SpringBoot中java操作excel【EasyExcel】
EasyExcel 处理Excel;简单记录,方便日后查询!
- 官方文档: Easy Excel (alibaba.com)
一、EasyExcel概述
Java解析、生成Excel比较有名的框架有Apache poi、jxl。但他们都存在一个严重的问题就是非常的耗内存,poi有一套SAX模式的API可以一定程度的解决一些内存溢出的问题,但POI还是有一些缺陷,比如07版Excel解压缩以及解压后存储都是在内存中完成的,内存消耗依然很大。
easyexcel重写了poi对07版Excel的解析,一个3M的excel用POI sax解析依然需要100M左右内存,改用easyexcel可以降低到几M,并且再大的excel也不会出现内存溢出;03版依赖POI的sax模式,在上层做了模型转换的封装,让使用者更加简单方便
二、导入依赖
以 SpringBoot项目为例
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webartifactId>
<version>2.6.7version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibabagroupId>
<artifactId>easyexcelartifactId>
<version>3.3.2version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.fastjson2groupId>
<artifactId>fastjson2artifactId>
<version>2.0.3version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombokgroupId>
<artifactId>lombokartifactId>
<version>1.18.24version>
dependency>
三、读Excel
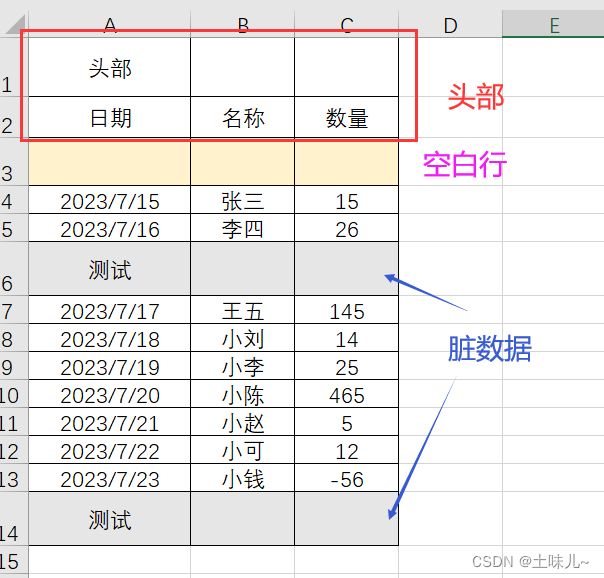
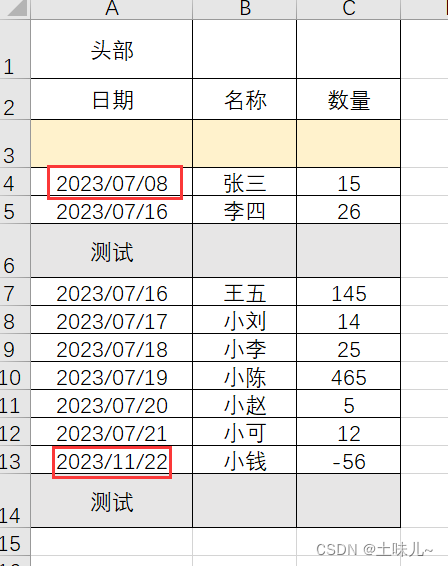
1、测试数据
test.xlsx读取该表中数据;文件放入resources目录下
2、创建实体类
所有字段都用
String类型来接收,接收后可以自行转换
@Data
public class DemoData {
@ExcelProperty("日期")
private String date;
@ExcelProperty("名称")
private String name;
@ExcelProperty("数量")
private String num;
}
3、读取监听器
@Slf4j
public class MyReadListener implements ReadListener<DemoData> {
/**
* 这个每一条数据解析都会来调用
*
* @param data one row value. Is is same as {@link AnalysisContext#readRowHolder()}
* @param context
*/
@Override
