【C++】图
目录
- 图的存储结构
-
-
- 邻接矩阵(Adjacency Matrix)
-
-
- 无向(网)图邻接矩阵代码实现:
-
- 邻接表(Adjacency Lists)
-
- 图的遍历
-
-
- 邻接矩阵深度和广度遍历DFS_BFS
- 邻接表深度和广度遍历DFS_BFS
-
- 最小生成树
-
-
- 普里姆(Prim)算法
- 克鲁斯卡尔(Kruskal)算法
- 总结
-
- 最短路径
-
-
- 迪杰斯特拉(Dijkstra)算法
- 迪杰斯特拉(Dijkstra)算法和普里姆(Prim)算法的区别
- 弗洛依德(Floyd)算法
-
- 拓扑排序
-
-
- 拓扑排序介绍
- 拓扑排序算法
-
- 关键路径
橙色
图的存储结构
邻接矩阵(Adjacency Matrix)
无向图:
0 - 1
/ |
3 - 2
邻接矩阵:
0 1 2 3
0 0 1 0 0
1 1 0 1 1
2 0 1 0 1
3 0 1 1 0
1表示相连, 0表示不相连
有向图:
0 -> 1
↗︎ ↓
3 <- 2
邻接矩阵
0 1 2 3
0 0 1 0 0
1 0 0 1 0
2 0 0 0 1
3 0 1 0 0
1表示相连, 0表示不相连
无向(网)图邻接矩阵代码实现:
#define MAXVEX 100 /* 最大顶点数,应由用户定义 */
#define GRAPH_INFINITY 65535 /* 用65535来代表∞ */
typedef char VertexType; /* 顶点类型应由用户定义 */
typedef int EdgeType; /* 边上的权值类型应由用户定义 */
typedef struct
{
VertexType vexs[MAXVEX]; /* 顶点表 */
EdgeType arc[MAXVEX][MAXVEX];/* 邻接矩阵,可看作边表 */
int numNodes, numEdges; /* 图中当前的顶点数和边数 */
}MGraph;
int LocateVex(MGraph *G, char vex){
for (int i = 0; i < G->numNodes;i++){
if(vex==G->vexs[i]){
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
/* 建立无向网图的邻接矩阵表示 */
void CreateMGraph(MGraph *G)
{
cout << "输入顶点数和边数:";
cin>>G->numNodes>>G->numEdges; /* 输入顶点数和边数 */
cout<<"请输入顶点:";
for(int i = 0;i <G->numNodes;i++) /* 读入顶点信息,建立顶点表 */{
// printf("%d\n", i);
cin>>G->vexs[i];
}
for(int i = 0;i <G->numNodes;i++)
for(int j = 0;j <G->numNodes;j++){
if(i==j){
G->arc[i][j] = 0;
continue;
}
G->arc[i][j]=GRAPH_INFINITY; /* 邻接矩阵初始化 */
}
char v1,v2;
int w;
for(int k = 0;k <G->numEdges;k++) /* 读入numEdges条边,建立邻接矩阵 */
{
cout<<"依次输入两个顶点和权值:";
cin>>v1>>v2>>w; /* 输入边(vi,vj)上的权w */
int i = LocateVex(G, v1);
int j = LocateVex(G, v2);
G->arc[i][j]=w;
G->arc[j][i]= G->arc[i][j]; /* 因为是无向图,矩阵对称 */
}
}
void Show(MGraph G){
cout<<"邻接矩阵如下:"<<endl;
for (int i = 0; i < G.numNodes; ++i){
for (int j = 0; j < G.numNodes; ++j) {
printf("%-10d",G.arc[i][j]);
}
putchar('\n');
}
}
int main(void)
{
MGraph G;
CreateMGraph(&G);
Show(G);
return 0;
}
有向网图邻接矩阵代码实现:
在这里插入代码片
邻接表(Adjacency Lists)
无向图:
0 - 1
/ |
3 - 2
邻接表:
0 1
1 0 2 3
2 1 3
3 1 2
有向图:
0 -> 1
↗︎ ↓
3 <- 2
邻接表:
0 1
1 2
2 3
3 1
邻接矩阵和邻接表
- 邻接表适合表示稀疏图(Sparse Graph) 节点的边比较少
- 邻接矩阵适合表示稠密图(Dense Graph) 节点的边比较多
图的遍历
邻接矩阵深度和广度遍历DFS_BFS
#include "stdio.h"
#include "stdlib.h"
#include "math.h"
#include "time.h"
#define OK 1
#define ERROR 0
#define TRUE 1
#define FALSE 0
typedef int Status; /* Status是函数的类型,其值是函数结果状态代码,如OK等 */
typedef int Boolean; /* Boolean是布尔类型,其值是TRUE或FALSE */
typedef char VertexType; /* 顶点类型应由用户定义 */
typedef int EdgeType; /* 边上的权值类型应由用户定义 */
#define MAXSIZE 9 /* 存储空间初始分配量 */
#define MAXEDGE 15
#define MAXVEX 9
typedef struct
{
VertexType vexs[MAXVEX]; /* 顶点表 */
EdgeType arc[MAXVEX][MAXVEX];/* 邻接矩阵,可看作边表 */
int numVertexes, numEdges; /* 图中当前的顶点数和边数 */
}MGraph;
/* 用到的队列结构与函数********************************** */
/* 循环队列的顺序存储结构 */
typedef struct
{
int data[MAXSIZE];
int front; /* 头指针 */
int rear; /* 尾指针,若队列不空,指向队列尾元素的下一个位置 */
}Queue;
/* 初始化一个空队列Q */
Status InitQueue(Queue *Q)
{
Q->front=0;
Q->rear=0;
return OK;
}
/* 若队列Q为空队列,则返回TRUE,否则返回FALSE */
Status QueueEmpty(Queue Q)
{
if(Q.front==Q.rear) /* 队列空的标志 */
return TRUE;
else
return FALSE;
}
/* 若队列未满,则插入元素e为Q新的队尾元素 */
Status EnQueue(Queue *Q,int e)
