matplotlib从起点出发(6)_Tutorial_6_Animations
1 在matplotlib中使用动画
基于其绘图功能,matplotlib还提供了一个使用动画模块生成动画animation的接口。动画是一系列帧,其中每个帧对应于图形Figure 上的一个绘图。本教程介绍了有关如何创建此类动画的一般准则以及可用的不同选项。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.animation as animation
import numpy as np
2 动画类
matplotlib中的动画可以用2种不同的方式来思考:
FuncAnimation: 为首帧生成数据,然后在首帧数据的基础上为后续的每一帧进行修改,进而生成一组动图;ArtistAnimation: 生成一列(可迭代的)artists,绘制每一帧,生成动图。
FuncAnimation在速度和内存方面更有效,因为它仅绘制artist一次,然后对其进行修改;另一方面,ArtistAnimation是灵活的,因为它允许任何可迭代的artist在一个序列中进行动画处理。
FuncAnimation
FuncAnimation类允许我们通过传递一个迭代修改绘图数据的函数来创建动画。这里通过在各种artist上使用setter方法来实现的(例如:Line2D、PathCollection等)。通常的FuncAnimation对象采用我们想要动画化的图形和修改绘制在图形上的数据的function函数。它使用帧参数来确定动画的长度。间隔参数用于确定绘制两帧之间的时间(以ms为单位)。使用FuncAnimation制作动画通常遵循以下结构:
- 绘制初始图形,包括所有必需的artists,将所有artists保存在变量中,以便以后可以在动画过程中更新它们;
- 创建一个动画函数,该函数更新每个artist中的数据,以便在每次函数调用时生成新帧;
- 使用Figure和动画函数以及确定动画属性的关键字参数创建
FuncAnimation对象; - 使用动画。
Animation.save或pyplot.show用于保存或显示动画。
更新函数使用set_*函数提供不同的artist修改数据。下表显示了几种打印方法、它们返回的artist类型以及可用于更新它们的一些方法。
| Plotting method | Artist | Set method |
|---|---|---|
Axes.plot |
lines.Line2D |
set_data |
Axes.scatter |
collections.PathCollection |
set_offsets |
Axes.imshow |
image.AxesImage |
AxesImage.set_data |
Axes.annotate |
text.Annotation |
update_positions |
Axes.barh |
patches.Rectangle |
set_angle,set_bounds,set_height,set_width,set_x,set_y,set_xy |
Axes.fill |
patches.Polygon |
set_xy |
Axes.add_patch(patches.Ellipse) |
patches.Ellipse |
set_angle,set_center,set_height,set_width |
涵盖所有类型的artist设置方法超过了本教程的范围,但可以在它们各自的文档中找到。用于Axes.scatter和Axes.plot的此类更新方法的示例如下:
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
t = np.linspace(0, 3, 40)
g = -9.81
v0 = 12
z = g * t**2 / 2 + v0 * t
v02 = 5
z2 = g * t**2 / 2 + v02 * t
scat = ax.scatter(t[0], z[0], c="b", s=5, label=f'v0 = {v0} m/s')
line2 = ax.plot(t[0], z2[0], label=f'v0 = {v02} m/s')[0]
ax.set(xlim=[0, 3], ylim=[-4, 10], xlabel='Time [s]', ylabel='Z [m]')
ax.legend()
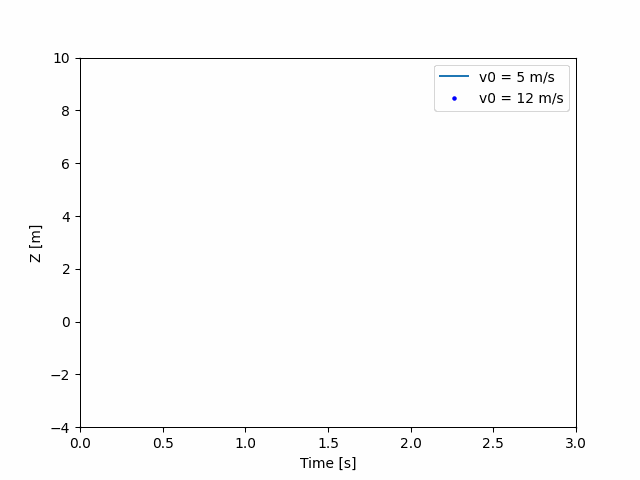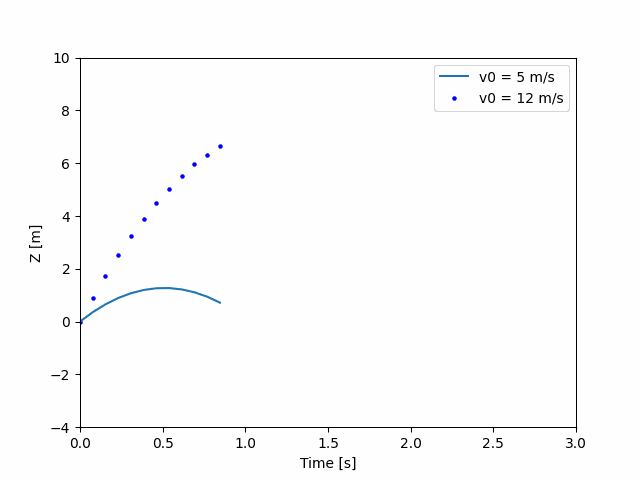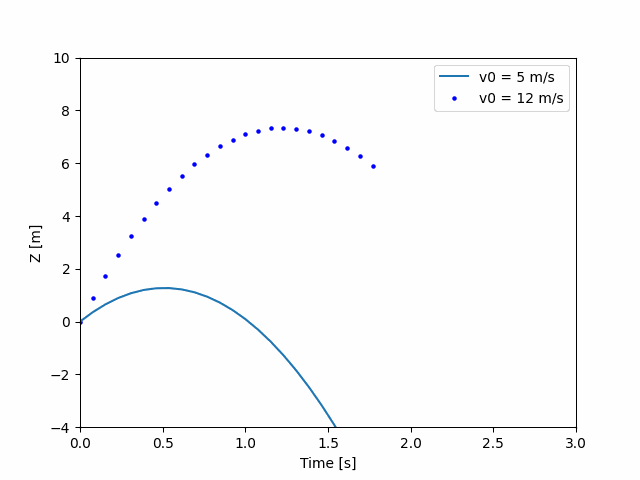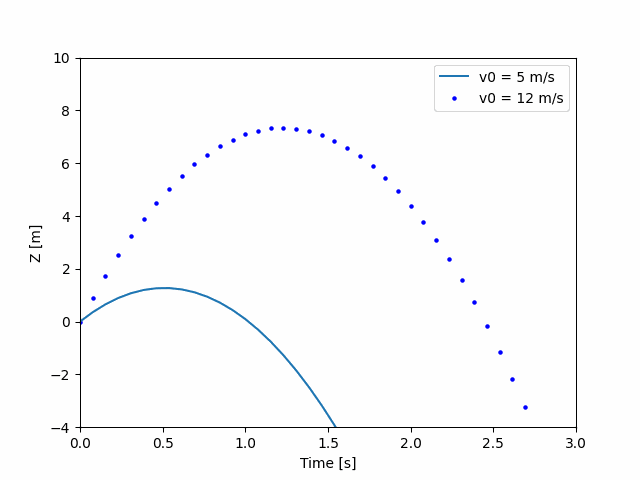
def update(frame):
# 为每一帧,更新每一个artist对象中存储的数据.
x = t[:frame]
y = z[:frame]
# 更新散点图scatter plot:
data = np.stack([x, y]).T
scat.set_offsets(data)
# 更新曲线图line plot:
line2.set_xdata(t[:frame])
line2.set_ydata(z2[:frame])
return (scat, line2)
ani = animation.FuncAnimation(fig=fig, func=update, frames=40, interval=30)
