Mysql语句层优化整理总结
语句层优化主要包括:使用更高效的SQL来达到同样的目的。
目录
一、SQL语句优化
1.SQL语句的执行时间所花的地方:
2.SQL语句的优化思路:
通过业务逻辑来计算:
精准查询:
3.explain的列分析:
explain出来的各个字段的解释:
eq_ref两种情况可能出现:
3.in型子查询引出的陷阱:
误区与事实:
原因与解决:
4.exists子查询:
exists子查询优化:
5.from 型子查询注意:
6.min/max优化:
7.count() 优化:
误区①Myisam的count()非常快:
假如id<100的商家都是假的,想查真实的商家有多少的技巧:
8.group by
9.union优化
二、慢查询SQL日志收集
三、MySQL使用内部临时表
官方链接:
使用临时表的原因:
临时表被创建的情况:
①group by的列没有索引:
②order by与group by为不同列:
③distinct与order by连用:
④使用SQL_SMALL_RESULT:
⑤union合并查询时会用到临时表:
确认是否使用了临时表:
一些情况下限制了内存临时表的使用而使用磁盘临时表:
一、SQL语句优化
SQL语句的所花的时间主要在等待时间、执行时间。这两个时间并非孤立的,如果单条语句执行的快了,对其他语句的锁定的也就少了。
1.SQL语句的执行时间所花的地方:
查:
沿着索引查,甚至全表扫描。
取:
查到行后,把数据取出来(sending data)。
2.SQL语句的优化思路:
通过业务逻辑来计算:
比如论坛的注册会员数,我们可以根据前3个月统计的每天注册数,用程序来估算。
精准查询:
少查,尽量精准数据,少取行。例如新闻网站、评论内容等,一般一次性取列表10-30条左右。
尽量在索引上查询:
尽量走在索引上查询行,取时,取尽量少的列。
比如 select * from tableA,就取出所有列,不建议这样。
比如 select * from tableA,tableB,取出A、B表的所有列。
3.explain的列分析:
explain出来的各个字段的解释:
mysql> explain select goods_id,goods_name from goods where goods_id in (
select goods_id from goods where cat_id=4) \G
*************************** 1. row***************************
id: 1
select_type: PRIMARY
table: goods
type: ALL
possible_keys: NULL
key: NULL
key_len: NULL
ref: NULL
rows: 31
Extra: Using where
*************************** 2. row***************************
id: 2
select_type: DEPENDENT SUBQUERY
table: goods
type: unique_subquery
possible_keys: PRIMARY,cat_id
key: PRIMARY
key_len: 3
ref: func
rows: 1
Extra: Using where
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
id:
代表select 语句的编号,如果是连接查询,表之间是平等关系,select 编号都是1,从1开始。如果某select中有子查询,则编号递增。
select_type:
查询类型:
table:
查询针对的表,有可能是实际的表名,如select * from t1;。也有可能是表的别名如select * from t2 as tmp;。
derived:
如from型子查询时。
null:直接计算得结果,不用走表。
possible_key:
可能用到的索引。需要注意的是,这是系统估计可能用的几个索引,但最终只能用1个.
