opencv+python(四)
十八、模板匹配
模板匹配和卷积原理很像,模板在原图像上从原点开始滑动,计算模板与(图像被模板覆盖的地方)的差别程度,这个差别程度的计算方法在opec里有6种,然
后将每次计算的结果放入一个矩车里,作为结果输出。假如原图形是AxB大小,而模板是xb大小,则输出结果的矩阵是(A-a+1)x(Bb+1)
# 模板匹配
import numpy as np
img = cv2.imread('cat.jpg', 0)
img1 = cv2.imread('cat_1.jpg', 0)
# print(img.shape)
# print(img1.shape)
w, h = img1.shape[:2] # 取出宽,长
print(w, h)
methods = ['cv2.TM_SQDIFF', 'cv2.TM_CCORR', 'cv2.TM_CCOEFF', 'cv2.TM_SQDIFF_NORMED', 'cv2.TM_CCORR_NORMED', 'cv2.TM_CCOEFF_NORMED']
# 2和3效果不行 'cv2.TM_CCORR', 'cv2.TM_CCOEFF'
# res = cv2.matchTemplate(img, img1, cv2.TM_CCOEFF)
# print(res.shape)
# min_val, max_val, min_loc, max_loc = cv2.minMaxLoc(res)
# print(min_val, max_val, min_loc, max_loc)
# cv2.imshow('img', img)
# cv2.imshow('img1', img1)
# cv2.imshow('img2', res)
for meth in methods:
img2 = img.copy()
method = eval(meth) # 传入的不能是字符串,要转为真值,即去掉''
print(meth)
res = cv2.matchTemplate(img, img1, method)
min_val, max_val, min_loc, max_loc = cv2.minMaxLoc(res)
if method in [cv2.TM_SQDIFF, cv2.TM_SQDIFF_NORMED]:
top_left = min_loc
else:
top_left = max_loc
bottom_right = (top_left[0] + w, top_left[1]+h)
img3 = cv2.rectangle(img2, top_left, bottom_right, 255, 2) # 在img2图像上画方框,top(左上)和bottom(右下)是两个坐标点
cv2.imshow(meth, img3)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()匹配多个对象
# 匹配多个对象
import numpy as np
img = cv2.imread('stars.png')
img3 = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
img1 = cv2.imread('star.png', 0)
w, h = img1.shape[:2] # 取出宽,长
print(w, h)
methods = ['cv2.TM_SQDIFF', 'cv2.TM_CCORR', 'cv2.TM_CCOEFF', 'cv2.TM_SQDIFF_NORMED', 'cv2.TM_CCORR_NORMED', 'cv2.TM_CCOEFF_NORMED']
# 2和3效果不行 'cv2.TM_CCORR', 'cv2.TM_CCOEFF'
res = cv2.matchTemplate(img3, img1, cv2.TM_CCOEFF_NORMED)
print(res.shape)
print(res.size)
threshold = 0.9
# 取匹配值程度大于80%的坐标
loc = np.where(res >= threshold)
print(loc[::-1])
for pt in zip(*loc[::-1]): # *号表示可选参数,zip()函数
# img3 = img.copy()
print(pt[0], pt[1])
bottom_right = (pt[0] + w, pt[1] + h)
