深入理解 SQL:从基本查询到高级聚合
目录
- 背景
- 理论知识
- 示例
-
- 1211. 查询结果的质量和占比(Round group by)
- 1204. 最后一个能进入巴士的人 (Having limit order by)
- 1193. 每月交易 I(if group by)
- 1179. 重新格式化部门表
- 1174. 即时食物配送 II(子查询)
- 1164. 指定日期的产品价格(union groupby having)
- 总结
背景
7月leetcode 中 sql集训
理论知识
SQL(Structured Query Language)是一种用于管理和操作关系型数据库的标准化语言。无论是在日常开发中还是数据分析领域,SQL都扮演着重要的角色。本博客将带您深入理解SQL,并探索从基本查询到高级聚合的关键概念。
- SELECT语句:从表中选择数据
SQL的核心是SELECT语句,它用于从数据库表中检索数据。SELECT语句的基本结构如下:
Copy code
SELECT 列名1, 列名2, ...
FROM 表名;
使用SELECT语句,我们可以从表中获取所需的列,并可选地应用过滤条件。
- WHERE子句:筛选数据
WHERE子句用于对SELECT语句的结果进行筛选,只返回满足特定条件的数据。
SELECT 列名1, 列名2, ...
FROM 表名
WHERE 条件;
条件可以是比较运算符(例如:=, <, >, <=, >=, <>)或逻辑运算符(例如:AND, OR, NOT)。通过WHERE子句,我们可以获取符合特定条件的数据行。
- ORDER BY子句:排序数据
ORDER BY子句用于对SELECT语句的结果进行排序,可以按照一个或多个列进行升序或降序排列。
SELECT 列名1, 列名2, ...
FROM 表名
ORDER BY 列名1 ASC/DESC, 列名2 ASC/DESC, ...;
这样,我们可以以特定的顺序获取数据,使其更容易理解和分析。
- 聚合函数:统计和分析数据
SQL提供了一组强大的聚合函数,用于对数据进行汇总和分析。
常见的聚合函数包括:
COUNT:统计行数
SUM:计算总和
AVG:计算平均值
MAX:找到最大值
MIN:找到最小值
SELECT COUNT(*), SUM(销售额), AVG(利润)
FROM 销售表;
- GROUP BY子句:分组汇总数据
GROUP BY子句用于对数据进行分组,并在每个分组上应用聚合函数。
SELECT 列名1, 列名2, 聚合函数1, 聚合函数2, ...
FROM 表名
GROUP BY 列名1, 列名2;
通过GROUP BY,我们可以对数据按照指定的列进行分组,并获得每个分组的汇总结果。
- HAVING子句:过滤分组后的数据
HAVING子句用于对GROUP BY子句生成的分组结果进行筛选,类似于WHERE子句,但WHERE用于筛选行,HAVING用于筛选分组。
SELECT 列名1, 列名2, 聚合函数1, 聚合函数2, ...
FROM 表名
GROUP BY 列名1, 列名2
HAVING 条件;
- JOIN操作:联结多个表
JOIN操作用于在多个表之间建立连接,并获得来自不同表的相关信息。
常见的JOIN类型包括:
INNER JOIN:获取两个表中匹配的行
LEFT JOIN:获取左表中所有行和右表中匹配的行
RIGHT JOIN:获取右表中所有行和左表中匹配的行
FULL JOIN:获取所有表中匹配的行
SELECT 列名1, 列名2, ...
FROM 表名1
JOIN 表名2 ON 表名1.列名 = 表名2.列名;
- 子查询:嵌套查询
子查询是指在SELECT语句中嵌套另一个SELECT语句,用于解决复杂的查询需求。
SELECT 列名1, 列名2, ...
