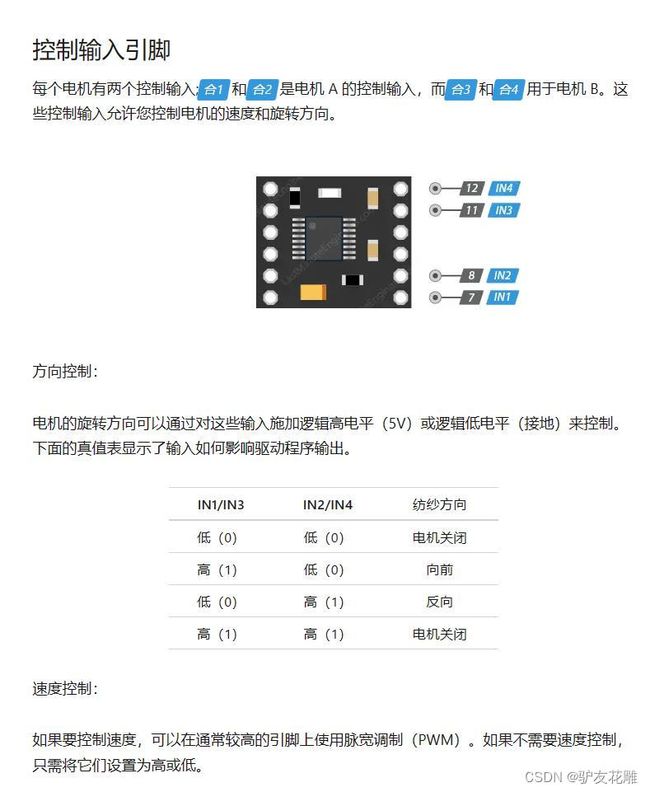
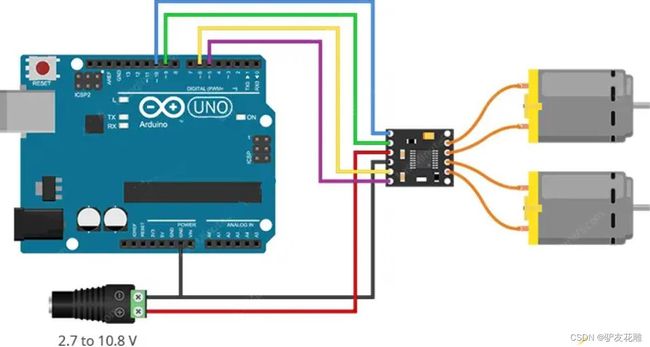
【雕爷学编程】Arduino动手做(182)---DRV8833双路电机驱动模块2
37款传感器与执行器的提法,在网络上广泛流传,其实Arduino能够兼容的传感器模块肯定是不止这37种的。鉴于本人手头积累了一些传感器和执行器模块,依照实践出真知(一定要动手做)的理念,以学习和交流为目的,这里准备逐一动手尝试系列实验,不管成功(程序走通)与否,都会记录下来—小小的进步或是搞不掂的问题,希望能够抛砖引玉。
【Arduino】168种传感器模块系列实验(资料代码+图形编程+仿真编程)
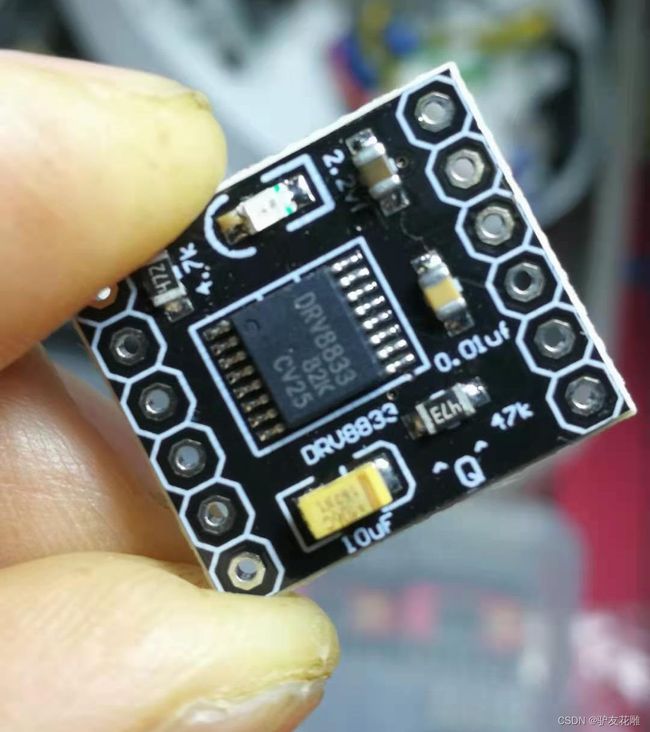
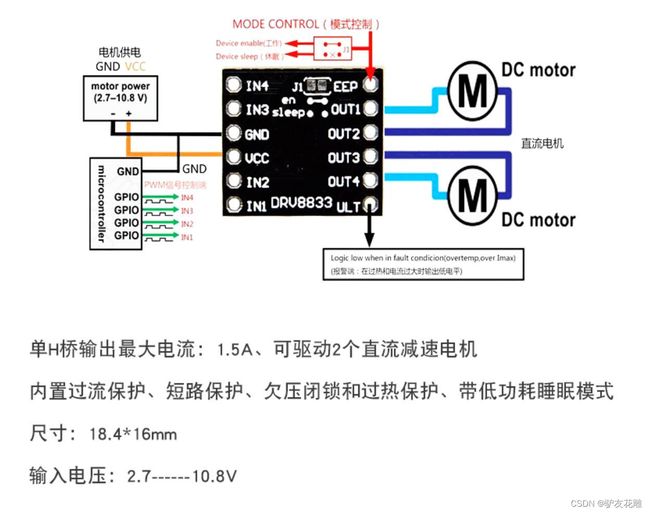
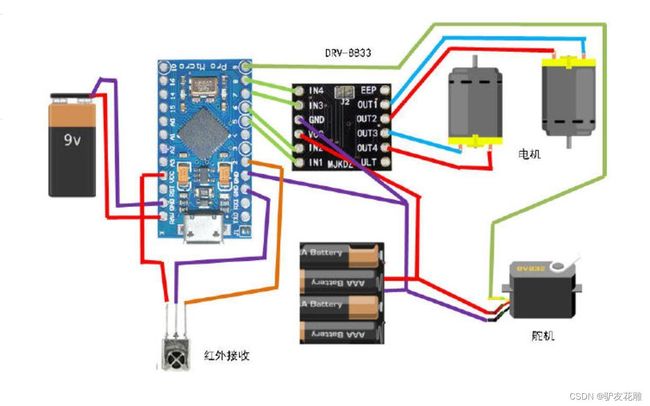
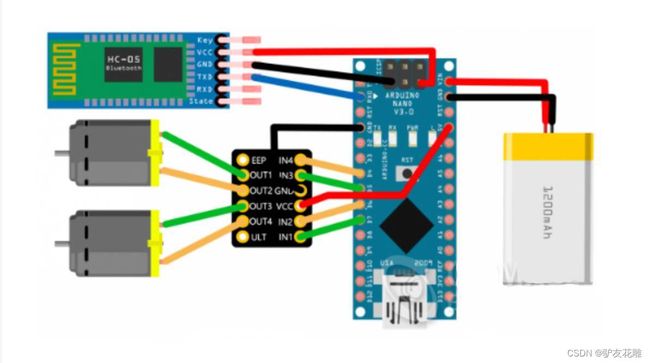
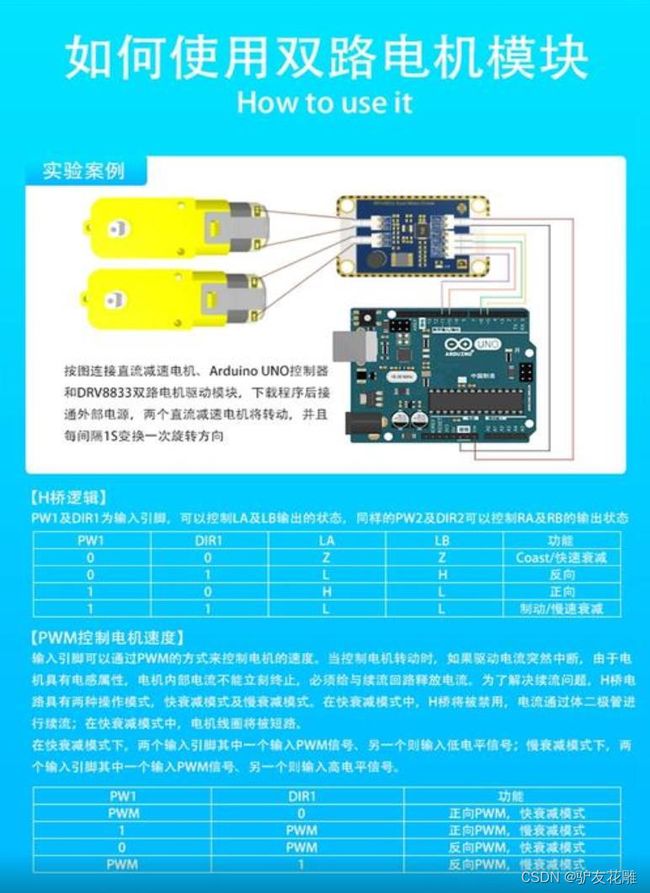
实验一百八十二:DRV8833 电机驱动板模块 小体积高性能 2路直流电机驱动板 自平衡小车 代替TB6612FNG
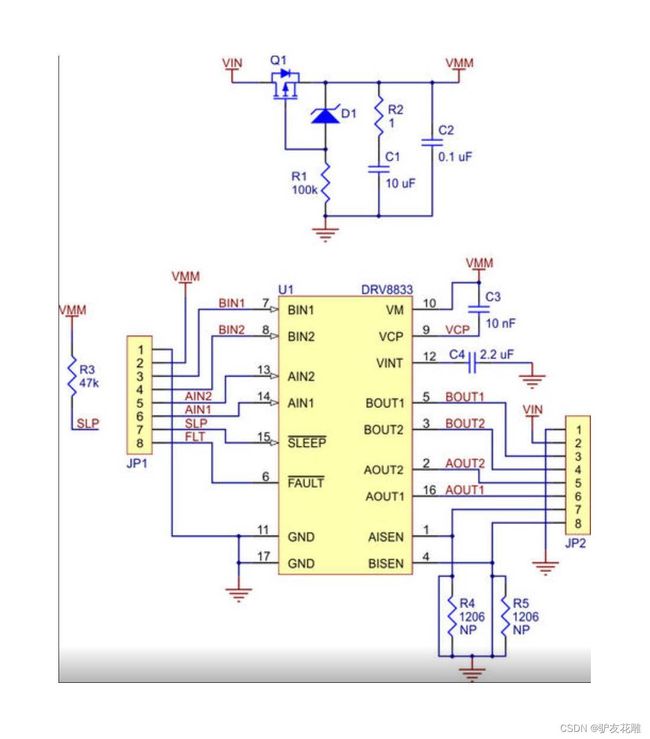
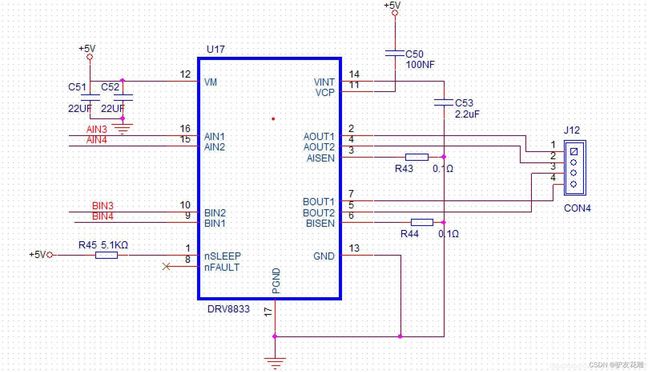
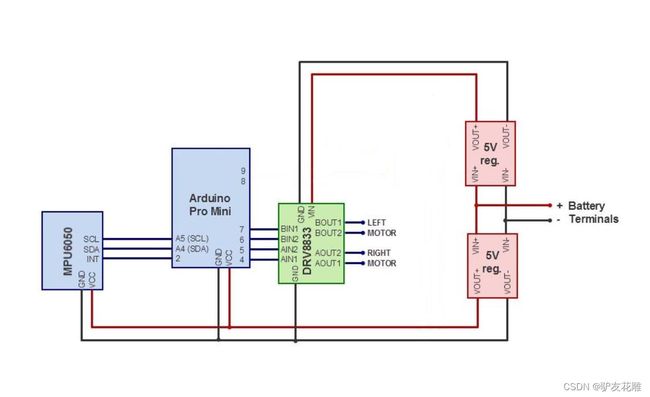
DRV8833电机驱动模块电原理图
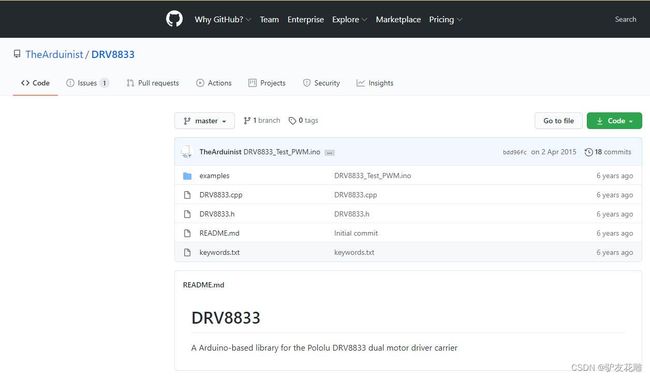
Arduino DRV8833电机控制器库
https://codeload.github.com/TheArduinist/DRV8833/zip/master
https://cfhcable.dl.sourceforge. … ler_library-0.2.zip
