【IMX6ULL驱动开发学习】21.Linux驱动之PWM子系统(以SG90舵机为例)
1.设备树部分
首先在 imx6ull.dtsi 文件中已经帮我们定义好了一些pwm的设备树节点,这里以pwm2为例
pwm2: pwm@02084000 {
compatible = "fsl,imx6ul-pwm", "fsl,imx27-pwm";
reg = <0x02084000 0x4000>;
interrupts = <GIC_SPI 84 IRQ_TYPE_LEVEL_HIGH>;
clocks = <&clks IMX6UL_CLK_DUMMY>,
<&clks IMX6UL_CLK_DUMMY>;
clock-names = "ipg", "per";
#pwm-cells = <2>;
};
我们要在设备树(.dts)文件中引用和使能该节点,同时指定好pwm映射到的GPIO引脚(即pinctrl子系统,我这里映射到了GPIO1_9上)
&iomuxc {
pinctrl-names = "default";
pinctrl-0 = <&pinctrl_hog_1>;
imx6ul-evk {
......
......
/* SG90 PWM2 GPIO1_IO09 */
pinctrl_pwm2: pwm2grp {
fsl,pins = <
MX6UL_PAD_GPIO1_IO09__PWM2_OUT 0x110b0
>;
};
......
......
}
......
......
&pwm2 {
pinctrl-names = "default";
pinctrl-0 = <&pinctrl_pwm2>;
clocks = <&clks IMX6UL_CLK_PWM2>,
<&clks IMX6UL_CLK_PWM2>;
status = "okay";
};
使用pwm 只需要在设备树节点中添加两条属性信息,如下所示
pwms = <“&PWMn id period_ns>;
pwm-names = "name";
-
pwms :属性是必须的,它共有三个属性值
-
&PWMn 指定使用哪个pwm,在imx6ull.dtsi文件中定义,总共有8个可选;
-
id :pwm的id通常设置为0。
-
period_ns :用于设置周期。单位是ns。
-
pwm-names :定义pwm设备名字。(可以不设置)
最后在根节点下添加自己定义的节点
hc_sg90 {
compatible = "hc-sg90";
pwms = <&pwm2 0 20000000>; /* 使用pwm1 id为0 周期为20000000ns = 20ms */
status = "okay";
};
2.驱动代码部分
老一套的字符设备驱动框架:
- 驱动入口出口
- 驱动入口定义注册字符设备、创建字符设备节点、注册platform设备;
- 驱动出口反注册platfrom设备、删除字符设备节点、反注册字符设备
- 构建file_operations结构体
- 构建platform_device结构体,编写probe函数
如下代码所示:
#include -
首先 struct device_node *node = pdev->dev.of_node; 获取子节点,在设备树插件中,我们把PWM相关信息保存在 hc_sg90 的子节点中, 所以这里首先获取子节点。
-
在子节点获取成功后我们使用 devm_of_pwm_get 函数获取pwm, 由于节点内只有一个PWM 这里将最后一个参数直接设置为NULL,这样它将获取第一个PWM。
-
依次调用 pwm_config、pwm_set_polarity、pwm_enable 函数配置**PWM、设置输出极性、 使能PWM输出,**需要注意的是这里设置的极性为正常极性, 这样pwm_config函数第二个参数设置的就是pwm波的一个周期内的高电平事件。
其中write函数中关于SG90的占空比计算就不多说了,根据如下图来计算吧
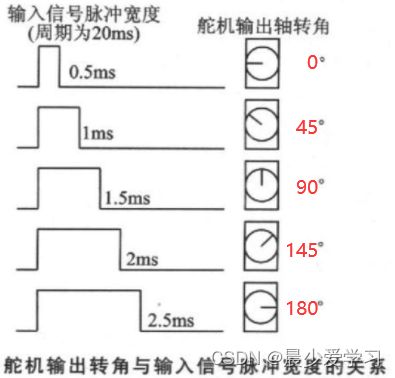
不难得出高电平时间每多出1ms(1000000ns) 对应角度多出9度的结论
则旋转到角度 1 度时,对应的高电平时间为 (500000 + 1000000)/9 ns(因为0度对应的高电平时间为0.5ms = 500000ns)
则旋转到角度 n 度时,高电平时间为 (500000 + n * 1000000)/9 ns
3.应用程序部分
运行示例: ./sg90_test 90 , 即转到90度的位置
#include