二叉树OJ(C)
文章目录
- 1.单值二叉树
-
- 1.1法一:无返回值
- 1.2法二:有返回值
- 2.相同的树
- 3.对称二叉树
- 4.二叉树的前序遍历
- 5.二叉树的中序遍历
- 6.二叉树的后序遍历
- 7.另一棵树的子树
- 8.二叉树遍历
1.单值二叉树
1.1法一:无返回值
struct TreeNode
{
int val;
struct TreeNode *left;
struct TreeNode *right;
};
bool flag = true;
void PreOrderCompare(struct TreeNode* root, int val)
{
//递归过程中 遇NULL 或flag已变假 返回上一层
if (root == NULL || flag == false)
return;
//遇非单值 更新flag 返回上一层
if (root->val != val)
{
flag = false;
return;
}
//结点数据相等 继续遍历
PreOrderCompare(root->left, val);
PreOrderCompare(root->right, val);
}
bool isUnivalTree(struct TreeNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return true;
else
{
//OJ题目会用程序测试多组样例
//若上个样例flag变为false 这里就会出错
//同时也提醒我们要慎用全局变量
flag = true;
PreOrderCompare(root, root->val);
return flag;
}
}
1.2法二:有返回值
根与左子树、右子树比较 不断递归
struct TreeNode
{
int val;
struct TreeNode *left;
struct TreeNode *right;
};
bool isUnivalTree(struct TreeNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return true;
if (root->left && root->left->val != root->val)
return false;
if (root->right && root->right->val != root->val)
return false;
return isUnivalTree(root->left) && isUnivalTree(root->right);
}
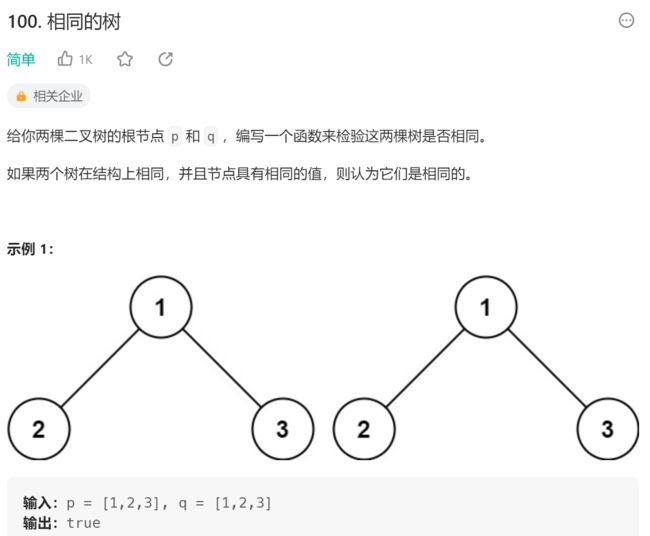
2.相同的树
struct TreeNode
{
int val;
struct TreeNode *left;
struct TreeNode *right;
};
bool isSameTree(struct TreeNode* p, struct TreeNode* q)
{