public void invoke(DemoData data, AnalysisContext context) {
//log.info("解析到一条数据:{}", JSON.toJSONString(data));
System.out.println(data.getDate() + " - " + data.getName() + " - " + data.getNum());
}
/**
* 所有数据解析完成了 都会来调用
*
* @param context
*/
@Override
public void doAfterAllAnalysed(AnalysisContext context) {
log.info("所有数据解析完成!");
}
}
4、读取类
@Slf4j
@Component
public class ExcelUtil {
/**
*
* 1. 创建excel对应的实体对象
*
* 2. 由于默认一行行的读取excel,所以需要创建excel一行一行的回调监听器
*
* 3. 直接读即可
*/
@SneakyThrows
public static void simpleRead() {
// 有个很重要的点 MyReadListener 不能被spring管理,要每次读取excel都要new,然后里面用到spring可以构造方法传进去
// 写法3:
File file = ResourceUtils.getFile("classpath:test.xlsx");
// 这里 需要指定读用哪个class去读,然后读取第一个sheet 文件流会自动关闭
EasyExcel.read(file, DemoData.class, new MyReadListener())
.sheet()
// 默认头部是1行;该测试数据中是2行
.headRowNumber(2)
.doRead();
}
}
5、测试运行
public class MyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExcelUtil.simpleRead();
}
}
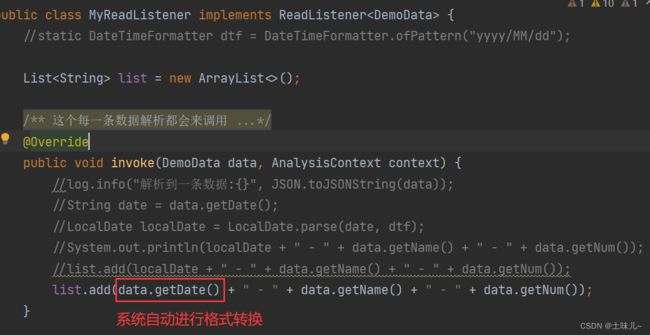
6、日期转换
在监听器中添加
DateTimeFormatter
@Slf4j
public class MyReadListener implements ReadListener<DemoData> {
static DateTimeFormatter dtf = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy/MM/dd");
/**
* 这个每一条数据解析都会来调用
*
* @param data one row value. Is is same as {@link AnalysisContext#readRowHolder()}
* @param context
*/
@Override
public void invoke(DemoData data, AnalysisContext context) {
//log.info("解析到一条数据:{}", JSON.toJSONString(data));