key:
最终用的索引。
key_len:
使用的索引的最大长度,越短越好。
type:
是指查询的方式,非常重要,是分析“查数据过程”的重要依据,它可能的值:
all:意味着从表的第1行,往后逐行做全表扫描,运气不好扫描到最后一行(从磁盘上扫描所有行)。
index:比all性能稍好一点(根据索引文件来扫描所有行),通俗的说all 扫描所有的数据行,相当于data_all,index 扫描所有的索引节点,相当于index_all。
range:意思是查询时,能根据索引做范围的扫描。
ref:意思是指通过索引列,可以直接引用到某些数据行 。
eq_ref:是指通过索引列,直接引用某1行数据常见于连接查询中。
const、system、null:这3个分别指查询优化到常量级别,甚至不需要查找时间,一般按照主键来查询时,易出现const、system。或者直接查询某个表达式,不经过表时出现NULL。
性能从好到坏的排序:system->const->eq_ref->ref->ref_or_null->index_merge->unique_subquery->index_subquery->range->index->all
eq_ref两种情况可能出现:
①索引覆盖的查询情况下,能利用上索引,但是又必须全索引扫描。
select goods_id from goods order by goods_id desc;
②利用索引来进行排序,但要取出所有的节点。
分析:没有加where条件,就得取所有索引节点。同时又没有回行,只取索引节点,再排序,经过所有索引节点。
ref:
指连接查询时,表之间的字段引用关系。
rows:
是指估计要扫描多少行。
extra列:
index:是指用到了索引覆盖,效率非常高。
using where:是指光靠索引定位不了,还得where判断一下才行。
using temporary:是指用上了临时表,group by与order by不同列或group by,order by别的表的列。
using filesort:文件排序(文件可能在磁盘,也可能在内存)。
3.in型子查询引出的陷阱:
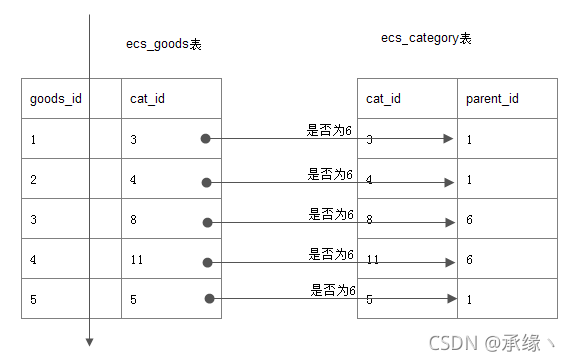
例如在一个ecshop商城表中,查询6号栏目的商品。(注:6号是一个大栏目),最直观的写法:
select goods_id,cat_id,goods_name from goods where cat_id in (
select cat_id from ecs_category where parent_id=6
);
误区与事实:
给我们的感觉是:
先查到内层的6号栏目的子栏目,如7、8、9、11。然后外层,cat_id in (7,8,9,11)。
然而事实是: 如下图goods表全扫描,并逐行与category表对照,看parent_id=6是否成立。
原因与解决:
原因:mysql的查询优化器针对in型做了优化,被改成了exists的执行效果。当goods表越大时,查询速度越慢。
改进:用连接查询来代替子查询:
explain select goods_id,g.cat_id,g.goods_name from goods as g
inner join (
select cat_id from ecs_category where parent_id=6 ) as t
using(cat_id) \G
内层select:cat_id from ecs_category where parent_id=6 ;,用到parent_id索引,返回4行。
+--------+
| cat_id |
+--------+
| 7 |
| 8 |
| 9 |
| 11 |
+--------+ 形成结果,设为t。
*************************** 3. row***************************
id: 2
select_type: DERIVED
table: ecs_category
type: ref
possible_keys: parent_id
key: parent_id
key_len: 2
ref:
rows: 4
Extra:
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
第2次查询:
t和goods通过cat_id 相连,因为cat_id在goods表中有索引,所以相当于用7、8、9、11快速匹配上goods的行。
*************************** 2. row*************************** id: 1
select_type: PRIMARY table: g
type: ref
possible_keys: cat_id key: cat_id
key_len: 2
ref: t.cat_id rows: 6 Extra:
第1次查询:
是把上面2次的中间结果,直接取回.
