day58 单调栈
单调栈
使用场景:通常是一维数组,要寻找任一个元素的右边或者左边第一个比自己大或者小的元素的位置
本质:空间换时间
三个判断条件:
当前遍历的元素T[i]小于栈顶元素T[st.top()]的情况
当前遍历的元素T[i]等于栈顶元素T[st.top()]的情况
当前遍历的元素T[i]大于栈顶元素T[st.top()]的情况
739. 每日温度
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> dailyTemperatures(vector<int>& temperatures) {
stack<int>s;
vector<int>result(temperatures.size(), 0);
s.push(0);
int index = 1;
while(index < temperatures.size()){
while(!s.empty() && temperatures[s.top()] < temperatures[index]){
int temp = s.top();
s.pop();
result[temp] = index - temp;
}
s.push(index);
index++;
}
return result;
}
};
496. 下一个更大元素 I
题目: 给你两个 没有重复元素 的数组 nums1 和 nums2 ,其中nums1 是 nums2 的子集。
请你找出 nums1 中每个元素在 nums2 中的下一个比其大的值。
思路 : num2作单调栈找下一个大的值,弹出时,判断是否在num1中出现过,如果出现则进行赋值,链接使用unordered_map
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> nextGreaterElement(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2) {
vector<int>result(nums1.size(), -1);
unordered_map<int, int>m;
stack<int>s;
for(int i=0; i<nums1.size();i++){
m[nums1[i]] = i;
}
s.push(0);
int index = 1;
while(index < nums2.size()){
while(!s.empty() && nums2[s.top()] < nums2[index]){ //弹出时判断
if(m.find(nums2[s.top()]) != m.end()){
result[m[nums2[s.top()]]] = nums2[index];
}
s.pop();
}
s.push(index);
index++;
}
return result;
}
};
503. 下一个更大元素 II
题目:循环数组
简单版: 两个数组拼接在一起,然后使用单调栈求下一个最大值
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> nextGreaterElements(vector<int>& nums) {
int n = nums.size();
vector<int>result(n , -1);
for(int i=0; i<n; i++) nums.push_back(nums[i]);
stack<int>s;
s.push(0);
for(int i=1; i<nums.size(); i++){
while(!s.empty() && nums[s.top()] < nums[i]){
if(s.top()<n){
result[s.top()] = nums[i];
}
s.pop();
}
s.push(i);
}
return result;
}
};
改进版: 不扩充nums,而是在遍历的过程中模拟走了两边nums
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> nextGreaterElements(vector<int>& nums) {
int n = nums.size();
vector<int>result(n , -1);
stack<int>s;
s.push(0);
for(int i=1; i<n*2; i++){
while(!s.empty() && nums[s.top()%n] < nums[i%n]){
if(s.top()<n){
result[s.top()] = nums[i%n];
}
s.pop();
}
s.push(i);
}
return result;
}
};
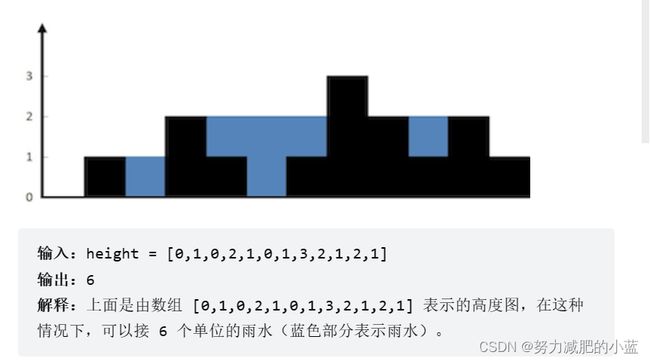
42. 接雨水
- 暴力
思路:如果按照列来计算的话,宽度一定是1了,我们再把每一列的雨水的高度求出来就可以了
每一列雨水的高度,取决于,该列左侧最高的柱子和右侧最高的柱子中最矮的那个柱子的高度。
问题:复杂度为O(n^2) 超时
class Solution {
public:
int trap(vector<int>& height) {
int sum = 0;
for(int i=1; i<height.size()-1; i++){
int left = 0;
int right = 0;
for(int j=i; j>=0; j--){
left = max(left, height[j]);
}
for(int j=i; j<height.size(); j++){
right = max(right, height[j]);
}
sum += min(left, right) - height[i];
}
return sum;
}
};
2.双指针改进暴力 空间换时间 提前将左右最高高度算出来
class Solution {
public:
int trap(vector<int>& height) {
int sum = 0;
vector<int>left(height.size(), 0);
vector<int>right(height.size(), 0);
int m_left = height[0];
int m_right = height[height.size()-1];
for(int i=0; i<height.size(); i++){
m_left = max(m_left, height[i]);