{
if ((Q->rear+1)%MAXSIZE == Q->front) /* 队列满的判断 */
return ERROR;
Q->data[Q->rear]=e; /* 将元素e赋值给队尾 */
Q->rear=(Q->rear+1)%MAXSIZE;/* rear指针向后移一位置, */
/* 若到最后则转到数组头部 */
return OK;
}
/* 若队列不空,则删除Q中队头元素,用e返回其值 */
Status DeQueue(Queue *Q,int *e)
{
if (Q->front == Q->rear) /* 队列空的判断 */
return ERROR;
*e=Q->data[Q->front]; /* 将队头元素赋值给e */
Q->front=(Q->front+1)%MAXSIZE; /* front指针向后移一位置, */
/* 若到最后则转到数组头部 */
return OK;
}
/* ****************************************************** */
void CreateMGraph(MGraph *G)
{
int i, j;
G->numEdges=15;
G->numVertexes=9;
/* 读入顶点信息,建立顶点表 */
G->vexs[0]='A';
G->vexs[1]='B';
G->vexs[2]='C';
G->vexs[3]='D';
G->vexs[4]='E';
G->vexs[5]='F';
G->vexs[6]='G';
G->vexs[7]='H';
G->vexs[8]='I';
for (i = 0; i < G->numVertexes; i++)/* 初始化图 */
{
for ( j = 0; j < G->numVertexes; j++)
{
G->arc[i][j]=0;
}
}
G->arc[0][1]=1;
G->arc[0][5]=1;
G->arc[1][2]=1;
G->arc[1][8]=1;
G->arc[1][6]=1;
G->arc[2][3]=1;
G->arc[2][8]=1;
G->arc[3][4]=1;
G->arc[3][7]=1;
G->arc[3][6]=1;
G->arc[3][8]=1;
G->arc[4][5]=1;
G->arc[4][7]=1;
G->arc[5][6]=1;
G->arc[6][7]=1;
for(i = 0; i < G->numVertexes; i++)
{
for(j = i; j < G->numVertexes; j++)
{
G->arc[j][i] =G->arc[i][j];
}
}
}
Boolean visited[MAXVEX]; /* 访问标志的数组 */
/* 邻接矩阵的深度优先递归算法 */
void DFS(MGraph G, int i)
{
int j;
visited[i] = TRUE;
printf("%c ", G.vexs[i]);/* 打印顶点,也可以其它操作 */
for(j = 0; j < G.numVertexes; j++)
if(G.arc[i][j] == 1 && !visited[j])
DFS(G, j);/* 对为访问的邻接顶点递归调用 */
}
/* 邻接矩阵的深度遍历操作 */
void DFSTraverse(MGraph G)
{
int i;
for(i = 0; i < G.numVertexes; i++)
visited[i] = FALSE; /* 初始所有顶点状态都是未访问过状态 */
for(i = 0; i < G.numVertexes; i++)
if(!visited[i]) /* 对未访问过的顶点调用DFS,若是连通图,只会执行一次 */
DFS(G, i);
}
/* 邻接矩阵的广度遍历算法 */
void BFSTraverse(MGraph G)
{
int i, j;
Queue Q;
for(i = 0; i < G.numVertexes; i++)
visited[i] = FALSE;
InitQueue(&Q); /* 初始化一辅助用的队列 */
for(i = 0; i < G.numVertexes; i++) /* 对每一个顶点做循环 */
{
if (!visited[i]) /* 若是未访问过就处理 */
{
visited[i]=TRUE; /* 设置当前顶点访问过 */
printf("%c ", G.vexs[i]);/* 打印顶点,也可以其它操作 */
EnQueue(&Q,i); /* 将此顶点入队列 */
while(!QueueEmpty(Q)) /* 若当前队列不为空 */
{
DeQueue(&Q,&i); /* 将队首元素出队列,赋值给i */
for(j=0;j<G.numVertexes;j++)
{
/* 判断其它顶点若与当前顶点存在边且未访问过 */
if(G.arc[i][j] == 1 && !visited[j])
{
visited[j]=TRUE; /* 将找到的此顶点标记为已访问 */
printf("%c ", G.vexs[j]); /* 打印顶点 */
EnQueue(&Q,j); /* 将找到的此顶点入队列 */
}
}
}
}
}
}
int main(void)
{
MGraph G;
CreateMGraph(&G);
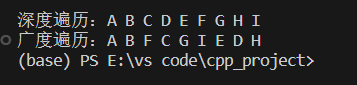
printf("\n深度遍历:");
DFSTraverse(G);
printf("\n广度遍历:");
BFSTraverse(G);
return 0;
}
邻接表深度和广度遍历DFS_BFS
#include "stdio.h"
#include "stdlib.h"
#include "math.h"
#include "time.h"
#define OK 1
#define ERROR 0
#define TRUE 1
#define FALSE 0
#define MAXSIZE 9 /* 存储空间初始分配量 */
#define MAXEDGE 15
#define MAXVEX 9
typedef int Status; /* Status是函数的类型,其值是函数结果状态代码,如OK等 */
typedef int Boolean; /* Boolean是布尔类型,其值是TRUE或FALSE */
typedef char VertexType; /* 顶点类型应由用户定义 */
typedef int EdgeType; /* 边上的权值类型应由用户定义 */
/* 邻接矩阵结构 */
typedef struct
{
VertexType vexs[MAXVEX]; /* 顶点表 */
EdgeType arc[MAXVEX][MAXVEX];/* 邻接矩阵,可看作边表 */
int numVertexes, numEdges; /* 图中当前的顶点数和边数 */
}MGraph;
/* 邻接表结构****************** */
typedef struct EdgeNode /* 边表结点 */
{
int adjvex; /* 邻接点域,存储该顶点对应的下标 */