if (p == NULL && q == NULL)
return true;
if (p == NULL || q == NULL)
return false;
if (p->val != q->val)
return false;
return isSameTree(p->left, q->left)
&& isSameTree(p->right, q->right);
}
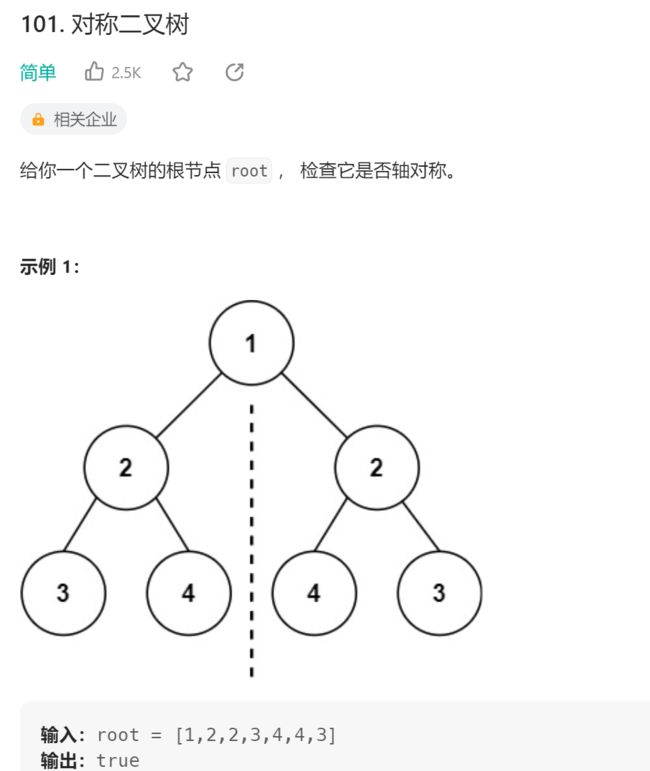
3.对称二叉树
struct TreeNode
{
int val;
struct TreeNode *left;
struct TreeNode *right;
};
bool isSymmetricSubTree(struct TreeNode* root1, struct TreeNode* root2)
{
if (root1 == NULL && root2 == NULL)
return true;
if (root1 == NULL || root2 == NULL)
return false;
if (root1->val != root2->val)
return false;
return isSymmetricSubTree(root1->left, root2->right)
&& isSymmetricSubTree(root1->right, root2->left);
}
bool isSymmetric(struct TreeNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return true;
return isSymmetricsubTree(root->left, root->right);
}
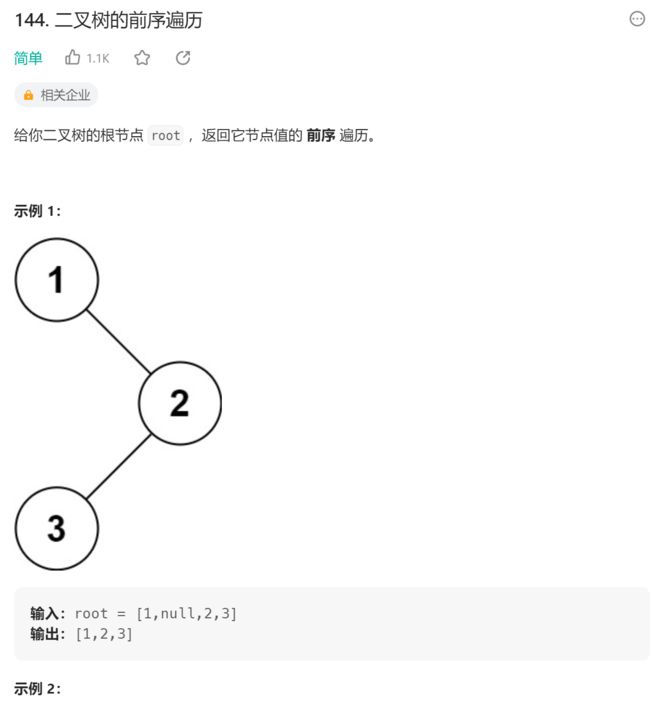
4.二叉树的前序遍历
struct TreeNode
{
int val;
struct TreeNode *left;
struct TreeNode *right;
};
//计算树的结点个数
int TreeSize(struct TreeNode* root)
{
return root == NULL ? 0 : TreeSize(root->left) + TreeSize(root->right) + 1;
}
//前序遍历
void preorder(struct TreeNode* root, int* a, int* i)
{
if (root == NULL)
return;
a[(*i)++] = root->val;
preorder(root->left, a, i);
preorder(root->right, a, i);
}
int* preorderTraversal(struct TreeNode* root, int* returnSize)
{
//调用TreeSize函数决定开多大的空间
*returnSize = TreeSize(root);