plt.show()
ArtistAnimation
如果存在存储在各种不同artist上的数据,则可以使用artist的列表逐帧转换为动画。例如,当我们使用Axes.barh绘制柱形图时,它会为每个柱形和误差柱创建许多的artist。要更新绘图,需要单独更新窗口中的每个柱形并重新绘制它们。相反,animation.artistAnimation可用于单独绘制每一帧,然后拼接在一起形成动画。柱形图竞赛就是一个简单的例子。
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
rng = np.random.default_rng(19680801)
data = np.array([20, 20, 20, 20])
x = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4])
artists = []
colors = ['tab:blue', 'tab:red', 'tab:green', 'tab:purple']
for i in range(20):
data += rng.integers(low=0, high=10, size=data.shape)
container = ax.barh(x, data, color=colors)
artists.append(container)
ani = animation.ArtistAnimation(fig=fig, artists=artists, interval=400)
plt.show()
3 动图保存器
动画对象可以使用各种多媒体写入器(例如:Pillow, ffpmeg, imagemagick)保存到磁盘。并非所有编写器都支持所有视频格式。有4种主要类型的artist:
PillowWriter- 使用Pillow库创建动图;HTMLWriter- 使用基于JavaScript的动图;- 基于管道的编写器 -
FFMpegWriter和ImageMagickWriter是基于管道的编写器。这些编写器将每个帧通过管道传输到实用程序(ffmpeg/imagemagick),然后将它们全部拼接在一起以创建动画; - 基于文件的编写器 -
FFMpegFileWriter和ImageMagickFileWriter是基于文件的编写器的示例。这些编写器比基于管道的替代方法慢,但对于调试更有用,因为它们在将它们拼接成动画之前将每个帧保存在文件中。
保存动图
| Writer | SupportedFormats |
|---|---|
PillowWriter |
.gif, .apng, .webp |
HTMLWriter |
.htm, .html, .png |
FFMpegWriter, FFMpegFileWriter |
所有ffmpeg支持的格式:ffmpeg -formats |
ImageMagickWriter, ImageMagickFileWriter |
所有imagemagick支持的格式:magick -list format |
要采用任何编写器保存动画,我们可以使用animation.Animation.save 方法。它采用我们要保存动画的文件名和编写器,该编写器可以是字符串或编写器对象。它还需要一个fps参数。此参数不同于FuncAnimation或ArtistAnimation使用的区间参数。FPS确定保存的动画使用的帧速率,而间隔确定显示的动画使用的帧速率。
下面是一些示例,演示如何使用不同的编写器保存动画。
Pillow 写入器
ani.save(filename="/tmp/pillow_example.gif", writer="pillow")
ani.save(filename="/tmp/pillow_example.apng", writer="pillow")
HTML 写入器
ani.save(filename="/tmp/html_example.html", writer="html")
ani.save(filename="/tmp/html_example.htm", writer="html")
ani.save(filename="/tmp/html_example.png", writer="html")
FFMpegWriter
ani.save(filename="/tmp/ffmpeg_example.mkv", writer="ffmpeg")
ani.save(filename="/tmp/ffmpeg_example.mp4", writer="ffmpeg")
ani.save(filename="/tmp/ffmpeg_example.mjpeg", writer="ffmpeg")
Imagemagick 写入器
ani.save(filename="/tmp/imagemagick_example.gif", writer="imagemagick")
ani.save(filename="/tmp/imagemagick_example.webp", writer="imagemagick")
ani.save(filename="apng:/tmp/imagemagick_example.apng",
writer="imagemagick", extra_args=["-quality", "100"])
(apng的extra_args需要减小文件大小~10X).