*************************** 1. row*************************** id: 1 select_type: PRIMARY table:
type: ALL
possible_keys: NULL key: NULL
key_len: NULL ref: NULL
rows: 4
Extra:
4.exists子查询:
查询有商品的栏目,首先我们用join来操作,如下:
mysql> select c.cat_id,cat_name from ecs_category as c inner join goods as g on c.cat_id=g.cat_id group by cat_name;
exists子查询优化:
优化1:
在group时,用带有索引的列来group速度会稍快一些,另外用int型比char型的列来分组也要快一些。
优化2:
在group时,假设只取了A表的内容,group by的列尽量用A表的列,会比这时使用B表的列要快。
优化3:
从语义上去优化:
select cat_id,cat_name from ecs_category where exists(
select * from goods where goods.cat_id=ecs_category.cat_id
)
优化后的语句与其执行的时间:
| select c.cat_id,cat_name from ecs_category as c inner join goods as g on c.cat_id=g.cat_id group by cat_name |
0.00039075 |
| select c.cat_id,cat_name from ecs_category as c inner join goods as g on c.cat_id=g.cat_id group by cat_id |
0.00038675 |
| select c.cat_id,cat_name from ecs_category as c inner join goods as g on c.cat_id=g.cat_id group by c.cat_id |
0.00035650 |
| select cat_id,cat_name from ecs_categorywhere exists(select * from goods where goods.cat_id=ecs_category.cat_id) |
0.00033500 |
5.from 型子查询注意:
内层from语句查到的临时表,是没有索引的。所以from的返回内容要尽量少。
6.min/max优化:
在数据库的表中一般都是经过优化存储的,如下地区表:
| id |
area |
pid |
| 1 |
中国 |
0 |
| 2 |
北京 |
1 |
| ... |
||
| 3115 |
3113 |
查min(id),id是主键时查min(id)非常快。但是pid上没有索引,现在要求查询3113地区的min(id):
select min(id) from it_area where pid=69;
试想id是有顺序的(默认索引是升续排列),因此,如果我们沿着id的索引方向走,那么第1个pid=69的索引结点它的id就正好是最小的id:
select id from it_area use index(primary)
where pid=69 limit 1;
注:改进后的速度虽然快,但语义已经非常不清晰,不建议这么做,仅仅是实验目的。
7.count() 优化:
误区①Myisam的count()非常快:
是比较快,但仅限于查询表的“所有行”时比较快,因为Myisam对行数进行了存储。一旦有条件的查询,速度就不再快了,尤其是where条件的列上没有索引。
假如id<100的商家都是假的,想查真实的商家有多少的技巧:
select count(*) from lx_com where id>=100; (1000多万行用了6.X秒)
小技巧:
select count(*) from lx_com; (快)
select count(*) from lx_com where id<100; (快)
select count(*) frol lx_com - select count(*) from lx_com where id<100; (快)
于是:
select (select count(*) from lx_com) - (select count(*) from lx_com where id<100)
8.group by
①分组用于统计,而不用于筛选数据:
比如统计平均分、最高分时适合使用group by,但用于筛选重复数据时则不适合。使用时最好用索引来避免临时表和文件排序。
②以A、B表连接为例,主要查询A表的列:
group by,order by的列应尽量相同,而且列应该显示声明为A的列。
9.union优化
union all不进行过滤,效率高,如非必须使用union all,union去重的代价非常高,要有去重的需求最好放在程序里去重。
二、慢查询SQL日志收集
要把系统里边一些执行速度非常慢的sql语句给收集起来,并做分析优化,使得其执行速度提升。
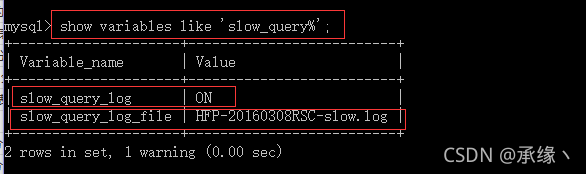
配置开启慢查询、设置时间阀值:
然后重启Mysql服务器,查看相关参数:
> show variables like ‘slow_query%’; //查看慢查询的相关参数:
> show variables like ‘long_query_time’; //查看慢sql语句的时间阀值
测试执行一条超过时间阀值的sql语句:
在日志文件中该sql已经被收集了:
三、MySQL使用内部临时表
如果一开始在内存中产生的临时表变大,会自动转化为磁盘临时表。内存中临时表的最大值为tmp_table_size和max_heap_size中较小值。这和create table时显示指定的内存表不一样,这些表只受max_heap_table_size系统参数影响。
当服务器创建内部临时表(无论在内存还是在磁盘),create_tmp_tables变量都会增加。
如果创建了在磁盘上内部临时表(无论是初始创建还是由in-memory转化),create_tmp_disk_tables 变量都会增加。
官方链接:
MySQL :: MySQL 8.0 Reference Manual :: 8.4.4 Internal Temporary Table Use in MySQL
使用临时表的原因:
在处理请求的某些场景中,服务器创建内部临时表,即表以MEMORY引擎在内存中处理,或以MyISAM引擎储存在磁盘上处理。如果表过大,服务器可能会把内存中的临时表转存在磁盘上,且用户不能直接控制服务器内部用内存还是磁盘存储临时表。
临时表被创建的情况:
①group by的列没有索引:
如果group by的列没有索引,必产生内部临时表。
②order by与group by为不同列:
如果order by与group by为不同列时,或多表联查时order by,group by包含的列不是第一张表的列,将会产生临时表。
mysql>explain select goods_id,cat_id from goods group by cat_id \G
