
3-1 String类
1、API概述-帮助文档的使用
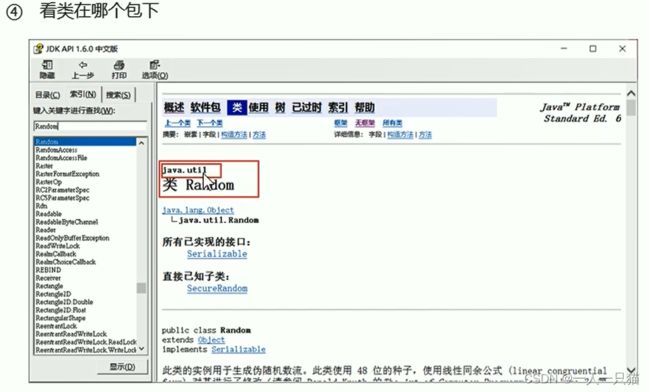
【1】API概述

【2】如何使用帮助文档





2、键盘录入字符串案例
【1】需求
- 需求:按照帮助文档的使用步骤学习Scanner类的使用,并实现键盘录入一个字符串,最后输出在控制台
【2】实现
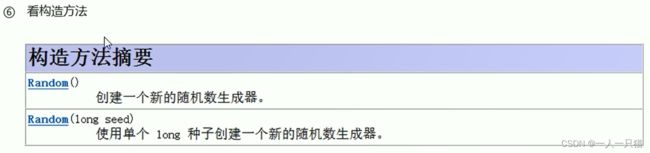
(1)nextLine()和next()的区别
package com.itheima.api;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Demo1Scanner {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("使用nextLine()方法");
System.out.println("请输入:");
String s = sc.nextLine();
System.out.println(s);
System.out.println("使用next()方法");
System.out.println("请输入:");
String next = sc.next();
System.out.println(next);
}
}
使用nextLine()方法
请输入:
abc abc abc
abc abc abc
使用next()方法
请输入:
abc abc abc
abc
进程已结束,退出代码 0
(2)nextLine和nextInt配合使用
package com.itheima.api;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Demo2Scanner {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入整数:");
int num = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("请输入字符串:");
String s = sc.nextLine();
System.out.println("输入的整数是:" + num);
System.out.println("输入的字符串是:" + s);
}
}
请输入整数:
10
请输入字符串:
输入的整数是:10
输入的字符串是:
进程已结束,退出代码 0
3、String概述
【1】概述

【2】案例
package com.itheima.string;
public class Demo1String {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "abc123";
int length = s1.length();
System.out.println(length);
s1 = "def";
System.out.println(s1);
}
}
6
def
进程已结束,退出代码 0
4、String类常见构造方法
【1】String常见构造方法
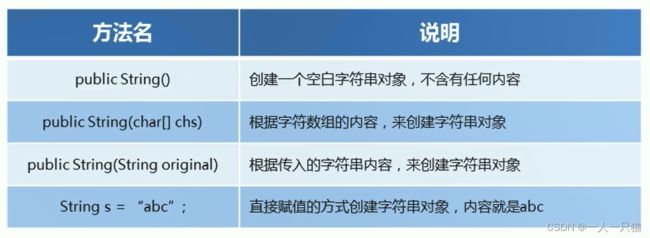
【2】案例
package com.itheima.string;
public class Demo2StringConstructor {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = new String();
System.out.println(s1);
char[] chs = {'a', 'b', 'c'};
String s2 = new String(chs);
System.out.println(s2);
String s3 = new String("123");
System.out.println(s3);
}
}
abc
123
进程已结束,退出代码 0
5、创建字符串对象的区别对别
【1】==号作比较