String date = data.getDate();
LocalDate localDate = LocalDate.parse(date, dtf);
System.out.println(localDate + " - " + data.getName() + " - " + data.getNum());
}
}
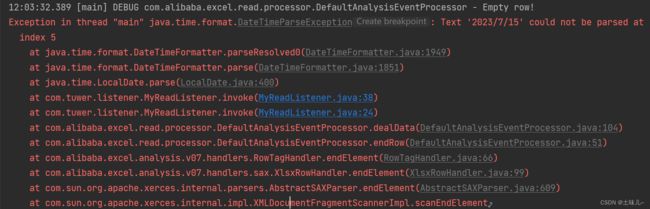
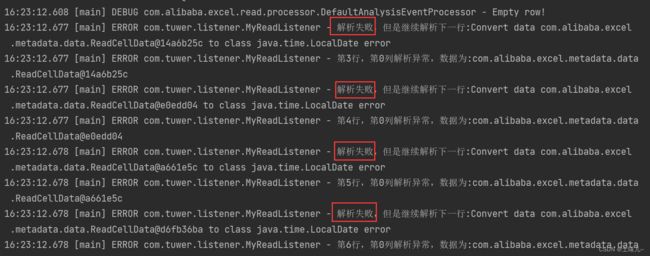
- 运行测试!转换出错
java.time.format.DateTimeParseException
原因:测试数据中日期不规范;月份或天数如果是一位时,前面要补0;
期望的格式是:yyyy/MM/dd;
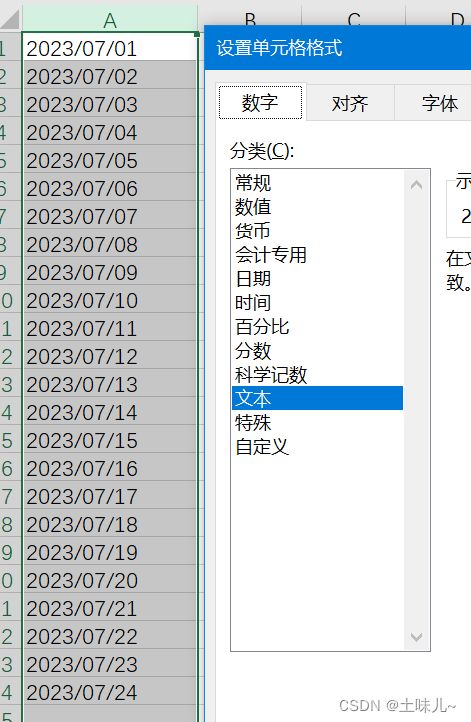
建议要读取的excel文件中所有单元格格式都是文本形式;
修改测试数据,重新测试。更新测试数据后,要 clean 项目后再测试;
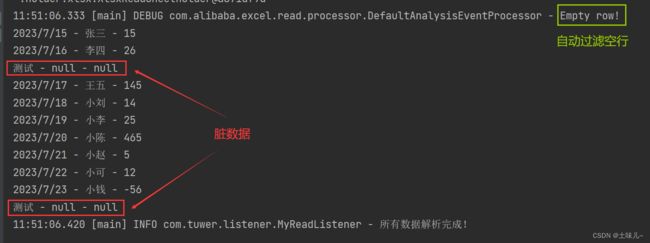
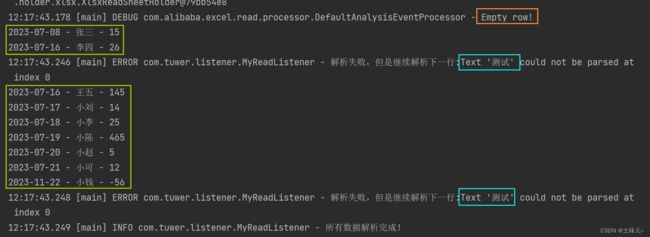
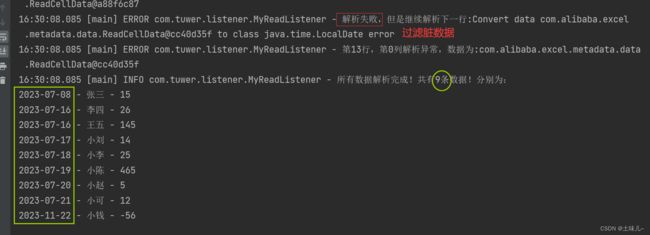
7、过滤脏数据
在监听器中加入异常处理
/**
* 在转换异常 获取其他异常下会调用本接口。抛出异常则停止读取。如果这里不抛出异常则 继续读取下一行。
*
* @param exception
* @param context
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void onException(Exception exception, AnalysisContext context) {
log.error("解析失败,但是继续解析下一行:{}", exception.getMessage());
// 如果是某一个单元格的转换异常 能获取到具体行号
// 如果要获取头的信息 配合invokeHeadMap使用
if (exception instanceof ExcelDataConvertException) {
ExcelDataConvertException excelDataConvertException = (ExcelDataConvertException)exception;
log.error("第{}行,第{}列解析异常,数据为:{}", excelDataConvertException.getRowIndex(),
excelDataConvertException.getColumnIndex(), excelDataConvertException.getCellData());
}
}
- 重新读取测试
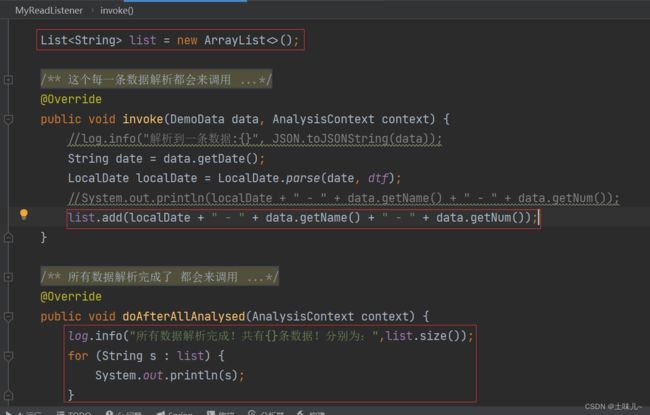
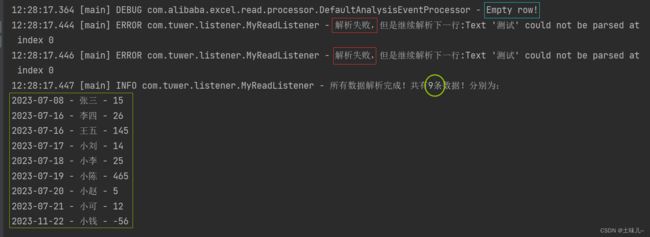
8、解析成功后统一输出
把解析成功数据先存入集合中,最后统一处理;
修改监听器类
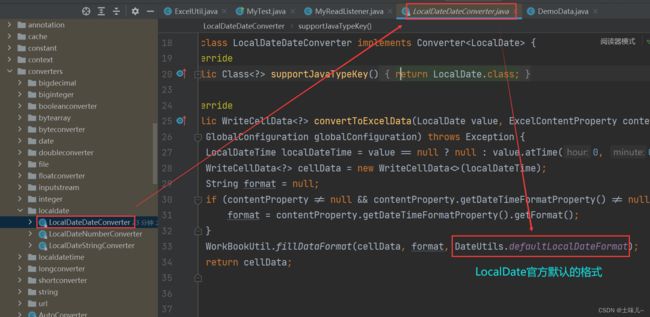
9、官方格式转换(推荐)
1> 原理剖析