cv2.rectangle(img3, pt, bottom_right, (0, 0, 255), 2)
# min_val, max_val, min_loc, max_loc = cv2.minMaxLoc(res)
# print(min_val, max_val, min_loc, max_loc)
cv2.imshow('res', res)
cv2.imshow('img3', img3)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()zip()函数的应用:
zip() 函数用于将可迭代的对象作为参数,将对象中对应的元素打包成一个个元组,然后返回由这些元组组成的列表。
如果各个迭代器的元素个数不一致,则返回列表长度与最短的对象相同,利用*号操作符,可以将元组解压为列表。
numpy.where()、python[::-1]、zip()三个知识点
十九、直方图
# 直方图
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 显示单通道
img = cv2.imread('cat.jpg', 0)
cv2.imshow('cat', img)
hist = cv2.calcHist([img], [0], None, [256], [0,256])
print(hist.shape)
plt.hist(img.ravel(),256)
plt.show()
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
# 显示多通道
img = cv2.imread('cat.jpg')
color = ('b', 'g', 'r')
for i, col in enumerate(color):
histr = cv2.calcHist([img],[i],None,[256],[0,256])
plt.plot(histr,color = col)
plt.xlim([0,256])
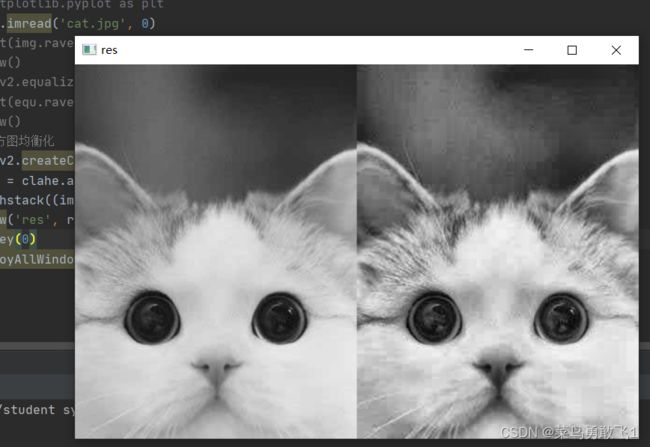
plt.show()直方图均衡化(增强对比度)
# 直方图均衡化
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
img = cv2.imread('child.jpg', 0)
# plt.hist(img.ravel(),256)
# plt.show()
# equ = cv2.equalizeHist(img) # 直方图均衡化
# plt.hist(equ.ravel(),256)
# plt.show()
# 自适应直方图均衡化
clahe = cv2.createCLAHE(clipLimit=2.0, tileGridSize=(8,8))
res_clahe = clahe.apply(img)
res = np.hstack((img, res_clahe))
cv2.imshow('res', res)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
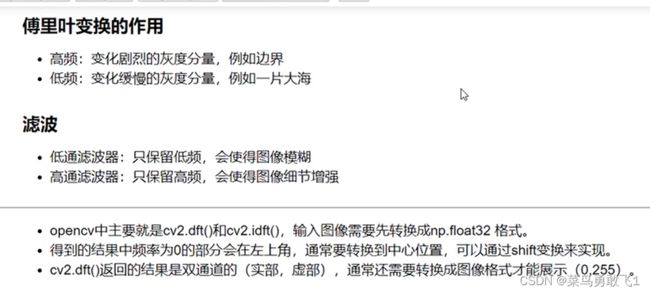
二十、傅里叶变换
心得:用傅里叶变换,转化到频域里处理时,在原始图像里要每个像素都处理,频域里只要处理频率就可以了,使得效率更高、速度更快
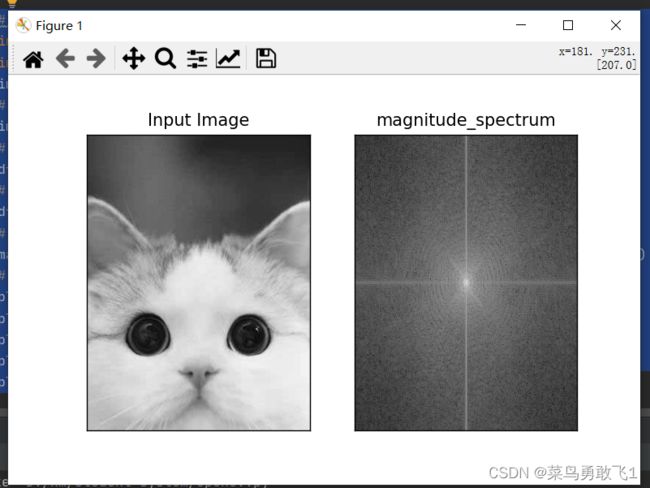
# 傅里叶变换
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
img = cv2.imread('cat.jpg',0)
# 先将图像转成float型
img_float32 = np.float32(img)
# 傅里叶变换
dft = cv2.dft(img_float32, flags=cv2.DFT_COMPLEX_OUTPUT)
# 将低频转移到坐标中心处
dft_shift = np.fft.fftshift(dft)
# 得到灰度图能表示的形式
magnitude_spectrum = 20*np.log(cv2.magnitude(dft_shift[:,:,0],dft_shift[:,:,1]))
# 显示
plt.subplot(121),plt.imshow(img,cmap='gray')
