慕课网Go-4.package、单元测试、并发编程
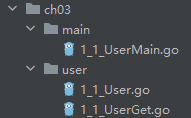
package
1_1_User.go
package user
type User struct {
Name string
}
1_1_UserGet.go
package user
func GetCourse(c User) string {
return c.Name
}
1_1_UserMain.go
package main
import (
"fmt"
Userch03 "goproj/IMOOC/ch03/user"//别名,防止同名歧义
)
func main() {
c := Userch03.User{
Name: "hi,user",
}
fmt.Println(Userch03.GetCourse(c))
}
gin
github链接
package main
import (
"net/http"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
)
func main() {
r := gin.Default()
r.GET("/ping", func(c *gin.Context) {
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{
"message": "pong",
})
})
r.Run() // listen and serve on 0.0.0.0:8080 (for windows "localhost:8080")
}
首次使用时,包的导入报错:
鼠标放在"github.com/gin-gonic/gin",出现提示框,点击Sycn…,等一会报错消失
Sync过程自动下载,可以在go.mod中看到
或者在终端打开、go mod tidy
单元测试
package main
func add(a, b int) int {
return a + b
}
package main
import "testing"
func TestAdd(t *testing.T) {
if testing.Short(){
t.Skip("short模式")
}
re := add(1, 2)
if re != 3 {
t.Errorf("expect:%d,actual:%d", 3, re)
}
}
基于表格
func TestAdd2(t *testing.T) {
var dataset = []struct {
a int
b int
out int
}{
{1, 1, 2},
{-9, 8, 1},
{0, 0, 0},
}
for _, value := range dataset {
re := add(value.a, value.b)
if re != value.out {
t.Errorf("expect:%d,actual:%d", 3, re)
}
}
}
性能测试
const numbers = 10000
func BenchmarkStringSprintf(b *testing.B) {
b.ResetTimer()
for i := 0; i < b.N; i++ {
var str string
for j := 0; j < numbers; j++ {
str = fmt.Sprintf("%s%d", str, j)
}
}
b.StopTimer()
}
func BenchmarkStringAdd(b *testing.B) {
b.ResetTimer()
for i := 0; i < b.N; i++ {
var str string
for j := 0; j < numbers; j++ {
str += strconv.Itoa(j)
}
}
b.StopTimer()
}
func BenchmarkStringBuilder(b *testing.B) {
b.ResetTimer()
for i := 0; i < b.N; i++ {
var builder strings.Builder
for j := 0; j < numbers; j++ {
builder.WriteString(strconv.Itoa(j))
}
_ = builder.String()
}
b.StopTimer()
}
并发编程
package main
import (
"fmt"
"time"
)
func asyncPrint() {
time.Sleep(time.Second)
fmt.Println("hi")
}
func main() {
go asyncPrint()
fmt.Println("main")
time.Sleep(2 * time.Second)
fmt.Println("main2")
}
import "fmt"
func main() {
fmt.Println("method1")
for i := 0; i < 100; i++ {
go func() {
fmt.Println(i)
}()
}
//fmt.Println("method2")
//for i := 0; i < 100; i++ {
// tmp := i
// go func() {
// fmt.Println(tmp)
// }()
//}
//fmt.Println("method3")
//for i := 0; i < 100; i++ {
// go func(i int) {
// fmt.Println(i)
// }(i)
//}
}
waitgroup
package main
import (
"fmt"
"sync"
)
func main() {
var wg sync.WaitGroup
wg.Add(100)
fmt.Println("method3")
for i := 0; i < 100; i++ {
go func(i int) {
defer wg.Done()
fmt.Println(i)
}(i)
}
wg.Wait()
}
互斥锁mutex
package main
import (
"fmt"
"sync"
"sync/atomic"
)
var total int32
var wg sync.WaitGroup
var lock sync.Mutex
func add() {
defer wg.Done()
for i := 0; i < 10000; i++ {
atomic.AddInt32(&total, 1)
//lock.Lock()
//total += 1
//lock.Unlock()
}
}
func sub() {
defer wg.Done()
for i := 0; i < 10000; i++ {
atomic.AddInt32(&total, -1)
//lock.Lock()
//total -= 1
//lock.Unlock()
}
}
func main() {
wg.Add(2)
go add()
go sub()
wg.Wait()
fmt.Println(total)
fmt.Println("all done")
}
读写锁rwlock