(个人理解)EasyExcel 会把每个单元格中的数据都当成 String 来读取,再通过各种转换器,转换成需要的类型(实体类中定义的类型),如果转换失败,就抛出异常。在 easyexcel-core-xxx.jar 中有大量的转换器
格式转换中容易出问题的是日期格式;
以日期转换为例;
2> 测试
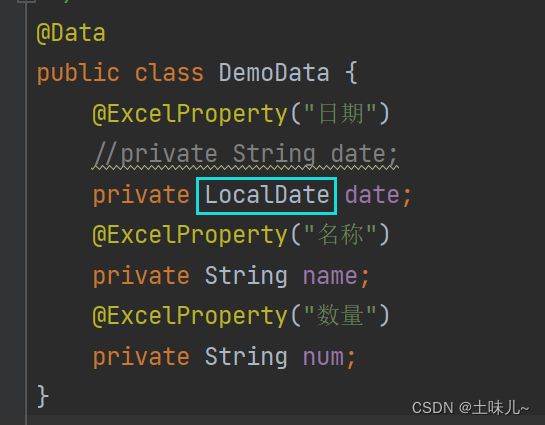
- 修改实体类;把日期类型由 String 改为 LocalDate
- 监听器中直接获取LocalDate字段值;让系统自动进行格式转换
- 运行测试
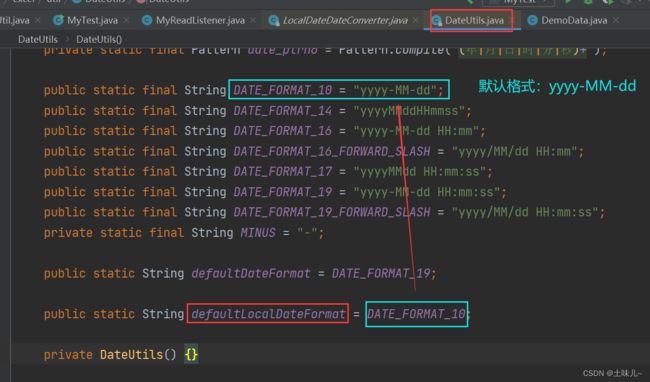
全部解析失败;原因很简单:系统默认期望的日期格式为 yyyy-MM-dd,而测试数据中的日期格式为 yyyy/MM/dd,二者不一致
3> @DateTimeFormat(“…”)
在实体类的日期字段上添加
@DateTimeFormat("yyyy/MM/dd")注解;与测试数据中的日期格式一致。如果测试数据中的日期格式与官方默认格式一致,可以省略。
- 运行测试
四、写Excel
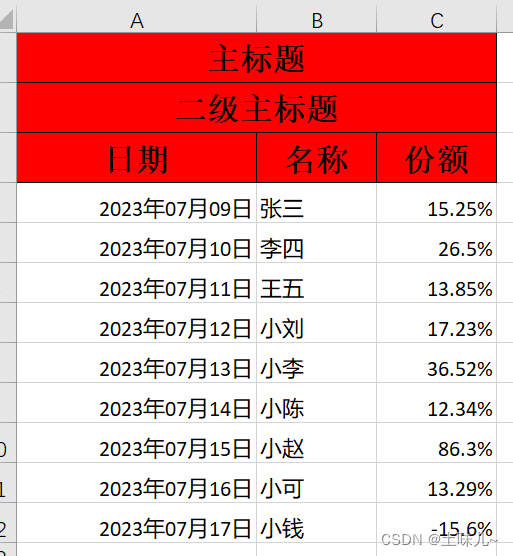
1、目标数据表
期望生成如下数据表
- 复杂表头:多行、字体、颜色、行高、列宽
- 指定数据格式:日期
yyyy年MM月dd日,百分比#.##%最多二位
2、实体类
WriteDemoData关键类;数据表中的样式都在这里面定义
- fillForegroundColor 为颜色枚举类中的颜色索引值
IndexedColors.RED.getIndex()- @DateTimeFormat(“yyyy年MM月dd日”) 为生成后的日期格式
- @NumberFormat(“#.##%”) 数字格式
@Getter
@Setter
@EqualsAndHashCode
// 头背景设置成红色 IndexedColors.RED.getIndex()
@HeadStyle(fillPatternType = FillPatternTypeEnum.SOLID_FOREGROUND, fillForegroundColor = 10)
// 头字体设置成16
@HeadFontStyle(fontHeightInPoints = 16)
// 内容的背景设置成绿色 IndexedColors.GREEN.getIndex()
//@ContentStyle(fillPatternType = FillPatternTypeEnum.SOLID_FOREGROUND, fillForegroundColor = 17)
// 内容字体设置成11
//@ContentFontStyle(fontHeightInPoints = 11)
// 内容行高
@ContentRowHeight(20)
// 头部行高
@HeadRowHeight(25)
// 列宽
@ColumnWidth(10)
@AllArgsConstructor
public class WriteDemoData {
@ExcelProperty({"主标题", "二级主标题", "日期"})
@DateTimeFormat("yyyy年MM月dd日")
