【Golang】Go实战--实现简单的restful api(The way to go)
目录
实现restfulApi
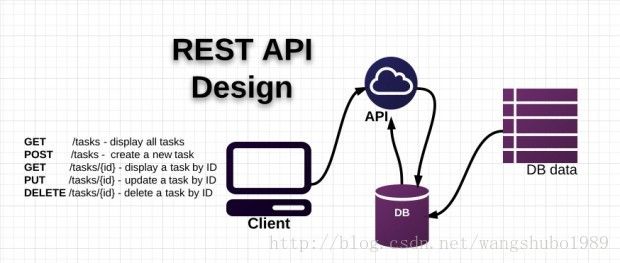
何为RESTful API
gorilla/mux
实现
完整代码与运行结果
使用Go调用Rest接口
实现restfulApi
原文:https://blog.csdn.net/wangshubo1989/article/details/71128972
生命不止,继续 go go go !!!
介绍过net/http package:
http://blog.csdn.net/wangshubo1989/article/details/70147079
介绍过实现一个简单的tcp服务端/客户端:
http://blog.csdn.net/wangshubo1989/article/details/70147079
介绍过如何实现一个简单的聊天室:
http://blog.csdn.net/wangshubo1989/article/details/70668916
今天跟大家介绍一下如何使用go创建一套restful api,我们依托于开源库gorilla/mux。
let’s go~~
何为RESTful API
A RESTful API is an application program interface (API) that uses HTTP requests to GET, PUT, POST and DELETE data.
A RESTful API – also referred to as a RESTful web service – is based on representational state transfer (REST) technology, an architectural style and approach to communications often used in web services development.
Wikipedia: 表征性状态传输(英文:Representational State Transfer,简称REST)是Roy Fielding博士于2000年在他的博士论文中提出来的一种软件架构风格。
Roy Fielding是HTTP协议(1.0版和1.1版)的主要设计者,事实上HTTP 1.1规范正是基于REST架构风格的指导原理来设计的。需要注意的是,REST是一种设计风格而不是标准,如果一个架构符合REST原则,我们就称它为RESTful架构。
gorilla/mux
github地址:
https://github.com/gorilla/mux
golang自带的http.SeverMux路由实现简单,本质是一个map[string]Handler,是请求路径与该路径对应的处理函数的映射关系。实现简单功能也比较单一:
- 不支持正则路由, 这个是比较致命的
- 只支持路径匹配,不支持按照Method,header,host等信息匹配,所以也就没法实现RESTful架构
而gorilla/mux是一个强大的路由,小巧但是稳定高效,不仅可以支持正则路由还可以按照Method,header,host等信息匹配,可以从我们设定的路由表达式中提取出参数方便上层应用,而且完全兼容http.ServerMux
设置好了go的环境变量,直接运行:
go get -u github.com/gorilla/mux
实现
定义结构体,用户构造json
type Person struct {
ID string `json:"id,omitemty"`
Firstname string `json:"firstname,omitempty"`
Lastname string `json:"lastname,omitempty"`
Address *Address `json:"address,omitempty"`
}
