软件体系结构-KWIC索引系统
引言
KWIC作为一个早年间在ACM的Paper提出的一个问题,被全世界各个大学的软件设计课程奉为课堂讲义或者作业的经典。(From Wiki,FYI,D. L. Parnas uses a KWIC Index as an example on how to perform modular design in his paper “On the Criteria To Be Used in Decomposing Systems into Modules” - Available as ACM Classic Paper)

这道题旨在深入理解模块和组件之间的划分,解法有多种,通过不同的解决方案来体会软件设计的体系结构。
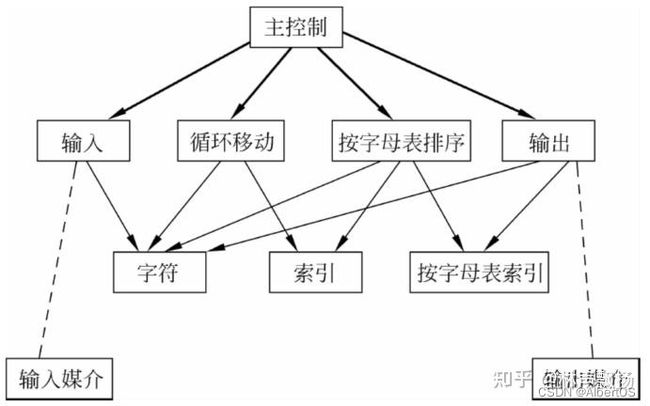
解决方案1:使用共享数据的主程序/子程序
解法:分解为四个组件:输入、移位、排列和输出,主程序依次对他们进行调用,数据通过共享存储在组件间共享,组件与数据之间读写不受约束,由主程序协调保证读写顺序。
优劣:
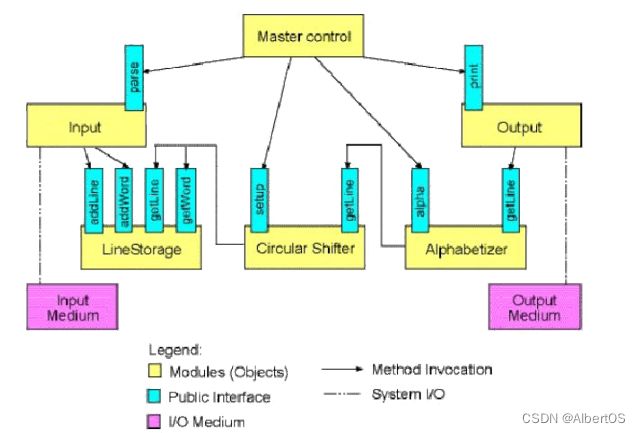
#include 解决方案2:抽象数据类型/面向对象风格
解法:对比方案一,分为五个模块,数据不再共享,而是相反做了接口隔离,将各个功能模块分开设计,并且利用权限控制保证了封装的特性,系统的扩展性和封装性增强,是个基本的面向对象方案。
优劣:
// C++参考代码:
#include 解决方案三:基于事件通知的方案/响应式
解法:类似方案一,但数据更抽象,而不是暴露数据格式,数据被修改时,隐式调用计算。
基于事件通知的系统中的各个功能并不是直接被调用的,而是通过组建通知或广播事件信息而触发的。其他组件可以通过注册一个与某个事件通知相关联的过程而与其发生联系。
优劣:
- 较容易支持新增功能、新增模块
- 计算与数据隔离
- 支持复用
- 比较难改变隐式调用的顺序
- 由于数据驱动通常导致空间占用问题
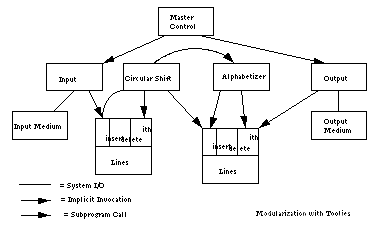
一般这样的方案有两种设计,一个是系统有一个分立出来的事件中心,专门负责接收所有传来的信息,并且将它们分发给系统的其他组件,它可以是广播,可以是针对某些特定事件而设定特定的反应。
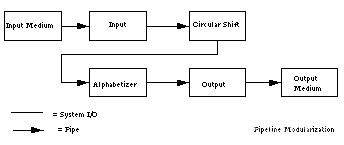
解决方案四:基于管道的方案
解法:在基于管道的方案中,每个组件都会有一组输入流和一组输出流,一个组件读入,然后处理后送出到下一个组件上。这个组件一般称为filter。连接器则称为pipes。filter之间不能有数据共享,并且彼此相互独立。
管道由一系列过滤器组成,通过数据流连接
分布式,每个过滤器只要有要计算的数据就可以运行
过滤器之间的数据共享严格限于在管道上传输的数据
优劣:
- 直观
- 支持重用,因为每个过滤器都可以独立运行
- 通过插入新的过滤器,容易新增功能(删除行除外
- 端口之间数据复制传递,有性能损耗。
#include 总结
KWIC索引系统是软件体系结构研究领域的一个经典案例,它为我们提供了一个理解软件架构设计原则和实践的框架。它的价值在于,可以帮助我们在设计大型软件系统时,更好地平衡复杂性、灵活性和性能,帮助我们更好地理解和应用软件体系结构设计原则。