plt.title('Input Image'), plt.xticks([]),plt.yticks([])
plt.subplot(122),plt.imshow(magnitude_spectrum,cmap='gray')
plt.title('magnitude_spectrum'), plt.xticks([]),plt.yticks([])
plt.show()效果图:
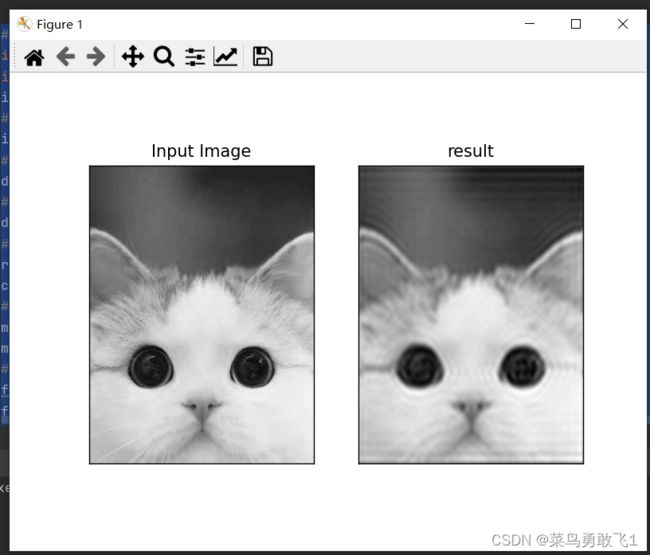
低通滤波器:
# 低通滤波器
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
img = cv2.imread('cat.jpg',0)
# 先将图像转成float型
img_float32 = np.float32(img)
# 傅里叶变换
dft = cv2.dft(img_float32, flags=cv2.DFT_COMPLEX_OUTPUT)
# 将低频转移到坐标中心处
dft_shift = np.fft.fftshift(dft)
# 求出图像的中心位置
rows, cols = img.shape
crow, ccol = int(rows/2), int(cols/2)
# mask掩码,低通滤波器
mask = np.zeros((rows, cols, 2),np.uint8)
mask[crow-30:crow+30, ccol-30:ccol+30] = 1 # 保留中间区域
# IDFT 傅里叶逆变换
fshift = dft_shift*mask
f_ishift = np.fft.ifftshift(fshift)
img_back = cv2.idft(f_ishift)
img_back = cv2.magnitude(img_back[:,:,0],img_back[:,:,0])
# 显示
plt.subplot(121),plt.imshow(img,cmap='gray')
plt.title('Input Image'), plt.xticks([]),plt.yticks([])
plt.subplot(122),plt.imshow(img_back,cmap='gray')
plt.title('result'), plt.xticks([]),plt.yticks([])
plt.show()效果图: (图像变得模糊)
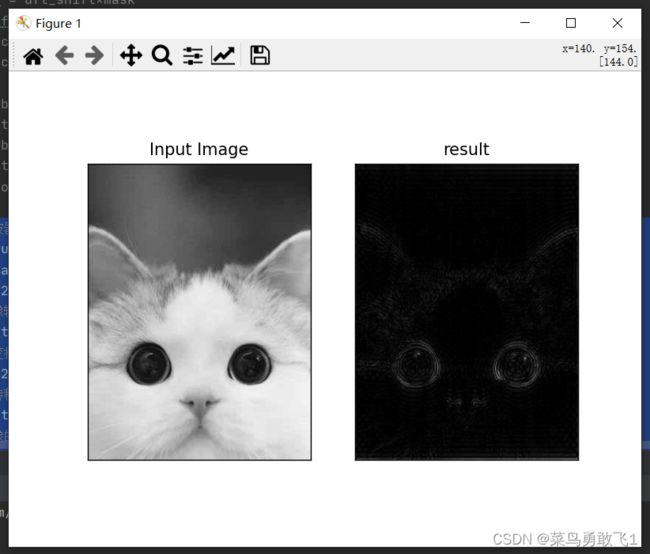
高通滤波器:
# 高通滤波器
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
img = cv2.imread('cat.jpg',0)
# 先将图像转成float型
img_float32 = np.float32(img)
# 傅里叶变换
dft = cv2.dft(img_float32, flags=cv2.DFT_COMPLEX_OUTPUT)
# 将低频转移到坐标中心处
dft_shift = np.fft.fftshift(dft)
# 求出图像的中心位置
rows, cols = img.shape
crow, ccol = int(rows/2), int(cols/2)
# mask掩码,低通滤波器
mask = np.ones((rows, cols, 2),np.uint8)
mask[crow-30:crow+30, ccol-30:ccol+30] = 0 # 将中间区域赋值为0
# IDFT 傅里叶逆变换
fshift = dft_shift*mask
f_ishift = np.fft.ifftshift(fshift)
img_back = cv2.idft(f_ishift)
img_back = cv2.magnitude(img_back[:,:,0],img_back[:,:,0])
# 显示
plt.subplot(121),plt.imshow(img,cmap='gray')
plt.title('Input Image'), plt.xticks([]),plt.yticks([])
plt.subplot(122),plt.imshow(img_back,cmap='gray')
plt.title('result'), plt.xticks([]),plt.yticks([])
plt.show()效果图:(提取轮廓)