type Address struct {
City string `json:"city,omitempty"`
Province string `json:"province,omitempty"`
}接下来,定义一个全局变量,用于存储资源(数据):
var people []Person对这个变量进行赋值:
people = append(people, Person{ID: "1", Firstname: "xi", Lastname: "dada", Address: &Address{City: "Shenyang", Province: "Liaoning"}})
people = append(people, Person{ID: "2", Firstname: "li", Lastname: "xiansheng", Address: &Address{City: "Changchun", Province: "Jinlin"}})如果对go中的struct不够了解的可以看这里:
http://blog.csdn.net/wangshubo1989/article/details/70040022
Get
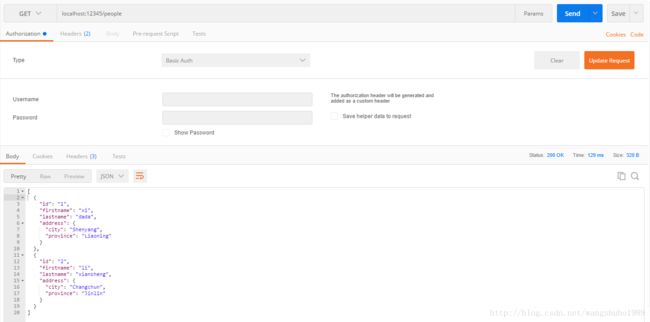
获取所有person,这里我们叫people:
func GetPeople(w http.ResponseWriter, req *http.Request) {
json.NewEncoder(w).Encode(people)
}
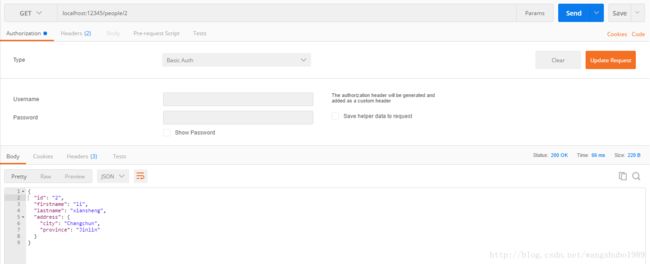
根据id获取person:
func GetPerson(w http.ResponseWriter, req *http.Request) {
params := mux.Vars(req)
for _, item := range people {
if item.ID == params["id"] {
json.NewEncoder(w).Encode(item)
return
}
}
json.NewEncoder(w).Encode(people)
}然后handle function:
router := mux.NewRouter()
router.HandleFunc("/people", GetPeople).Methods("GET")
router.HandleFunc("/people/{id}", GetPerson).Methods("GET")post
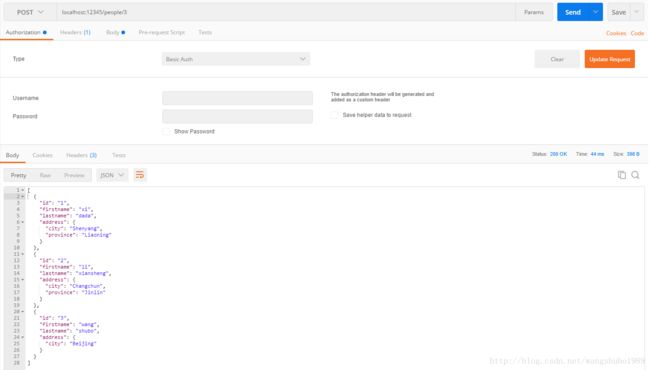
同样可以,通过post操作向服务器添加数据:
func PostPerson(w http.ResponseWriter, req *http.Request) {
params := mux.Vars(req)
var person Person
_ = json.NewDecoder(req.Body).Decode(&person)
person.ID = params["id"]
people = append(people, person)
json.NewEncoder(w).Encode(people)
}然后handle function:
router.HandleFunc("/people/{id}", PostPerson).Methods("POST")Delete
根据id进行删除操作:
func DeletePerson(w http.ResponseWriter, req *http.Request) {
params := mux.Vars(req)
for index, item := range people {
if item.ID == params["id"] {
people = append(people[:index], people[index+1:]...)