FROM 表名
WHERE 列名 IN (SELECT 列名 FROM 表名 WHERE 条件);
子查询可以嵌套多层,使得我们能够在一个查询中获取更具体和复杂的结果。
示例
1211. 查询结果的质量和占比(Round group by)
select query_name,
ROUND(AVG(rating/position),2) 'quality',
ROUND(avg(rating < 3)*100,2) 'poor_query_percentage'
from queries group by query_name;
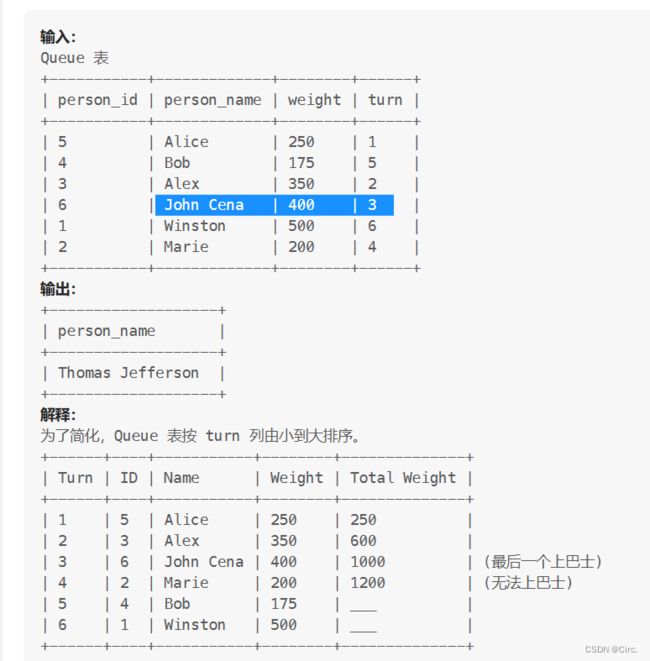
1204. 最后一个能进入巴士的人 (Having limit order by)
SELECT a.person_name
FROM Queue a, Queue b
WHERE a.turn >= b.turn
GROUP BY a.person_id
HAVING SUM(b.weight) <= 1000
ORDER BY a.turn DESC
LIMIT 1
1193. 每月交易 I(if group by)
SELECT
DATE_FORMAT(trans_date,'%Y-%m') AS month,
country,
COUNT(id) AS trans_count,
COUNT(IF(state = 'approved',id,null)) AS approved_count,
SUM(amount) AS trans_total_amount,
SUM(IF(state = 'approved',amount,0)) AS approved_total_amount
FROM Transactions
GROUP BY country,DATE_FORMAT(trans_date,'%Y-%m')
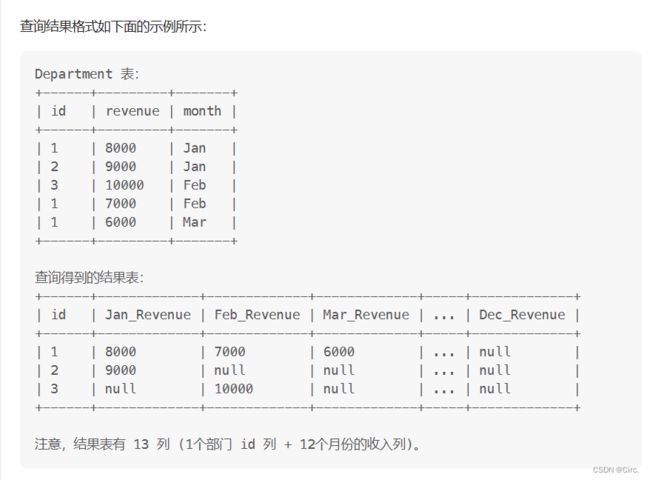
1179. 重新格式化部门表
select distinct id,
sum(IF(month="Jan",revenue,null)) as Jan_Revenue,
sum(IF(month="Feb",revenue,null)) as Feb_Revenue,
sum(IF(month="Mar",revenue,null)) as Mar_Revenue,
sum(IF(month="Apr",revenue,null)) as Apr_Revenue,
sum(IF(month="May",revenue,null)) as May_Revenue,
sum(IF(month="Jun",revenue,null)) as Jun_Revenue,
sum(IF(month="Jul",revenue,null)) as Jul_Revenue,
sum(IF(month="Aug",revenue,null)) as Aug_Revenue,
sum(IF(month="Sep",revenue,null)) as Sep_Revenue,
sum(IF(month="Oct",revenue,null)) as Oct_Revenue,
sum(IF(month="Nov",revenue,null)) as Nov_Revenue,
sum(IF(month="Dec",revenue,null)) as Dec_Revenue
from Department group by id ;
1174. 即时食物配送 II(子查询)
select
round(sum(order_date = customer_pref_delivery_date)/count(*)*100,2) immediate_percentage
from Delivery
where (customer_id,order_date) in
(select customer_id,min(order_date) from Delivery group by customer_id)
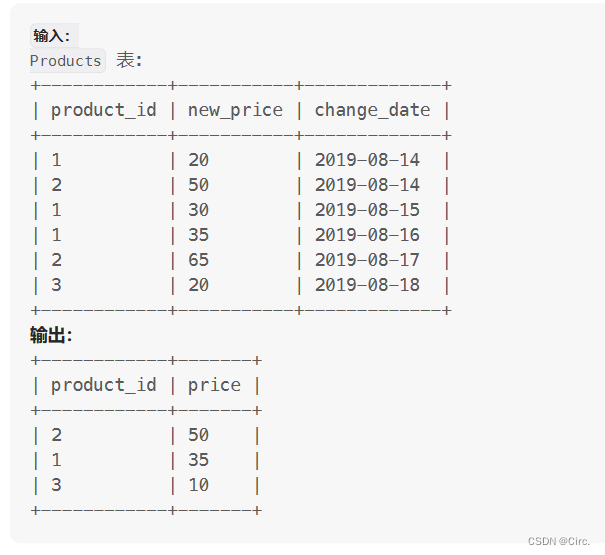
1164. 指定日期的产品价格(union groupby having)
select t.product_id, t.new_price as price
from (select *, row_number() over (PARTITION BY product_id order by change_date desc) as row_num
from Products
where change_date<='2019-08-16') as t
where t.row_num=1
union
select product_id, 10 as price
from Products
group by product_id
having min(change_date)>'2019-08-16'
总结
SQL是一种强大且灵活的语言,它能够帮助我们轻松地管理和分析数据库中的数据。了解基本查询、过滤、聚合以及联结多个表等操作,将使您在应用开发和数据分析领域更具优势。随着不断练习和深入学习SQL,我已经驾轻就熟了。你也试试吧