//开空间
int* a = (int*)malloc(*returnSize * sizeof(int));
//若在子函数用局部变量i -- 在下一层递归改变i后 -- 返回到上一层用的仍是旧i -- 出现错误
int i = 0;
preorder(root, a, &i);
return a;
}
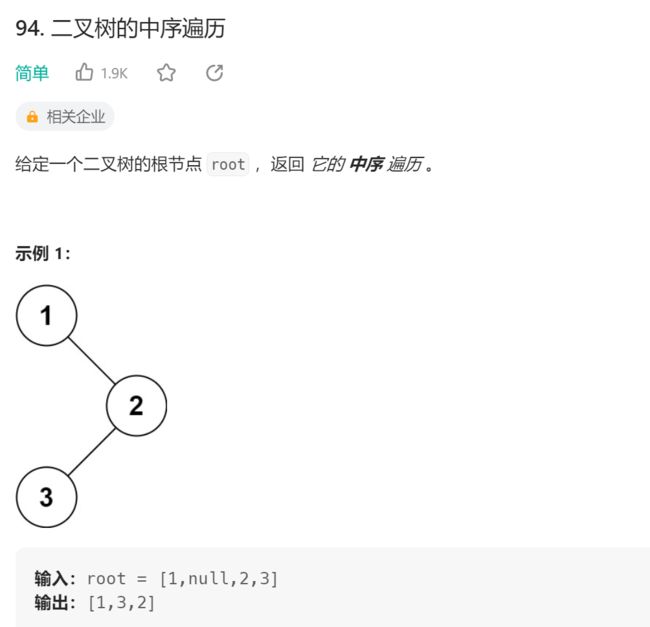
5.二叉树的中序遍历
struct TreeNode
{
int val;
struct TreeNode* left;
struct TreeNode* right;
};
int TreeSize(struct TreeNode* root)
{
return root == NULL ? 0 : TreeSize(root->left) + TreeSize(root->right) + 1;
}
void inorder(struct TreeNode* root, int* a, int* i)
{
if (root == NULL)
return;
inorder(root->left, a, i);
a[(*i)++] = root->val;
inorder(root->right, a, i);
}
int* inorderTraversal(struct TreeNode* root, int* returnSize)
{
*returnSize = TreeSize(root);
int* a = (int*)malloc(*returnSize * sizeof(int));
int i = 0;
inorder(root, a, &i);
return a;
}
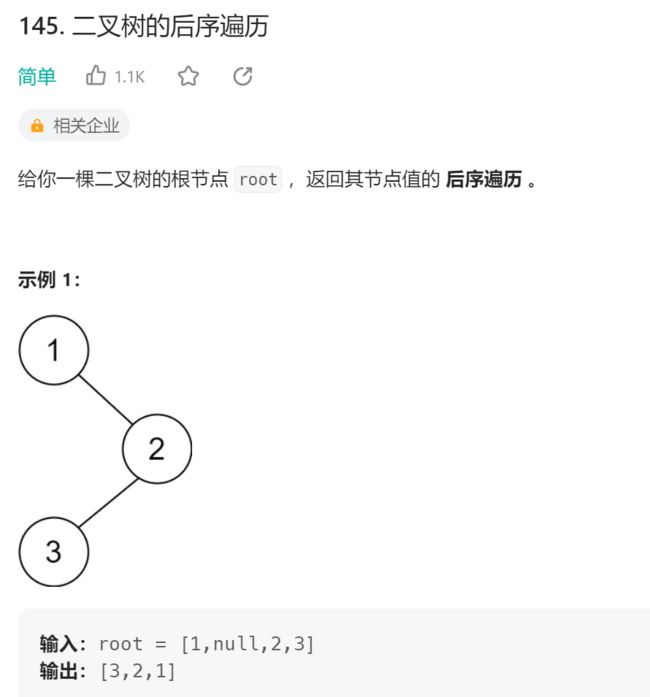
6.二叉树的后序遍历
struct TreeNode
{
int val;
struct TreeNode* left;
struct TreeNode* right;
};
int TreeSize(struct TreeNode* root)
{
return root == NULL ? 0 : TreeSize(root->left) + TreeSize(root->right) + 1;
}
void posorder(struct TreeNode* root, int* a, int* i)
{
if (root == NULL)
return;
posorder(root->left, a, i);
posorder(root->right, a, i);
a[(*i)++] = root->val;
}
int* posorderTraversal(struct TreeNode* root, int* returnSize)
{
*returnSize = TreeSize(root);
int* a = (int*)malloc(*returnSize * sizeof(int));
int i = 0;