break
}
}
json.NewEncoder(w).Encode(people)
}然后handle function:
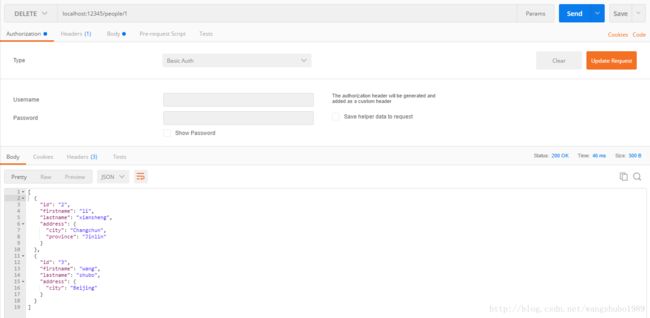
router.HandleFunc("/people/{id}", DeletePerson).Methods("DELETE")
完整代码与运行结果
代码:
package main
import (
"encoding/json"
"log"
"net/http"
"github.com/gorilla/mux"
)
type Person struct {
ID string `json:"id,omitemty"`
Firstname string `json:"firstname,omitempty"`
Lastname string `json:"lastname,omitempty"`
Address *Address `json:"address,omitempty"`
}
type Address struct {
City string `json:"city,omitempty"`
Province string `json:"province,omitempty"`
}
var people []Person
func GetPerson(w http.ResponseWriter, req *http.Request) {
params := mux.Vars(req)
for _, item := range people {
if item.ID == params["id"] {
json.NewEncoder(w).Encode(item)
return
}
}
json.NewEncoder(w).Encode(people)
}
func GetPeople(w http.ResponseWriter, req *http.Request) {
json.NewEncoder(w).Encode(people)
}
func PostPerson(w http.ResponseWriter, req *http.Request) {
params := mux.Vars(req)
var person Person
_ = json.NewDecoder(req.Body).Decode(&person)
person.ID = params["id"]
people = append(people, person)
json.NewEncoder(w).Encode(people)
}
func DeletePerson(w http.ResponseWriter, req *http.Request) {
params := mux.Vars(req)
for index, item := range people {
if item.ID == params["id"] {
people = append(people[:index], people[index+1:]...)
break
}
}
json.NewEncoder(w).Encode(people)
}
func main() {
router := mux.NewRouter()
people = append(people, Person{ID: "1", Firstname: "xi", Lastname: "dada", Address: &Address{City: "Shenyang", Province: "Liaoning"}})
people = append(people, Person{ID: "2", Firstname: "li", Lastname: "xiansheng", Address: &Address{City: "Changchun", Province: "Jinlin"}})
router.HandleFunc("/people", GetPeople).Methods("GET")
router.HandleFunc("/people/{id}", GetPerson).Methods("GET")
router.HandleFunc("/people/{id}", PostPerson).Methods("POST")
router.HandleFunc("/people/{id}", DeletePerson).Methods("DELETE")
log.Fatal(http.ListenAndServe(":12345", router))
}
package main
import (
"fmt"
"net/http"
"io/ioutil"
)
func main() {
url := "http://localhost:12345/people"
req, _ := http.NewRequest("GET", url, nil)
req.Header.Add("accept", "application/json")
req.Header.Add("authorization", "Basic d2FuZ3NodWJvOndhbmdzaHVibw==")
req.Header.Add("cache-control", "no-cache")
req.Header.Add("postman-token", "18774413-0c11-e312-7ed6-7bc4f8151f5a")
res, _ := http.DefaultClient.Do(req)
defer res.Body.Close()
body, _ := ioutil.ReadAll(res.Body)
fmt.Println(res)
fmt.Println(string(body))
}package main
import (
"fmt"
"strings"
"net/http"
"io/ioutil"
)
func main() {
url := "http://localhost:12345/people/1"
payload := strings.NewReader("{\n \"firstname\": \"wang\",\n \"lastname\": \"shubo\",\n \"address\": {\n \"city\": \"Beijing\",\n \"state\": \"Beijng\"\n }\n}")
req, _ := http.NewRequest("DELETE", url, payload)
req.Header.Add("content-type", "application/json")
req.Header.Add("cache-control", "no-cache")
req.Header.Add("postman-token", "4a894ad6-2887-259a-c953-5d26fed70963")
res, _ := http.DefaultClient.Do(req)
defer res.Body.Close()
body, _ := ioutil.ReadAll(res.Body)
fmt.Println(res)
fmt.Println(string(body))
}package main
import (
"fmt"
"strings"
"net/http"
"io/ioutil"
)
func main() {
url := "http://localhost:12345/people/3"
payload := strings.NewReader("{\n \"firstname\": \"wang\",\n \"lastname\": \"shubo\",\n \"address\": {\n \"city\": \"Beijing\",\n \"state\": \"Beijng\"\n }\n}")
req, _ := http.NewRequest("POST", url, payload)