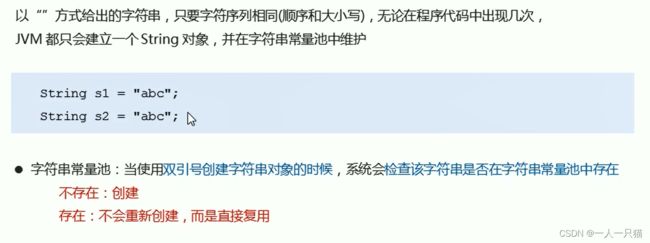
【2】双引号创建字符串-字符串常量池

【3】new创建字符串

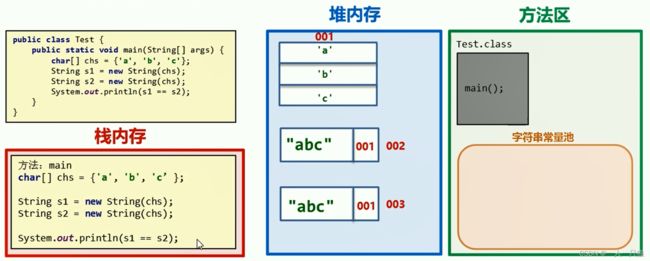
【4】代码分析

6、String特点-常见面试题
【1】String特点
- Java程序中所有的双引号字符串,都是String类对象
- 字符串不可变,他们的值在创建后不能被更改
- 虽然String的值是不可变的,但是他们可以被共享
【2】问题1

【3】问题2
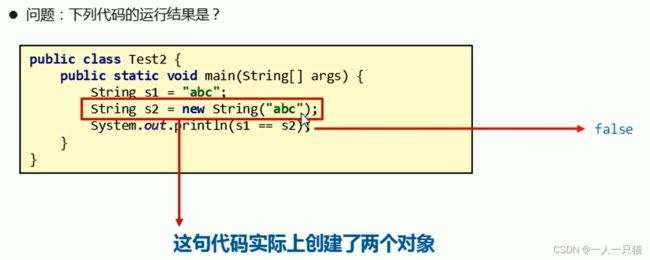
【4】问题3


【5】问题4

7、字符串比较
【1】字符串比较

【2】案例
package com.itheima.stringmethod;
public class Demo1Equals {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "abc";
String s2 = "ABC";
String s3 = "abc";
System.out.println(s1.equals(s2));
System.out.println(s1.equals(s3));
System.out.println(s1.equalsIgnoreCase(s2));
}
}
false
true
true
进程已结束,退出代码 0
8、用户登录案例
【1】需求
- 需求:已知用户名和密码,请用程序实现模拟用户登录。总共给三次机会,登录之后,给出相应的提示
【2】分析

【3】实现
package com.itheima.test;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String username = "admin";
String password = "123456";
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
for (int i = 1; i <= 3; i++) {
System.out.println("请输入用户名:");
String scUsername = sc.nextLine();
System.out.println("请输入密码:");
String scPassword = sc.nextLine();
if(username.equals(scUsername) && password.equals(scPassword)){
System.out.println("登录成功");
break;
}else{
if(i == 3){
System.out.println("您的登录次数已达今日上限,请明天再来");
}else{
System.out.println("登录失败,您还剩余"+(3-i)+"次机会");
}
}
}
}
}
请输入用户名:
a
请输入密码:
a
登录失败,您还剩余2次机会
请输入用户名:
dd
请输入密码:
ddd
登录失败,您还剩余1次机会
请输入用户名:
acmin
请输入密码:
123456
您的登录次数已达今日上限,请明天再来
进程已结束,退出代码 0
9、字符串遍历
【1】需求
- 需求:键盘录入一个字符串,使用程序实现在控制台遍历该字符串
【2】分析
- 思路1

- 思路2

【3】实现
package com.itheima.test;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入:");
String s = sc.nextLine();
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
char c = s.charAt(i);
System.out.println(c);
}
}
}
请输入:
黑马程序员
黑
马
程
序
员
进程已结束,退出代码 0
package com.itheima.test;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Test3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入:");
String s = sc.nextLine();
char[] chars = s.toCharArray();
for (int i = 0; i < chars.length; i++) {
System.out.println(chars[i]);
}
}
}
请输入:
itheima
i
t
h
e
i
m
a
进程已结束,退出代码 0
10、统计字符次数
【1】需求
- 需求:键盘录入一个字符串,统计该字符串中大写字母字符,小写字母字符,数字字符出现的次数(不考虑其他字符)
【2】分析