【Arduino】168种传感器模块系列实验(资料代码+图形编程+仿真编程)
实验一百八十二:DRV8833 电机驱动板模块 小体积高性能 2路直流电机驱动板 自平衡小车 代替TB6612FNG
Arduino实验开源代码
/*
【Arduino】168种传感器模块系列实验(资料代码+图形编程+仿真编程)
实验一百八十二:DRV8833 电机驱动板模块 小体积高性能 2路直流电机驱动板 自平衡小车 代替TB6612FNG
*/
#define mode_pin 10
#define IN1_PIN 9
#define IN4_PIN 6
#define IN3_PIN 5
#define IN4_PIN 3
void setup() {
pinMode(IN1_PIN, OUTPUT);
pinMode(IN4_PIN, OUTPUT);
pinMode(IN3_PIN, OUTPUT);
pinMode(IN4_PIN, OUTPUT);
pinMode(mode_pin, INPUT);
digitalWrite(IN1_PIN, LOW);
digitalWrite(IN4_PIN, LOW);
digitalWrite(IN3_PIN, LOW);
digitalWrite(IN4_PIN, LOW);
}
void loop() {
int sensorValue = analogRead(A0);
int sensorValue1 = analogRead(A1);
if (digitalRead(mode_pin) == LOW)
{
digitalWrite(IN3_PIN, LOW);
analogWrite(IN4_PIN, sensorValue);
digitalWrite(IN1_PIN, LOW);
analogWrite(IN4_PIN, sensorValue1);
}
if (digitalRead(mode_pin) == HIGH)
{
digitalWrite(IN4_PIN, LOW);