req.Header.Add("content-type", "application/json")
req.Header.Add("cache-control", "no-cache")
req.Header.Add("postman-token", "a9d590dd-1819-15f6-962e-0eabf4b7e707")
res, _ := http.DefaultClient.Do(req)
defer res.Body.Close()
body, _ := ioutil.ReadAll(res.Body)
fmt.Println(res)
fmt.Println(string(body))
}package main
import (
"fmt"
"strings"
"net/http"
"io/ioutil"
)
func main() {
url := "http://localhost:12345/people/1"
payload := strings.NewReader("{\n \"firstname\": \"wang\",\n \"lastname\": \"shubo\",\n \"address\": {\n \"city\": \"Beijing\",\n \"state\": \"Beijng\"\n }\n}")
req, _ := http.NewRequest("DELETE", url, payload)
req.Header.Add("content-type", "application/json")
req.Header.Add("cache-control", "no-cache")
req.Header.Add("postman-token", "4c8d290e-4c6c-53f7-64e9-1d1f6ed19b09")
res, _ := http.DefaultClient.Do(req)
defer res.Body.Close()
body, _ := ioutil.ReadAll(res.Body)
fmt.Println(res)
fmt.Println(string(body))
}
使用Go调用Rest接口
package main
import (
"fmt"
"net/http"
"encoding/json"
"bytes"
"strings"
"io/ioutil"
"github.com/garyburd/redigo/redis"
"errors"
"time"
)
// 请求URL
const COUNT_URL ="http://localhost:8080/me/count"
// 定义一个Count结构体
type Count struct {
Count int `json:"count"`
}
func main(){
// 测试查询函数
count,err := getCount()
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
fmt.Println("count: ", count) // 初始计数为0,预计结果为0
// 测试设置函数
err = setCount(200)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
count,err = getCount()
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
fmt.Println("count: ", count) // 设置函数设置为了200,预计查询结果为200
// 测试增加函数
err = addCount(50)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
count,err = getCount()
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
fmt.Println("count: ", count) // 增加函数增加了50,预计查询结果为250
}
/**
给Count加上一个值
*/
func addCount(count int) error {
reqCount := Count{Count:count} // 构造请求结构体
reqCountBytes, err :=json.Marshal(reqCount) // 把请求结构体解析为json
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("marshal failed. the error info: ",err)
}
_,err = http.Post(COUNT_URL,"application/json", bytes.NewBuffer(reqCountBytes)) // 调用rest接口
if err != nil {
return err
}
return nil
}
/**
给Count加上一个值,比如Count初始为10,输入20,Count会变为30
*/
func setCount(count int) error {
reqCount := Count{Count:count} // 构造请求结构体
reqCountBytes, err :=json.Marshal(reqCount) // 把请求结构体解析为json
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("marshal failed. the error info: ",err)
return err
}
req,err :=http.NewRequest(http.MethodPut,COUNT_URL,strings.NewReader(string(reqCountBytes))) // 因为要调用的Rest接口是PUT类型的,需要先构造Request
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("new request failed with error: %s", err)
return err
}
req.Header.Set("Content-Type", "application/json") // 注意要给Request的请求头添加上内容类型
client := http.Client{} // 创建一个httpClient
_,err=client.Do(req) // 调用rest接口
if err != nil {
return err
}
return nil
}
/**
获取Count值
*/
func getCount() (count int, err error) {
rsp,err :=http.Get(COUNT_URL) // Get接口直接调用就行了
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("get count has some error. the error info: ",err)
return -1, err
}
defer rsp.Body.Close() // defer语句类似于java中的try-catch-finally的finally,即在函数推出的时候,执行defer中的语句
body, err := ioutil.ReadAll(rsp.Body) // 读取响应中的数据
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("get count has some error. the error info: ",err)
return -1, err
}
rspCount := &Count{}
json.Unmarshal(body, rspCount) // 解析请求到结构体
return rspCount.Count, nil
}