【3】实现
package com.itheima.test;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Test4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入:");
String s = sc.nextLine();
int bigCount = 0;
int smallCount = 0;
int numCount = 0;
char[] chars = s.toCharArray();
for (int i = 0; i < chars.length; i++) {
char c = chars[i];
if(c >= 'A' && c <= 'Z'){
bigCount++;
}else if(c >= 'a' && c <= 'z'){
smallCount++;
}else if(c >= '0' && c <= '9'){
numCount++;
}
}
System.out.println("大写字母字符:" + bigCount);
System.out.println("小写字母字符:" + smallCount);
System.out.println("数字字符:" + numCount);
}
}
请输入:
111aaa222bbb333CCC
大写字母字符:3
小写字母字符:6
数字字符:9
进程已结束,退出代码 0
11、手机号屏蔽-字符串截取
【1】字符串的截取
package com.itheima.stringmethod;
public class Demo2SubString {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "itheima";
String ss = s.substring(2);
System.out.println(ss);
String sss = s.substring(0, 2);
System.out.println(sss);
}
}
heima
it
进程已结束,退出代码 0
【2】需求
- 需求:以字符串的形式从键盘接收一个手机号,将中间四位号码屏蔽
- 最终效果为:189****4151
【3】思路

【4】实现
package com.itheima.test;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Test5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入手机号:");
String telString = sc.nextLine();
String start = telString.substring(0, 3);
String end = telString.substring(7);
System.out.println(start + "****" + end);
}
}
请输入手机号:
18900004151
189****4151
进程已结束,退出代码 0
12、敏感词替换-字符串替换
【1】需求
- 需求:键盘录入一个字符串,如果字符串中包含(TMD),则使用***替换
【2】分析

【3】实现
package com.itheima.test;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Test6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入:");
String s = sc.nextLine();
String result = s.replace("TMD", "***");
System.out.println(result);
}
}
请输入:
你TMD真是个人才!
你***真是个人才!
进程已结束,退出代码 0
13、切割字符串
【1】需求
- 需求:以字符串的形式从键盘录入学生信息,例如:“张三,23” 从该字符串中切割出有效数据封装为Student学生对象
【2】分析