package main
import (
"fmt"
"sync"
"time"
)
func main() {
var rwlock sync.RWMutex
var wg sync.WaitGroup
wg.Add(6)
//写锁
go func() {
time.Sleep(3 * time.Second)
rwlock.Lock()
defer rwlock.Unlock()
fmt.Println("writing")
time.Sleep(5 * time.Second)
fmt.Println("write finish")
}()
time.Sleep(time.Second)
//读锁
for i := 0; i < 5; i++ {
go func() {
defer wg.Done()
for j := 0; j < 10; j++ {
rwlock.RLock()
time.Sleep(500 * time.Millisecond)
fmt.Println("read")
rwlock.RUnlock()
}
}()
}
wg.Wait()
}
channel
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
//有缓存
var msg1 chan string
msg1 = make(chan string, 1) //1是缓存空间大小
msg1 <- "harry"
data := <-msg1
fmt.Println(data)
//无缓存,happen-before机制
var msg2 chan string
msg2 = make(chan string, 0)
go func(msg2 chan string) {
data2 := <-msg2
fmt.Println(data2)
}(msg2)
msg2 <- "potter"
var msg3 chan int
msg3 = make(chan int, 2)
go func(msg3 chan int) {
for data3 := range msg3 {
fmt.Println(data3)
}
fmt.Println("all done")
}(msg3)
msg3 <- 1
msg3 <- 2
close(msg3)
var ch1 chan int //双向
var ch2 chan<- int //只写入
var ch3 <-chan int //只读取
c := make(chan int, 3)
var send chan<- int = c
var receive <-chan int = c
}
打印数字和字母
package main
import (
"fmt"
"time"
)
var number, letter = make(chan bool), make(chan bool)
func printNum() {
i := 1
for {
<-number
fmt.Printf("%d%d", i, i+1)
i += 2
letter <- true
}`在这里插入代码片`
}
func printLetter() {
i := 0
str := "ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ"
for {
<-letter
if i >= len(str) {
return
}
fmt.Print(str[i : i+2])
i += 2
number <- true
}
}
func main() {
go printNum()
go printLetter()
number <- true
time.Sleep(100 * time.Second)
}
select
package main
import (
"fmt"
"time"
)
// 空结构体不占内存、channel多线程安全
var done = make(chan struct{})
func g1(ch1 chan struct{}) {
time.Sleep(time.Second)
ch1 <- struct{}{}
}
func g2(ch2 chan struct{}) {
time.Sleep(1 * time.Second)
ch2 <- struct{}{}
}
func main() {
ch1 := make(chan struct{})
ch2 := make(chan struct{})
go g1(ch1)
go g2(ch2)
//执行先就绪的channel,都就绪则随机(防止饥饿)
//select {
//case <-ch1:
// fmt.Println("g1 done")
//case <-ch2:
// fmt.Println("g2 done")
//default:
// fmt.Println("default")
//}
timer := time.NewTimer(5 * time.Second)
select {
case <-ch1:
fmt.Println("g1 done")
case <-ch2:
fmt.Println("g2 done")
case <-timer.C:
fmt.Println("time our")
return
}
}
context
package main
import (
"fmt"
"sync"
"time"
)
var wgc sync.WaitGroup
func cpuInfo(stop chan struct{}) {
defer wgc.Done()
for {
select {
case <-stop:
fmt.Println("退出CPU监控")
return
default:
time.Sleep(2 * time.Second)
fmt.Println("CPU信息")
}
}
}
func main() {
var stop = make(chan struct{})
wgc.Add(1)
go cpuInfo(stop)
time.Sleep(6 * time.Second)
stop <- struct{}{}
wgc.Wait()
fmt.Println("监控完成")
}
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"sync"
"time"
)
var wgc2 sync.WaitGroup
func cpuInfo2(ctx context.Context) {
defer wgc2.Done()
for {
select {
case <-ctx.Done():
fmt.Println("退出CPU监控")
return
default:
time.Sleep(2 * time.Second)
fmt.Println("CPU信息")
}
}
}
func main() {
wgc2.Add(1)
ctx, cancel := context.WithCancel(context.Background())
go cpuInfo2(ctx)
time.Sleep(6 * time.Second)
cancel()
wgc2.Wait()
fmt.Println("监控完成")
}