数空间从半径 r r r,圆心 ( a , b ) (a,b) (a,b)三维,变成了只有圆心 ( a , b ) (a,b) (a,b)的二维空间,利用这种方法检测圆其计算量明显减少了。
但这种改进的Hough变换检测圆的方法其检测精度并不高,原因在于,此种方法利用了边界斜率。
从本质上讲,边界斜率其实是用曲线在某一点的弦的斜率来代替的,这种情况下,要保证不存在误差,只有在弦长为零的情况。但在数字图像中,曲线的表现形式是离散的,其在某一点处的斜率指的是此点右向n步斜率或是左向n步斜率。如果弦长过小了,斜率的量化误差就会增大。这种方法比较适用于干扰较少的完整圆形目标。
主要代码:
def AHTforCircles(edge,center_threhold_factor = None,score_threhold = None,min_center_dist = None,minRad = None,maxRad = None,center_axis_scale = None,radius_scale = None,halfWindow = None,max_circle_num = None):
if center_threhold_factor == None:
center_threhold_factor = 10.0
if score_threhold == None:
score_threhold = 15.0
if min_center_dist == None:
min_center_dist = 80.0
if minRad == None:
minRad = 0.0
if maxRad == None:
maxRad = 1e7*1.0
if center_axis_scale == None:
center_axis_scale = 1.0
if radius_scale == None:
radius_scale = 1.0
if halfWindow == None:
halfWindow = 2
if max_circle_num == None:
max_circle_num = 6
min_center_dist_square = min_center_dist**2
sobel_kernel_y = np.array([[-1.0, -2.0, -1.0], [0.0, 0.0, 0.0], [1.0, 2.0, 1.0]])
sobel_kernel_x = np.array([[-1.0, 0.0, 1.0], [-2.0, 0.0, 2.0], [-1.0, 0.0, 1.0]])
edge_x = convolve(sobel_kernel_x,edge,[1,1,1,1],[1,1])
edge_y = convolve(sobel_kernel_y,edge,[1,1,1,1],[1,1])
center_accumulator = np.zeros((int(np.ceil(center_axis_scale*edge.shape[0])),int(np.ceil(center_axis_scale*edge.shape[1]))))
k = np.array([[r for c in range(center_accumulator.shape[1])] for r in range(center_accumulator.shape[0])])
l = np.array([[c for c in range(center_accumulator.shape[1])] for r in range(center_accumulator.shape[0])])
minRad_square = minRad**2
maxRad_square = maxRad**2
points = [[],[]]
edge_x_pad = np.pad(edge_x,((1,1),(1,1)),'constant')
edge_y_pad = np.pad(edge_y,((1,1),(1,1)),'constant')
Gaussian_filter_3 = 1.0 / 16 * np.array([(1.0, 2.0, 1.0), (2.0, 4.0, 2.0), (1.0, 2.0, 1.0)])
for i in range(edge.shape[0]):
for j in range(edge.shape[1]):
if not edge[i,j] == 0:
dx_neibor = edge_x_pad[i:i+3,j:j+3]
dy_neibor = edge_y_pad[i:i+3,j:j+3]
dx = (dx_neibor*Gaussian_filter_3).sum()
dy = (dy_neibor*Gaussian_filter_3).sum()
if not (dx == 0 and dy == 0):
t1 = (k/center_axis_scale-i)
t2 = (l/center_axis_scale-j)
t3 = t1**2 + t2**2
temp = (t3 > minRad_square)&(t3 < maxRad_square)&(np.abs(dx*t1-dy*t2) < 1e-4)
center_accumulator[temp] += 1
points[0].append(i)
points[1].append(j)
M = center_accumulator.mean()
for i in range(center_accumulator.shape[0]):
for j in range(center_accumulator.shape[1]):
neibor = \
center_accumulator[max(0, i - halfWindow + 1):min(i + halfWindow, center_accumulator.shape[0]),
max(0, j - halfWindow + 1):min(j + halfWindow, center_accumulator.shape[1])]
if not (center_accumulator[i,j] >= neibor).all():
center_accumulator[i,j] = 0
# 非极大值抑制
plt.imshow(center_accumulator,cmap='gray')
plt.axis('off')
plt.show()
center_threshold = M * center_threhold_factor
possible_centers = np.array(np.where(center_accumulator > center_threshold)) # 阈值化
sort_centers = []
for i in range(possible_centers.shape[1]):
sort_centers.append([])
sort_centers[-1].append(possible_centers[0,i])
sort_centers[-1].append(possible_centers[1,i])
sort_centers[-1].append(center_accumulator[sort_centers[-1][0],sort_centers[-1][1]])
sort_centers.sort(key=lambda x:x[2],reverse=True)
centers = [[],[],[]]
points = np.array(points)
for i in range(len(sort_centers)):
radius_accumulator = np.zeros(
(int(np.ceil(radius_scale * min(maxRad, np.sqrt(edge.shape[0] ** 2 + edge.shape[1] ** 2)) + 1))),dtype=np.float32)
if not len(centers[0]) < max_circle_num:
break
iscenter = True
for j in range(len(centers[0])):
d1 = sort_centers[i][0]/center_axis_scale - centers[0][j]
d2 = sort_centers[i][1]/center_axis_scale - centers[1][j]
if d1**2 + d2**2 < min_center_dist_square:
iscenter = False
break
if not iscenter:
continue
temp = np.sqrt((points[0,:] - sort_centers[i][0] / center_axis_scale) ** 2 + (points[1,:] - sort_centers[i][1] / center_axis_scale) ** 2)
temp2 = (temp > minRad) & (temp < maxRad)
temp = (np.round(radius_scale * temp)).astype(np.int32)
for j in range(temp.shape[0]):
if temp2[j]:
radius_accumulator[temp[j]] += 1
for j in range(radius_accumulator.shape[0]):
if j == 0 or j == 1:
continue
if not radius_accumulator[j] == 0:
radius_accumulator[j] = radius_accumulator[j]*radius_scale/np.log(j) #radius_accumulator[j]*radius_scale/j
score_i = radius_accumulator.argmax(axis=-1)
if radius_accumulator[score_i] < score_threhold:
iscenter = False
if iscenter:
centers[0].append(sort_centers[i][0]/center_axis_scale)
centers[1].append(sort_centers[i][1]/center_axis_scale)
centers[2].append(score_i/radius_scale)
centers = np.array(centers)
centers = centers.astype(np.float64)
return centers
全部代码可见本人GitHub仓库,如果代码有用,please click star and watching
hough检测之前需要canny算子检测基础的边缘,点击这里可以查看有关canny算法相关内容
如果本文对你有帮助,关注加点赞!!!!!