int weight; /* 用于存储权值,对于非网图可以不需要 */
struct EdgeNode *next; /* 链域,指向下一个邻接点 */
}EdgeNode;
typedef struct VertexNode /* 顶点表结点 */
{
int in; /* 顶点入度 */
char data; /* 顶点域,存储顶点信息 */
EdgeNode *firstedge;/* 边表头指针 */
}VertexNode, AdjList[MAXVEX];
typedef struct
{
AdjList adjList;
int numVertexes,numEdges; /* 图中当前顶点数和边数 */
}graphAdjList,*GraphAdjList;
/* **************************** */
/* 用到的队列结构与函数********************************** */
/* 循环队列的顺序存储结构 */
typedef struct
{
int data[MAXSIZE];
int front; /* 头指针 */
int rear; /* 尾指针,若队列不空,指向队列尾元素的下一个位置 */
}Queue;
/* 初始化一个空队列Q */
Status InitQueue(Queue *Q)
{
Q->front=0;
Q->rear=0;
return OK;
}
/* 若队列Q为空队列,则返回TRUE,否则返回FALSE */
Status QueueEmpty(Queue Q)
{
if(Q.front==Q.rear) /* 队列空的标志 */
return TRUE;
else
return FALSE;
}
/* 若队列未满,则插入元素e为Q新的队尾元素 */
Status EnQueue(Queue *Q,int e)
{
if ((Q->rear+1)%MAXSIZE == Q->front) /* 队列满的判断 */
return ERROR;
Q->data[Q->rear]=e; /* 将元素e赋值给队尾 */
Q->rear=(Q->rear+1)%MAXSIZE;/* rear指针向后移一位置, */
/* 若到最后则转到数组头部 */
return OK;
}
/* 若队列不空,则删除Q中队头元素,用e返回其值 */
Status DeQueue(Queue *Q,int *e)
{
if (Q->front == Q->rear) /* 队列空的判断 */
return ERROR;
*e=Q->data[Q->front]; /* 将队头元素赋值给e */
Q->front=(Q->front+1)%MAXSIZE; /* front指针向后移一位置, */
/* 若到最后则转到数组头部 */
return OK;
}
/* ****************************************************** */
void CreateMGraph(MGraph *G)
{
int i, j;
G->numEdges=15;
G->numVertexes=9;
/* 读入顶点信息,建立顶点表 */
G->vexs[0]='A';
G->vexs[1]='B';
G->vexs[2]='C';
G->vexs[3]='D';
G->vexs[4]='E';
G->vexs[5]='F';
G->vexs[6]='G';
G->vexs[7]='H';
G->vexs[8]='I';
for (i = 0; i < G->numVertexes; i++)/* 初始化图 */
{
for ( j = 0; j < G->numVertexes; j++)
{
G->arc[i][j]=0;
}
}
G->arc[0][1]=1;
G->arc[0][5]=1;
G->arc[1][2]=1;
G->arc[1][8]=1;
G->arc[1][6]=1;
G->arc[2][3]=1;
G->arc[2][8]=1;
G->arc[3][4]=1;
G->arc[3][7]=1;
G->arc[3][6]=1;
G->arc[3][8]=1;
G->arc[4][5]=1;
G->arc[4][7]=1;
G->arc[5][6]=1;
G->arc[6][7]=1;
for(i = 0; i < G->numVertexes; i++)
{
for(j = i; j < G->numVertexes; j++)
{
G->arc[j][i] =G->arc[i][j];
}
}
}
/* 利用邻接矩阵构建邻接表 */
void CreateALGraph(MGraph G,GraphAdjList *GL)
{
int i,j;
EdgeNode *e;
*GL = (GraphAdjList)malloc(sizeof(graphAdjList));
(*GL)->numVertexes=G.numVertexes;
(*GL)->numEdges=G.numEdges;
for(i= 0;i <G.numVertexes;i++) /* 读入顶点信息,建立顶点表 */
{
(*GL)->adjList[i].in=0;
(*GL)->adjList[i].data=G.vexs[i];
(*GL)->adjList[i].firstedge=NULL; /* 将边表置为空表 */
}
for(i=0;i<G.numVertexes;i++) /* 建立边表 */
{
for(j=G.numVertexes-1;j>=0;j--)
{
if (G.arc[i][j]==1)
{
e=(EdgeNode *)malloc(sizeof(EdgeNode));
e->adjvex=j; /* 邻接序号为j */
//正常代码下如下
//e->adjvex=j; /* 邻接序号为j */
e->next=(*GL)->adjList[i].firstedge; /* 将当前顶点上的指向的结点指针赋值给e */
(*GL)->adjList[i].firstedge=e; /* 将当前顶点的指针指向e */
(*GL)->adjList[j].in++;
}
}
}
}
Boolean visited[MAXSIZE]; /* 访问标志的数组 */
/* 邻接表的深度优先递归算法 */
void DFS(GraphAdjList GL, int i)
{
EdgeNode *p;
visited[i] = TRUE;
printf("%c ",GL->adjList[i].data);/* 打印顶点,也可以其它操作 */
p = GL->adjList[i].firstedge;
while(p)
{
if(!visited[p->adjvex])
DFS(GL, p->adjvex);/* 对为访问的邻接顶点递归调用 */
p = p->next;
}
}
/* 邻接表的深度遍历操作 */
void DFSTraverse(GraphAdjList GL)
{
int i;
for(i = 0; i < GL->numVertexes; i++)