***************************1. row ***************************
id: 1
select_type: SIMPLE
table: goods
type: ALL
possible_keys: NULL
key: NULL
key_len: NULL
ref: NULL
rows: 20
Extra: Using temporary; Using filesort
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql>alter table goods add index cat_id(cat_id);
mysql>explain select goods_id,cat_id from goods group by cat_id \G
***************************1. row ***************************
id: 1
select_type: SIMPLE
table: goods
type: index
possible_keys: NULL
key: cat_id
key_len: 2
ref: NULL
rows: 20
Extra: Using index
mysql>explain select goods_id,cat_id from goods group by cat_id order by 1 \G
***************************1. row ***************************
id: 1
select_type: SIMPLE
table: goods
type: index
possible_keys: NULL
key: PRIMARY
key_len: 3
ref: NULL
rows: 20
Extra: Using temporary
③distinct与order by连用:
distinct 与order by 一起使用可能会产生临时表。
mysql>explain select distinct cat_id from goods order by 1 \G
***************************1. row ***************************
id: 1
select_type: SIMPLE
table: goods
type: index
possible_keys: NULL
key: cat_id
key_len: 2
ref: NULL
rows: 20
Extra: Using index
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql>explain select distinct cat_id from goods order by goods_id \G
***************************1. row ***************************
id: 1
select_type: SIMPLE
table: goods
type: index
possible_keys: NULL
key: PRIMARY
key_len: 3
ref: NULL
rows: 20
Extra: Using temporary
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql>explain select distinct cat_id from goods order by click_count\G
***************************1. row ***************************
id: 1
select_type: SIMPLE
table: goods
type: index
possible_keys: NULL
key: cat_id
key_len: 2
ref: NULL
rows: 20
Extra: Using temporary; Using filesort
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
④使用SQL_SMALL_RESULT:
如果使用SQL_SMALL_RESULT,MySQL会使用内存临时表,除非查询中有一些必须要把临时表建立在磁盘上的语句。
⑤union合并查询时会用到临时表:
某些视图会用到临时表,如使用temptable方式建立或使用union或聚合查询的视图。
确认是否使用了临时表:
用EXPLAIN查询计划,并查看Extra列,看是否有Using temporary。
一些情况下限制了内存临时表的使用而使用磁盘临时表:
1.(使用了内部临时表的前提下)语句中存在BLOB或TEXT列。
2.在GROUP BY或DISTINCT子句中有大于512字节的string列。
3.在UNION或UNION ALL时,SELECT语句里有大于512字节的string列。
mysql>create table t1 (
num int,
intro text(1000)
);
mysql>insert into t1 values (3,'this is USA' , 4,'China');
mysql>show status like '%tmp%';
+-------------------------+-------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+-------------------------+-------+
| Created_tmp_disk_tables | 5 |
| Created_tmp_files | 9 |
| Created_tmp_tables | 74 |
+-------------------------+-------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql>select * from t1 group by num;
+------+-------------+
| num | intro |
+------+-------------+
| 3 | this is USA |
| 4 | China |
+------+-------------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql>show status like '%tmp%';
+-------------------------+-------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+-------------------------+-------+
| Created_tmp_disk_tables | 6 |
| Created_tmp_files | 9 |
| Created_tmp_tables | 75 |
+-------------------------+-------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)