left[i] = m_left;
}
for(int i=height.size()-1; i>=0; i--){
m_right = max(m_right, height[i]);
right[i] = m_right;
}
for(int i=1; i<height.size()-1; i++){
sum += min(left[i], right[i]) - height[i];
}
return sum;
}
};
- 双指针
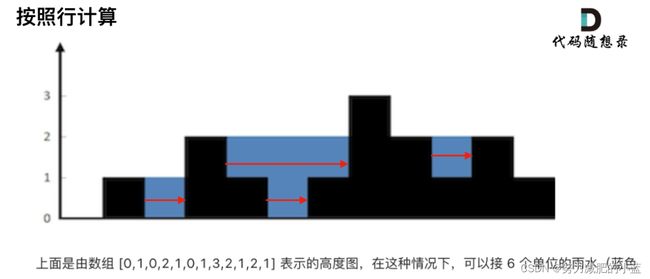
思路:
单调栈是按照行方向来计算雨水
栈顶和栈顶的下一个元素以及要入栈的元素,三个元素来接水
雨水高度是 min(凹槽左边高度, 凹槽右边高度) - 凹槽底部高度
水的宽度是 凹槽右边的下标 - 凹槽左边的下标 - 1
class Solution {
public:
int trap(vector<int>& height) {
stack<int>s;
int sum = 0;
s.push(0);
for(int i=1; i<height.size(); i++){
while(!s.empty() && height[s.top()] < height[i]){
int cur = s.top();
s.pop();
if(!s.empty()){ //来避免 栈内[2] 元素3 村水量 0 只要弹出就可以了
int h = min(height[i], height[s.top()]) - height[cur];
sum += h * (i-s.top()-1);
}
}
s.push(i);
}
return sum;
}
};
84. 柱状图中最大的矩形
题目给定 n 个非负整数,用来表示柱状图中各个柱子的高度。每个柱子彼此相邻,且宽度为 1 。
求在该柱状图中,能够勾勒出来的矩形的最大面积。
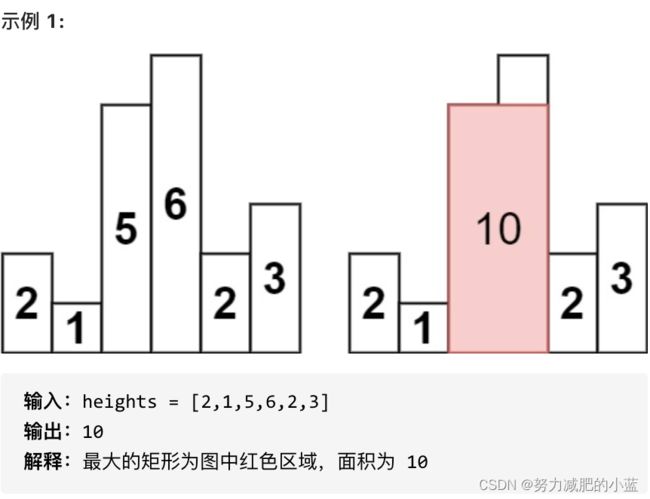
主体思路:
每一个位置能达到的最大面积取决于它左右两侧小于它的高度位置。
int w = right-left - 1;
int h = heights[i];
sum = max(sum, w*h);
暴力超时
class Solution {
public:
int largestRectangleArea(vector<int>& heights) {
int sum = 0;
for(int i=0; i<heights.size(); i++){
int left = i;
int right = i;
while(left >= 0){
if(heights[left] < heights[i]) break;
left--;
}
while(right < heights.size()){
if(heights[right] < heights[i]) break;
right++;
}
int w = right-left - 1;
int h = heights[i];
sum = max(sum, w*h);
}
return sum;
}
};
双指针优化,空间换时间,提前记录左右两侧的位置信息没有数组保存时,需要一个一个跳进行比较。有数组后,那么可以利用之前的比较信息进行跳着比较。
heights[left] >= heights[i]) 时
直接跳到 left[left]指向的位置
注意
left是往左跳 则遍历顺序从左到右
right 向右跳,则右边的先算,遍历顺序从右向左
class Solution {
public:
int largestRectangleArea(vector<int>& heights) {
int n = heights.size();
vector<int>left(n, -1);
vector<int>right(n, n);
for(int i=0; i<n; i++){
int l = i-1;
while(l>=0 && (heights[l] >= heights[i])) l = left[l];
left[i] = l;
}
for(int i=n-1; i>=0; i--){
int r = i+1;
while(r < n && (heights[r] >= heights[i])) r = right[r];
right[i] =r;
}
int sum=0;
for(int i=0; i<n; i++){
sum = max(sum, heights[i] *(right[i]-left[i]-1));
}
return sum;
}
};
单调栈:目的找到左右两侧第一个比它小的元素
栈内元素从小到大,
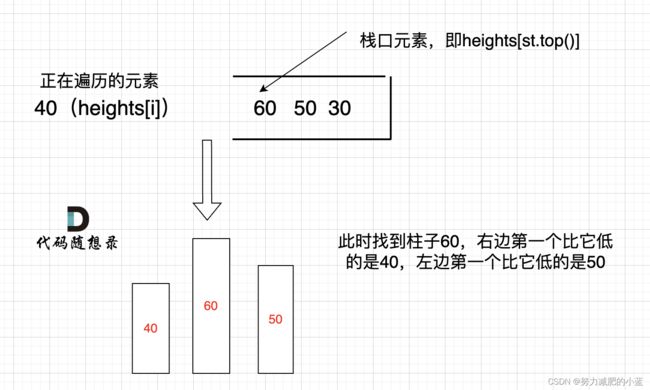
当前元素小于栈顶元素时, 当前元素就是右边界,栈顶元素的下一个元素就是左边界, w = right - left - 1 h = height[s.top()] sum = max(sum, h*w)
注意两种情况
- 2 3 4 5 递增序列没有机会弹出 所以在最后面加入一个0 —> 2 3 4 5 0
- 8 7 6 5 第一个元素没有左边界 所以在最前面加入一个0 —> 0 8 7 6 5
class Solution {
public:
int largestRectangleArea(vector<int>& heights) {
heights.push_back(0);
heights.insert(heights.begin(), 0);
int n = heights.size();
stack<int>s;
s.push(0);
int sum = 0;
for(int i=1; i<n; i++){
if(heights[i] > heights[s.top()]){
s.push(i);
}else if(heights[i] == heights[s.top()]){
s.pop();
s.push(i);
}else{
while(!s.empty() && (heights[i] < heights[s.top()])){
int mid = s.top();
s.pop();
if(!s.empty()){
int left = s.top();
int w = i-left-1;
int h = heights[mid];
sum = max(sum, w*h);
}
}
s.push(i);
}
}
return sum;
}
};