visited[i] = FALSE; /* 初始所有顶点状态都是未访问过状态 */
for(i = 0; i < GL->numVertexes; i++)
if(!visited[i]) /* 对未访问过的顶点调用DFS,若是连通图,只会执行一次 */
DFS(GL, i);
}
/* 邻接表的广度遍历算法 */
void BFSTraverse(GraphAdjList GL)
{
int i;
EdgeNode *p;
Queue Q;
for(i = 0; i < GL->numVertexes; i++)
visited[i] = FALSE;
InitQueue(&Q);
for(i = 0; i < GL->numVertexes; i++)
{
if (!visited[i])
{
visited[i]=TRUE;
printf("%c ",GL->adjList[i].data);/* 打印顶点,也可以其它操作 */
EnQueue(&Q,i);
while(!QueueEmpty(Q))
{
DeQueue(&Q,&i);
p = GL->adjList[i].firstedge; /* 找到当前顶点的边表链表头指针 */
while(p)
{
if(!visited[p->adjvex]) /* 若此顶点未被访问 */
{
visited[p->adjvex]=TRUE;
printf("%c ",GL->adjList[p->adjvex].data);
EnQueue(&Q,p->adjvex); /* 将此顶点入队列 */
}
p = p->next; /* 指针指向下一个邻接点 */
}
}
}
}
}
int main(void)
{
MGraph G;
GraphAdjList GL;
CreateMGraph(&G);
CreateALGraph(G,&GL);
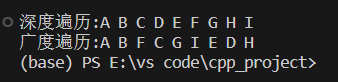
printf("\n深度遍历:");
DFSTraverse(GL);
printf("\n广度遍历:");
BFSTraverse(GL);
return 0;
}
最小生成树
普里姆(Prim)算法
其基础概念及代码可参考该文章:图论算法:普里姆算法(C++实现+图解)
//普里姆算法
void Prim(MGraph& g, int u)
{
//以u为最小生成树的起点
//两个辅助数组
//lowcost如果为0,则点已在U中,否则则记录着离U中所有点最小的权值。
//比如U中已有0、1,2离1最近权重为5,则lowcost[2]=5,closet[2]=1
int closet[MAXVEX], lowcost[MAXVEX];
for (int i = 0; i < g.numNodes; i++)
{
closet[i] = u; //i: 顶点
lowcost[i] = g.arc[u][i]; //edge[u][i]: u->i 这条边所具有的权值
}
int min, k;
for (int i = 1; i < g.numNodes; i++)//循环(numNodes-1)次
{
min = GRAPH_INFINITY, k = -1;
for (int j = 0; j < g.numNodes; j++)
{
//lowcost[j] != 0 表示所选的点不能是U中的点,只能是V-E中的
//lowcost[j] < min 表示依次选取权值最小的边
if (lowcost[j] != 0 && lowcost[j] < min) //在V-E中找出离U最近的顶点
{
min = lowcost[j];
k = j; //k为最近顶点编号
}
}
//k:记录了权值最小的边在V-E中的顶点编号
//min:记录了这个最小权值
printf(" 边(%d -> %d) 权值:%d\n", closet[k],k, min);
//修正数组
lowcost[k] = 0; //这个边已经选过了
for (int j = 0; j < g.numNodes; j++)
{
//以k作为起点,寻找与k点连接的边的权值是否比之前记录的权值小
if (lowcost[j] != 0 && g.arc[k][j] < lowcost[j])
{
lowcost[j] = g.arc[k][j]; //更新为最小权值
closet[j] = k; //记录这个点
}
}
}
}
克鲁斯卡尔(Kruskal)算法
其基础概念及代码可参考该文章:Kruskal算法实现最小生成树(C++实现)
其中的find函数以及parent数组的设计涉及到了并查集的运用,可参考该篇文章:并查集(Union-Find)算法介绍
所输入的图的相关数据来自大话数据结构P209
#include总结
对比两个算法,克鲁斯卡尔算法主要针对边来展开,边数少时效率会非常高,所以对于稀疏图有很大的优势;而普里姆算法对于稠密图,即边数非常多的情况会更好一点。
最短路径
迪杰斯特拉(Dijkstra)算法
关于概念可参考该篇文章:Dijkstra算法图文详解
值得注意的是主函数中对数据进行了打印,该打印默认了源节点就是0节点,所以如果设置的源节点不是0结点的话,就需要对主函数当中的打印部分作相应的修改。
所输入的图的相关数据来自大话数据结构P209
#include "stdio.h"
#define MAXEDGE 20
#define MAXVEX 20
#define GRAPH_INFINITY 65535
typedef struct
{
int vexs[MAXVEX];
int arc[MAXVEX][MAXVEX];
int numVertexes, numEdges;
}MGraph;
typedef int Patharc[MAXVEX]; /* 用于存储最短路径下标的数组 */
typedef int ShortPathTable[MAXVEX];/* 用于存储到各点最短路径的权值和 */
/* 构件图 */
void CreateMGraph(MGraph *G)
{
int i, j;
/* printf("请输入边数和顶点数:"); */
G->numEdges=16;
G->numVertexes=9;
for (i = 0; i < G->numVertexes; i++)/* 初始化图 */
{
G->vexs[i]=i;
}
for (i = 0; i < G->numVertexes; i++)/* 初始化图 */
{
for ( j = 0; j < G->numVertexes; j++)
{
if (i==j)
G->arc[i][j]=0;
else
G->arc[i][j] = G->arc[j][i] = GRAPH_INFINITY;
}
}
G->arc[0][1]=1;
G->arc[0][2]=5;
G->arc[1][2]=3;
G->arc[1][3]=7;
G->arc[1][4]=5;
G->arc[2][4]=1;
G->arc[2][5]=7;
G->arc[3][4]=2;
G->arc[3][6]=3;
G->arc[4][5]=3;
G->arc[4][6]=6;
G->arc[4][7]=9;
G->arc[5][7]=5;
G->arc[6][7]=2;