analogWrite(IN3_PIN, sensorValue);
digitalWrite(IN4_PIN, LOW);
analogWrite(IN1_PIN, sensorValue1);
}
}
【Arduino】168种传感器模块系列实验(资料代码+图形编程+仿真编程)
实验一百八十二:DRV8833 电机驱动板模块 小体积高性能 2路直流电机驱动板 自平衡小车 代替TB6612FNG
Arduino实验开源代码
/*
【Arduino】168种传感器模块系列实验(资料代码+图形编程+仿真编程)
实验一百八十二:DRV8833 电机驱动板模块 小体积高性能 2路直流电机驱动板 自平衡小车 代替TB6612FNG
*/
// Define the control inputs
#define MOT_A1_PIN 10
#define MOT_A2_PIN 9
#define MOT_B1_PIN 6
#define MOT_B2_PIN 5
void setup(void){
// Set all the motor control inputs to OUTPUT
pinMode(MOT_A1_PIN, OUTPUT);
pinMode(MOT_A2_PIN, OUTPUT);
pinMode(MOT_B1_PIN, OUTPUT);
pinMode(MOT_B2_PIN, OUTPUT);
// Turn off motors - Initial state
digitalWrite(MOT_A1_PIN, LOW);
digitalWrite(MOT_A2_PIN, LOW);
digitalWrite(MOT_B1_PIN, LOW);
digitalWrite(MOT_B2_PIN, LOW);
// Initialize the serial UART at 9600 baud
Serial.begin(9600);
}
void loop(void){
// Generate a fixed motion sequence to demonstrate the motor modes.