@ColumnWidth(20)
private LocalDate date;
// 字符串的头背景设置成粉红 IndexedColors.PINK.getIndex()
//@HeadStyle(fillPatternType = FillPatternTypeEnum.SOLID_FOREGROUND, fillForegroundColor = 14)
// 字符串的头字体设置成20
//@HeadFontStyle(fontHeightInPoints = 30)
// 字符串的内容的背景设置成天蓝 IndexedColors.SKY_BLUE.getIndex()
//@ContentStyle(fillPatternType = FillPatternTypeEnum.SOLID_FOREGROUND, fillForegroundColor = 40)
// 字符串的内容字体设置成20
//@ContentFontStyle(fontHeightInPoints = 30)
@ExcelProperty({"主标题", "二级主标题", "名称"})
private String name;
@ExcelProperty({"主标题", "二级主标题", "份额"})
@NumberFormat("#.##%")
private Double num;
}
3、目标数据
@Slf4j
public class ExcelUtil {
/**
* 测试数据
*
* @return
*/
private static List<WriteDemoData> data() {
List<WriteDemoData> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(new WriteDemoData(LocalDate.parse("2023-07-09"), "张三", 0.1525));
list.add(new WriteDemoData(LocalDate.parse("2023-07-10"), "李四", 0.2650));
list.add(new WriteDemoData(LocalDate.parse("2023-07-11"), "王五", 0.1385));
list.add(new WriteDemoData(LocalDate.parse("2023-07-12"), "小刘", 0.1723));
list.add(new WriteDemoData(LocalDate.parse("2023-07-13"), "小李", 0.3652));
list.add(new WriteDemoData(LocalDate.parse("2023-07-14"), "小陈", 0.1234));
list.add(new WriteDemoData(LocalDate.parse("2023-07-15"), "小赵", 0.863));
list.add(new WriteDemoData(LocalDate.parse("2023-07-16"), "小可", 0.1329));
list.add(new WriteDemoData(LocalDate.parse("2023-07-17"), "小钱", -0.1560));