G->arc[6][8]=7;
G->arc[7][8]=4;
for(i = 0; i < G->numVertexes; i++)
{
for(j = i; j < G->numVertexes; j++)
{
G->arc[j][i] =G->arc[i][j];
}
}
}
/* Dijkstra算法,求有向网G的v0顶点到其余顶点v的最短路径P[v]及带权长度D[v] */
/* P[v]的值为前驱顶点下标(即连接着点v的上一个点下标),D[v]表示v0到v的最短路径长度和 */
void ShortestPath_Dijkstra(MGraph G, int v0, Patharc *P, ShortPathTable *D)
{
int v,w,k,min;
int final[MAXVEX];/* final[w]=1表示求得顶点v0至vw的最短路径 */
for(v=0; v<G.numVertexes; v++) /* 初始化数据 */
{
final[v] = 0; /* 全部顶点初始化为未知最短路径状态 */
(*D)[v] = G.arc[v0][v];/* 将与v0点有连线的顶点加上权值 */
(*P)[v] = -1; /* 初始化路径数组P为-1 */
}
(*D)[v0] = 0; /* v0至v0最短路径为0 */
final[v0] = 1; /* v0至v0不需要求路径 */
/* 开始主循环,每次求得v0到某个v顶点的最短路径,其实是循环(G.numVertexes-1)次 */
for(v=1; v<G.numVertexes; v++)
{
min=GRAPH_INFINITY; /* 当前所知离v0顶点的最近距离 */
for(w=0; w<G.numVertexes; w++) /* 寻找离v0最近的顶点 */
{
if(!final[w] && (*D)[w]<min)
{
k=w;
min = (*D)[w]; /* w顶点离v0顶点更近 */
}
}
final[k] = 1; /* 将以目前找到的离v0最近的顶点为索引在final的值置为1 */
for(w=0; w<G.numVertexes; w++) /* 修正当前最短路径及距离 */
{
//如果经过v顶点的路径比现在这条路径的长度短的话,(*D)[w]代表当前v0顶点与w顶点之间的距离
//min+G.arc[k][w]代表了(v0顶点与k顶点的最短距离+k顶点与w顶点之间的距离)
if(!final[w] && (min+G.arc[k][w]<(*D)[w]))
{ /* 说明找到了更短的路径,修改D[w]和P[w] */
(*D)[w] = min + G.arc[k][w]; /* 修改当前路径长度 */
(*P)[w]=k;
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
int i,j,v0;
MGraph G;
Patharc P;
ShortPathTable D; /* 求某点到其余各点的最短路径 */
v0=0;
CreateMGraph(&G);
ShortestPath_Dijkstra(G, v0, &P, &D);
printf("最短路径倒序如下:\n");
for(i=1;i<G.numVertexes;++i)
{
printf("v%d - v%d : ",v0,i);
j=i;
while(P[j]!=-1)
{
printf("%d ",P[j]);
j=P[j];
}
printf("\n");
}
printf("\n源点到各顶点的最短路径长度为:\n");
for(i=1;i<G.numVertexes;++i)
printf("v%d - v%d : %d \n",G.vexs[0],G.vexs[i],D[i]);
return 0;
}
迪杰斯特拉(Dijkstra)算法和普里姆(Prim)算法的区别
- 在图论中,Prim算法解决的问题是连通无向有权图中最小生成树问题,而Dijkstra算法解决的问题是源点到目标点的最短路径问题
- 虽然这两个算法在添加新结点时,都是选择“距离最短”的结点加入集合,但是Prim算法中,“距离最短”是指未访问的结点到已经访问的所有结点距离最小,即将已经访问的结点视为一个整体,将距离最小的结点加入到已访问的集合中;而在Dijkstra算法中,“距离最短”是指所有未访问结点(通过已访问的结点)到源点距离最小。
- 在Prim算法中,数组元素dis[i]表示未访问结点i到已访问结点集合的最短距离,所以此时需要len记录最短距离。而Dijkstra算法中,数组元素dis[i]表示未访问结点i到源点的最短距离。
弗洛依德(Floyd)算法
该算法可以一次性求的所有顶点到所有顶点的最短路径。
概念可参考该文章:弗洛伊德(Floyd)算法求图的最短路径
#include "stdio.h"
#define MAXEDGE 20
#define MAXVEX 20
#define GRAPH_INFINITY 65535
typedef struct
{
int vexs[MAXVEX];
int arc[MAXVEX][MAXVEX];
int numVertexes, numEdges;
}MGraph;
typedef int Patharc[MAXVEX][MAXVEX];
typedef int ShortPathTable[MAXVEX][MAXVEX];
/* 构件图 */
void CreateMGraph(MGraph *G)
{
int i, j;
/* printf("请输入边数和顶点数:"); */
G->numEdges=16;
G->numVertexes=9;
for (i = 0; i < G->numVertexes; i++)/* 初始化图 */
{
G->vexs[i]=i;
}
for (i = 0; i < G->numVertexes; i++)/* 初始化图 */
{
for ( j = 0; j < G->numVertexes; j++)
{
if (i==j)
G->arc[i][j]=0;
else
G->arc[i][j] = G->arc[j][i] = GRAPH_INFINITY;
}
}
G->arc[0][1]=1;
G->arc[0][2]=5;
G->arc[1][2]=3;
G->arc[1][3]=7;
G->arc[1][4]=5;
G->arc[2][4]=1;
G->arc[2][5]=7;
G->arc[3][4]=2;
G->arc[3][6]=3;
G->arc[4][5]=3;
G->arc[4][6]=6;
G->arc[4][7]=9;
G->arc[5][7]=5;
G->arc[6][7]=2;
G->arc[6][8]=7;
G->arc[7][8]=4;
for(i = 0; i < G->numVertexes; i++)
{
for(j = i; j < G->numVertexes; j++)
{
G->arc[j][i] =G->arc[i][j];
}
}
}
/* Floyd算法,求网图G中各顶点v到其余顶点w的最短路径P[v][w]及带权长度D[v][w]。 */