posorder(root, a, &i);
return a;
}
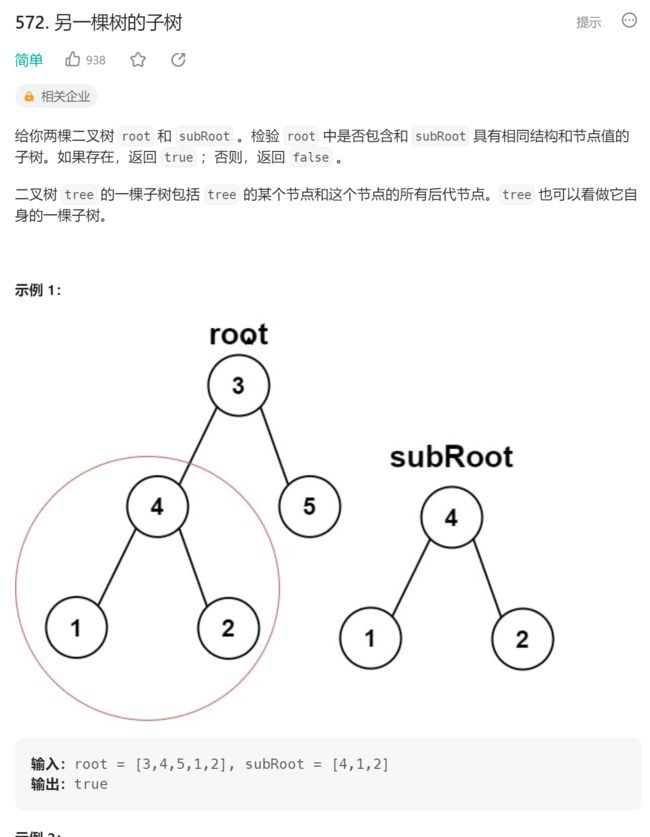
7.另一棵树的子树
struct TreeNode
{
int val;
struct TreeNode *left;
struct TreeNode *right;
};
bool isSameTree(struct TreeNode* p, struct TreeNode* q)
{
if (p == NULL && q == NULL)
return true;
if (p == NULL || q == NULL)
return false;
if (p->val != q->val)
return false;
return isSameTree(p->left, q->left)
&& isSameTree(p->right, q->right);
}
bool isSubtree(struct TreeNode* root, struct TreeNode* subRoot)
{
if (root == NULL)
return false;
if (isSameTree(root, subRoot))
return true;
return isSubtree(root->left, subRoot)
|| isSubtree(root->right, subRoot);
}
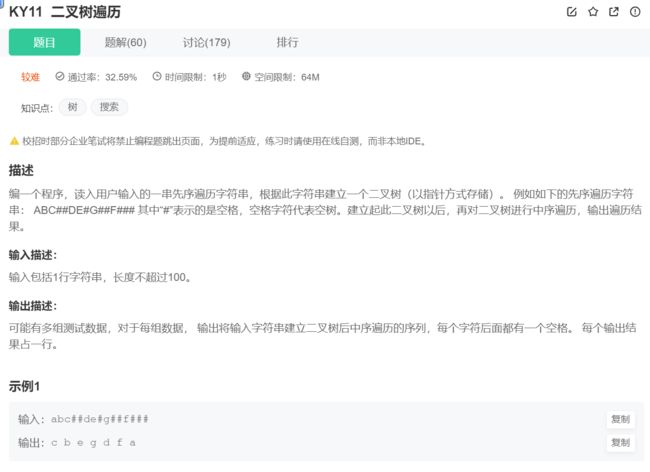
8.二叉树遍历
typedef char BTDataType;
typedef struct BinaryTreeNode
{
struct BinaryTreeNode* left;
struct BinaryTreeNode* right;
BTDataType data;
}BTNode;
//创建新结点
BTNode* CreatNode(BTDataType x)
{
BTNode* node = (BTNode*)malloc(sizeof(BTNode));
assert(node);
node->data = x;
node->left = NULL;
node->right = NULL;
return node;
}
//建树
BTNode* CreateTree(char* str, int* i)
{
if (str[*i] == '#')
{
(*i)++;
return NULL;
}
//创建结点
BTNode* root = CreatNode(str[(*i)++]);
//连接子树
root->left = CreateTree(str, i);
root->right = CreateTree(str, i);
return root;
}
int main()
{
char str[100] = { 0 };
scanf("%s", str);
int i = 0;
BTNode* root = CreateTree(str, &i);
return 0;
}