【3】实现
package com.itheima.test;
import com.itheima.domain.Student;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Test7 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入学生信息:");
String stuInfo = sc.nextLine();
String[] sArr = stuInfo.split(",");
Student stu = new Student(sArr[0], sArr[1]);
System.out.println(stu.getName() + "..." + stu.getAge());
}
}
请输入学生信息:
张三,23
张三...23
进程已结束,退出代码 0
14、String方法小结
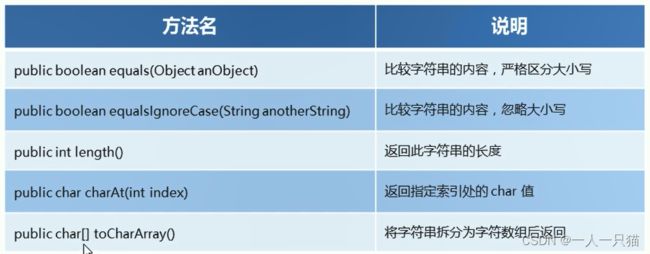
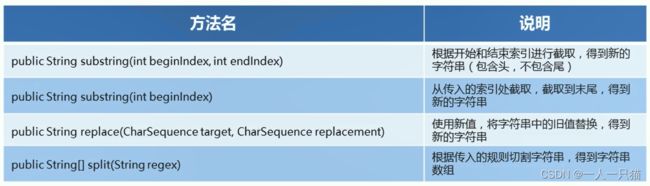
3-2 StringBuilder
15、StringBuilder概述
【1】概述
- StringBuilder是一个可变的字符串类,我们可以把它看成是一个容器
【2】案例
package com.itheima.stringbuilder;
public class Demo1StringBuilder {
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringTest();
StringBuliderTest();
}
private static void StringBuliderTest() {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < 50000; i++) {
sb.append(i);
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("使用StringBuilder来进行拼接1-50000花费的时间是:" + (end - start) +"毫秒");
}
private static void StringTest() {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
String s = "";
for (int i = 0; i < 50000; i++) {
s += i;
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("使用String来进行拼接1-50000花费的时间是:" + (end - start) + "毫秒");
}
}
使用String来进行拼接1-50000花费的时间是:5889毫秒
使用StringBuilder来进行拼接1-50000花费的时间是:1毫秒
进程已结束,退出代码 0
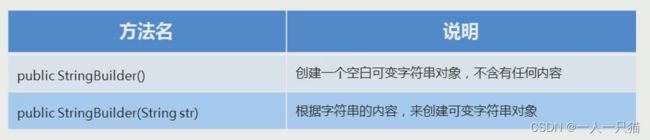
16、StringBuilder的构造方法
【1】构造方法
【2】案例
package com.itheima.stringbuilder;
public class Demo2StringBuilder {
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
System.out.println(sb);
StringBuilder sb2 = new StringBuilder("abc");
System.out.println(sb2);
}
}
abc
Process finished with exit code 0
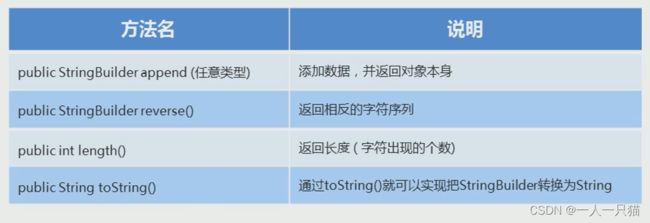
17、StringBuilder常用成员方法
【1】常用方法
【2】案例
package com.itheima.stringbuilder;
public class Demo3StringBuilder {
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append("红色").append("蓝色").append("绿色");
System.out.println("反转前:" + sb);
sb.reverse();
System.out.println("反转后:" + sb);
System.out.println("sb中字符的个数为:" + sb.length());
String s = sb.toString();
System.out.println(s);
}
}
反转前:红色蓝色绿色
反转后:色绿色蓝色红
sb中字符的个数为:6
色绿色蓝色红
Process finished with exit code 0
18、StringBuilder提高效率的原理
【1】原理图
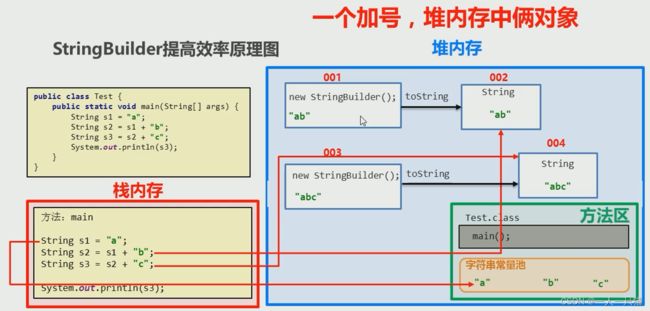

【2】StringBuilder和String的区别
- String:内容是不可变的
- StringBuilder:内容是可变的
19、对称字符串案例-String和StringBuilder之间的转换
【1】需求
- 需求:键盘接收一个字符串,程序判断出该字符串是否是对称字符串,并在控制台打印是或不是
- 对称字符串 :123321、 111
- 非对称字符串:123123
【2】分析

【3】实现
package com.itheima.test;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Test8 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入对称字符串:");
String s = sc.nextLine();
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(s);
sb.reverse();
String reverseStr = sb.toString();
if(s.equals(reverseStr)){
System.out.println("是对称字符串");
}else {
System.out.println("不是对称字符串");
}
}
}
请输入对称字符串:
上海自来水来自海上
是对称字符串
进程已结束,退出代码 0
【4】StringBuilder和String相互转换

20、StringBuilder拼接字符串案例
【1】需求

【2】分析

【3】实现
package com.itheima.test;
public class Test9 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {1,2,3};
String s = arrayToString(arr);
System.out.println(s);
}
public static String arrayToString(int[] arr){
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("[");
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if(i == arr.length - 1){
sb.append(arr[i]).append("]");
}else{
sb.append(arr[i]).append(", ");
}
}
return sb.toString();
}
}
[1, 2, 3]
进程已结束,退出代码 0







