void ShortestPath_Floyd(MGraph G, Patharc *P, ShortPathTable *D)
{
int v,w,k;
for(v=0; v<G.numVertexes; ++v) /* 初始化D与P */
{
for(w=0; w<G.numVertexes; ++w)
{
(*D)[v][w]=G.arc[v][w]; /* D[v][w]值即为对应点间的权值 */
(*P)[v][w]=w; /* 初始化P */
}
}
for(k=0; k<G.numVertexes; ++k)
{
for(v=0; v<G.numVertexes; ++v)
{
for(w=0; w<G.numVertexes; ++w)
{
if ((*D)[v][w]>(*D)[v][k]+(*D)[k][w])
{/* 如果经过下标为k顶点路径比原两点间路径更短 */
(*D)[v][w]=(*D)[v][k]+(*D)[k][w];/* 将当前两点间权值设为更小的一个 */
(*P)[v][w]=(*P)[v][k];/* 路径设置为经过下标为k的顶点 */
}
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
int v,w,k;
MGraph G;
Patharc P;
ShortPathTable D; /* 求某点到其余各点的最短路径 */
CreateMGraph(&G);
ShortestPath_Floyd(G,&P,&D);
printf("各顶点间最短路径如下:\n");
for(v=0; v<G.numVertexes; ++v)
{
for(w=v+1; w<G.numVertexes; w++)
{
printf("v%d-v%d weight: %d ",v,w,D[v][w]);
k=P[v][w]; /* 获得第一个路径顶点下标 */
printf(" path: %d",v); /* 打印源点 */
while(k!=w) /* 如果路径顶点下标不是终点 */
{
printf(" -> %d",k); /* 打印路径顶点 */
k=P[k][w]; /* 获得下一个路径顶点下标 */
}
printf(" -> %d\n",w); /* 打印终点 */
}
printf("\n");
}
printf("最短路径D\n");
for(v=0; v<G.numVertexes; ++v)
{
for(w=0; w<G.numVertexes; ++w)
{
printf("%d\t",D[v][w]);
}
printf("\n");
}
printf("最短路径P\n");
for(v=0; v<G.numVertexes; ++v)
{
for(w=0; w<G.numVertexes; ++w)
{
printf("%d ",P[v][w]);
}
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
拓扑排序
拓扑排序介绍
在一个表示工程的有向图中,用顶点表示活动,用弧表示活动之间的优先关系,这样的有向图为顶点表示活动的网,称为AOV网(Activity On Vertex).
概念参考该文:拓扑排序及算法实现
或者大话数据结构P229
拓扑排序算法
该算法中,第140行gettop=stack[top–];是为了把栈顶的顶点删除,而第147行if( !(–GL->adjList[k].in) )中的–GL->adjList[k].in则是为了把以该顶点为弧尾的弧删除。

#include "stdio.h"
#include "stdlib.h"
#define OK 1
#define ERROR 0
#define TRUE 1
#define FALSE 0
#define MAXEDGE 20
#define MAXVEX 14
typedef int Status; /* Status是函数的类型,其值是函数结果状态代码,如OK等 */
/* 邻接矩阵结构 */
typedef struct
{
int vexs[MAXVEX];
int arc[MAXVEX][MAXVEX];
int numVertexes, numEdges;
}MGraph;
/* 邻接表结构****************** */
typedef struct EdgeNode /* 边表结点 */
{
int adjvex; /* 邻接点域,存储该顶点对应的下标 */
int weight; /* 用于存储权值,对于非网图可以不需要 */
struct EdgeNode *next; /* 链域,指向下一个邻接点 */
}EdgeNode;
typedef struct VertexNode /* 顶点表结点 */
{
int in; /* 顶点入度 */
int data; /* 顶点域,存储顶点信息 */
EdgeNode *firstedge;/* 边表头指针 */
}VertexNode, AdjList[MAXVEX];
typedef struct
{
AdjList adjList; //一个 AdjList 类型的变量,用于存储图的邻接表
int numVertexes,numEdges; /* 图中当前顶点数和边数 */
}graphAdjList,*GraphAdjList;
/* **************************** */
void CreateMGraph(MGraph *G)/* 构件图 */
{
int i, j;
/* printf("请输入边数和顶点数:"); */
G->numEdges=MAXEDGE;
G->numVertexes=MAXVEX;
for (i = 0; i < G->numVertexes; i++)/* 初始化图 */
{
G->vexs[i]=i;
}
for (i = 0; i < G->numVertexes; i++)/* 初始化图 */
{
for ( j = 0; j < G->numVertexes; j++)
{
G->arc[i][j]=0;
}
}
G->arc[0][4]=1;
G->arc[0][5]=1;
G->arc[0][11]=1;
G->arc[1][2]=1;
G->arc[1][4]=1;
G->arc[1][8]=1;
G->arc[2][5]=1;
G->arc[2][6]=1;
G->arc[2][9]=1;
G->arc[3][2]=1;
G->arc[3][13]=1;
G->arc[4][7]=1;
G->arc[5][8]=1;
G->arc[5][12]=1;
G->arc[6][5]=1;
G->arc[8][7]=1;
G->arc[9][10]=1;
G->arc[9][11]=1;
G->arc[10][13]=1;
G->arc[12][9]=1;
}
/* 利用邻接矩阵构建邻接表 */
//GraphAdjList是graphAdjList *类型指针,传进来的GL是指向graphAdjList *类型指针的指针
void CreateALGraph(MGraph G,GraphAdjList *GL)
{
int i,j;
EdgeNode *e; //创建一个指向边表节点类型的指针