return list;
}
}
LocalDate.parse(“2023-07-09”) 中的日期格式与系统默认的格式一致,parse时可以省略DateTimeFormatter
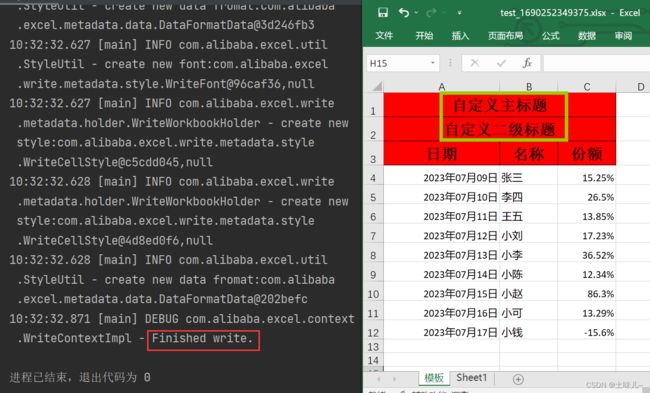
4、写入文件
@Slf4j
public class ExcelUtil {
@SneakyThrows
public static void write() {
// 类路径目录
Resource resource = new ClassPathResource("");
String resourceDir = resource.getFile().getAbsolutePath();
File file = new File(resourceDir, "test_" + System.currentTimeMillis() + ".xlsx");
// 这里 需要指定写用哪个class去写,然后写到第一个sheet,名字为模板 然后文件流会自动关闭
EasyExcel.write(file, WriteDemoData.class).sheet("模板").doWrite(data());
}
}
5、运行测试
public class MyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExcelUtil.write();
}
}
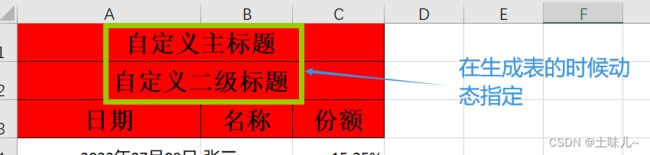
6、自定义表头
如果表头随内容而变化,需要在生成表的时候才能确定,如下图
1> 修改实体类
去掉原来实体类中注解定义的表头
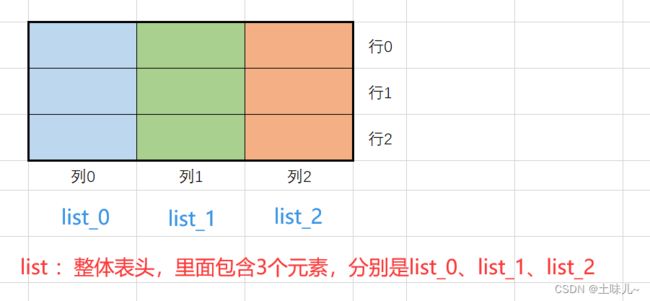
2> 准备表头数据
/**
* 动态表头
* @return
*/
private static List<List<String>> head() {
String mainTitle = "自定义主标题";
String secondTitle = "自定义二级标题";
List<List<String>> list = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> head0 = new ArrayList<>();
head0.add(mainTitle);
head0.add(secondTitle);
head0.add("日期");
List<String> head1 = new ArrayList<>();
head1.add(mainTitle);
head1.add(secondTitle);
head1.add("名称");
List<String> head2 = new ArrayList<>();
head2.add(mainTitle);
head2.add(secondTitle);
head2.add("份额");
list.add(head0);
list.add(head1);
list.add(head2);
return list;
}
表头整体上是一个list,list中元素又是list,内部的每个list表示表头中的一列,表头有几行,内部list中就有几个元素