*GL = (GraphAdjList)malloc(sizeof(graphAdjList));
(*GL)->numVertexes=G.numVertexes;
(*GL)->numEdges=G.numEdges;
for(i= 0;i <G.numVertexes;i++) /* 读入顶点信息,建立顶点表 */
{
(*GL)->adjList[i].in=0;
(*GL)->adjList[i].data=G.vexs[i];
(*GL)->adjList[i].firstedge=NULL; /* 将边表置为空表 */
}
for(i=0;i<G.numVertexes;i++) /* 建立边表 */
{
for(j=0;j<G.numVertexes;j++)
{
if (G.arc[i][j]==1)
{
e=(EdgeNode *)malloc(sizeof(EdgeNode));
e->adjvex=j; /* 邻接序号为j */
e->next=(*GL)->adjList[i].firstedge; /* 头插法,将当前顶点上的指向的结点指针赋值给e */
(*GL)->adjList[i].firstedge=e; /* 将当前顶点的指针指向e */
(*GL)->adjList[j].in++;
}
}
}
}
/* 拓扑排序,若GL无回路,则输出拓扑排序序列并返回1,若有回路返回0。 */
Status TopologicalSort(GraphAdjList GL)
{
EdgeNode *e;
int i,k,gettop;
int top=0; /* 用于栈指针下标 */
int count=0;/* 用于统计输出顶点的个数 */
int *stack; /* 建栈将入度为0的顶点入栈,这里直接用数组模拟栈 */
stack=(int *)malloc(GL->numVertexes * sizeof(int) );
for(i = 0; i<GL->numVertexes; i++)
if(0 == GL->adjList[i].in) /* 在该for循环中,将入度为0的顶点入栈 */
stack[++top]=i;
while(top!=0)
{
gettop=stack[top--];
//整个过程中只打印栈中的元素,top始终指向stack数组的最后一个元素
printf("%d -> ",GL->adjList[gettop].data);
count++; /* 输出i号顶点,并计数 */
for(e = GL->adjList[gettop].firstedge; e; e = e->next)
{
k=e->adjvex;
if( !(--GL->adjList[k].in) ) /* 将i号顶点的邻接点的入度减1,如果减1后为0,则入栈 */
stack[++top]=k;
}
}
printf("\n");
if(count < GL->numVertexes)
return ERROR;
else
return OK;
}
int main()
{
MGraph G;
GraphAdjList GL;
int result;
CreateMGraph(&G);
CreateALGraph(G,&GL);
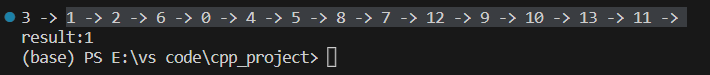
result=TopologicalSort(GL);
printf("result:%d",result);
return 0;
}
关键路径
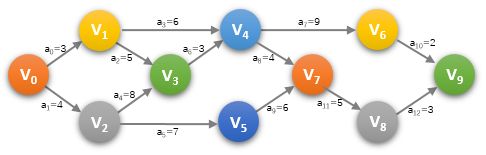
在一个表示工程的带权有向图中,用顶点表示事件,用有向边表示活动,用边上的权值表示活动的持续时间,这种有向图的边表示活动的网,称之为AOE(Activity On Edge)
在求etv[k]的最早发生时间的公式中,之所以从前往后求取的是最大值,以P239最上面的V3为例,仅当V1和V2都完成时,才能进行V3。即V3的最早发生时间应该是取最大值。
在求ltv[k]的最晚发生时间的公式中,之所以从后往前求取的是最小值,以P241最上面的V4为例,ltv[6]=25,ltv[7]=19,V6和V7两个节点的前一个节点都是V4。而求V4的最晚发生时间的限制是什么呢?即(ltv[4]+len
#include "stdio.h"
#include "stdlib.h"
#define OK 1
#define ERROR 0
#define TRUE 1
#define FALSE 0
#define MAXEDGE 30
#define MAXVEX 30
#define GRAPH_INFINITY 65535
typedef int Status; /* Status是函数的类型,其值是函数结果状态代码,如OK等 */
int *etv,*ltv; /* 事件最早发生时间和最迟发生时间数组 */
int *stack2; /* 用于存储拓扑序列的栈 */
int top2; /* 用于stack2的指针 */
/* 邻接矩阵结构 */
typedef struct
{
int vexs[MAXVEX];
int arc[MAXVEX][MAXVEX];
int numVertexes, numEdges;
}MGraph;
/* 邻接表结构****************** */
typedef struct EdgeNode /* 边表结点 */
{
int adjvex; /* 邻接点域,存储该顶点对应的下标 */
int weight; /* 用于存储权值,对于非网图可以不需要 */
struct EdgeNode *next; /* 链域,指向下一个邻接点 */
}EdgeNode;
typedef struct VertexNode /* 顶点表结点 */
{
int in; /* 顶点入度 */
int data; /* 顶点域,存储顶点信息 */
EdgeNode *firstedge;/* 边表头指针 */
}VertexNode, AdjList[MAXVEX];
typedef struct
{
AdjList adjList;
int numVertexes,numEdges; /* 图中当前顶点数和边数 */
}graphAdjList,*GraphAdjList;
/* **************************** */
void CreateMGraph(MGraph *G)/* 构件图 */
{
int i, j;
/* printf("请输入边数和顶点数:"); */
G->numEdges=13;
G->numVertexes=10;
for (i = 0; i < G->numVertexes; i++)/* 初始化图 */
{
G->vexs[i]=i;
}
for (i = 0; i < G->numVertexes; i++)/* 初始化图 */
{
for ( j = 0; j < G->numVertexes; j++)
{
if (i==j)
G->arc[i][j]=0;
else
G->arc[i][j]=GRAPH_INFINITY;
}
}
G->arc[0][1]=3;
G->arc[0][2]=4;
G->arc[1][3]=5;
G->arc[1][4]=6;
G->arc[2][3]=8;
G->arc[2][5]=7;
G->arc[3][4]=3;
G->arc[4][6]=9;
G->arc[4][7]=4;
G->arc[5][7]=6;
G->arc[6][9]=2;
G->arc[7][8]=5;
G->arc[8][9]=3;
}
/* 利用邻接矩阵构建邻接表 */
void CreateALGraph(MGraph G,GraphAdjList *GL)
{
int i,j;
EdgeNode *e;
*GL = (GraphAdjList)malloc(sizeof(graphAdjList));
(*GL)->numVertexes=G.numVertexes;
(*GL)->numEdges=G.numEdges;
for(i= 0;i <G.numVertexes;i++) /* 读入顶点信息,建立顶点表 */
{
(*GL)->adjList[i].in=0;
(*GL)->adjList[i].data=G.vexs[i];
(*GL)->adjList[i].firstedge=NULL; /* 将边表置为空表 */
}
for(i=0;i<G.numVertexes;i++) /* 建立边表 */
{
for(j=0;j<G.numVertexes;j++)
{
if (G.arc[i][j]!=0 && G.arc[i][j]<GRAPH_INFINITY)
{
e=(EdgeNode *)malloc(sizeof(EdgeNode));
e->adjvex=j; /* 邻接序号为j */
e->weight=G.arc[i][j];
e->next=(*GL)->adjList[i].firstedge; /* 将当前顶点上的指向的结点指针赋值给e */
(*GL)->adjList[i].firstedge=e; /* 将当前顶点的指针指向e */
(*GL)->adjList[j].in++;
}
}
}
}
/* 拓扑排序 */
Status TopologicalSort(GraphAdjList GL)
{ /* 若GL无回路,则输出拓扑排序序列并返回1,若有回路返回0。 */
EdgeNode *e;
int i,k,gettop;
int top=0; /* 用于栈指针下标 */
int count=0;/* 用于统计输出顶点的个数 */
int *stack; /* 建栈将入度为0的顶点入栈 */
stack=(int *)malloc(GL->numVertexes * sizeof(int) );
for(i = 0; i<GL->numVertexes; i++)
if(0 == GL->adjList[i].in) /* 将入度为0的顶点入栈 */
stack[++top]=i;
top2=0;
etv=(int *)malloc(GL->numVertexes * sizeof(int) ); /* 事件最早发生时间数组 */
for(i=0; i<GL->numVertexes; i++)
etv[i]=0; /* 初始化 */
stack2=(int *)malloc(GL->numVertexes * sizeof(int) );/* 初始化拓扑序列栈 */
printf("TopologicalSort:\t");
while(top!=0)
{
gettop=stack[top--];
printf("%d -> ",GL->adjList[gettop].data);
count++; /* 输出i号顶点,并计数 */
stack2[++top2]=gettop; /* 将弹出的顶点序号压入拓扑序列的栈 */
for(e = GL->adjList[gettop].firstedge; e; e = e->next)
{
k=e->adjvex;
if( !(--GL->adjList[k].in) ) /* 将i号顶点的邻接点的入度减1,如果减1后为0,则入栈 */
stack[++top]=k;
if((etv[gettop] + e->weight)>etv[k]) /* 求各顶点事件的最早发生时间etv值 */
etv[k] = etv[gettop] + e->weight;
}
}
printf("\n");
if(count < GL->numVertexes)
return ERROR;
else
return OK;
}
/* 求关键路径,GL为有向网,输出G的各项关键活动 */
void CriticalPath(GraphAdjList GL)
{
EdgeNode *e;
int i,gettop,k,j;
int ete,lte; /* 声明活动最早发生时间和最迟发生时间变量 */
TopologicalSort(GL); /* 求拓扑序列,计算数组etv和stack2的值 */
ltv=(int *)malloc(GL->numVertexes*sizeof(int));/* 事件最晚发生时间数组 */
for(i=0; i<GL->numVertexes; i++)
ltv[i]=etv[GL->numVertexes-1]; /* 初始化 */
printf("etv:\t");
for(i=0; i<GL->numVertexes; i++)
printf("%d -> ",etv[i]);
printf("\n");
while(top2!=0) /* 出栈是求ltv */
{
gettop=stack2[top2--];
for(e = GL->adjList[gettop].firstedge; e; e = e->next) /* 求各顶点事件的最迟发生时间ltv值 */
{
k=e->adjvex;
if(ltv[k] - e->weight < ltv[gettop])
ltv[gettop] = ltv[k] - e->weight;
}
}
printf("ltv:\t");
for(i=0; i<GL->numVertexes; i++)
printf("%d -> ",ltv[i]);
printf("\n");
for(j=0; j<GL->numVertexes; j++) /* 求ete,lte和关键活动 */
{
for(e = GL->adjList[j].firstedge; e; e = e->next)
{
k=e->adjvex;
ete = etv[j]; /* 活动最早发生时间 */
lte = ltv[k] - e->weight; /* 活动最迟发生时间 */
if(ete == lte) /* 两者相等即在关键路径上 */
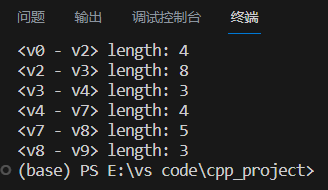
printf(" length: %d \n" ,GL->adjList[j].data,GL->adjList[k].data,e->weight);
}
}
}
int main(void)
{
MGraph G;
GraphAdjList GL;
CreateMGraph(&G);
CreateALGraph(G,&GL);
CriticalPath(GL);
return 0;
}