// Ramp speed up.
for (int i = 0; i < 11; i++) {
spin_and_wait(25*i, 25*i, 500);
}
// Full speed forward.
spin_and_wait(255,255,2000);
// Ramp speed into full reverse.
for (int i = 0; i < 21 ; i++) {
spin_and_wait(255 - 25*i, 255 - 25*i, 500);
}
// Full speed reverse.
spin_and_wait(-255,-255,2000);
// Stop.
spin_and_wait(0,0,2000);
// Full speed, forward, turn, reverse, and turn for a two-wheeled base.
spin_and_wait(255, 255, 2000);
spin_and_wait(0, 0, 1000);
spin_and_wait(-255, 255, 2000);
spin_and_wait(0, 0, 1000);
spin_and_wait(-255, -255, 2000);
spin_and_wait(0, 0, 1000);
spin_and_wait(255, -255, 2000);
spin_and_wait(0, 0, 1000);
}
/// Set the current on a motor channel using PWM and directional logic.
///
/// \param pwm PWM duty cycle ranging from -255 full reverse to 255 full forward
/// \param IN1_PIN pin number xIN1 for the given channel
/// \param IN2_PIN pin number xIN2 for the given channel
void set_motor_pwm(int pwm, int IN1_PIN, int IN2_PIN)
{
if (pwm < 0) { // reverse speeds
analogWrite(IN1_PIN, -pwm);
digitalWrite(IN2_PIN, LOW);
} else { // stop or forward
digitalWrite(IN1_PIN, LOW);
analogWrite(IN2_PIN, pwm);
}
}
/// Set the current on both motors.
///
/// \param pwm_A motor A PWM, -255 to 255
/// \param pwm_B motor B PWM, -255 to 255
void set_motor_currents(int pwm_A, int pwm_B)
{
set_motor_pwm(pwm_A, MOT_A1_PIN, MOT_A2_PIN);
set_motor_pwm(pwm_B, MOT_B1_PIN, MOT_B2_PIN);
// Print a status message to the console.
Serial.print("Set motor A PWM = ");
Serial.print(pwm_A);
Serial.print(" motor B PWM = ");
Serial.println(pwm_B);
}
/// Simple primitive for the motion sequence to set a speed and wait for an interval.
///
/// \param pwm_A motor A PWM, -255 to 255
/// \param pwm_B motor B PWM, -255 to 255
/// \param duration delay in milliseconds
void spin_and_wait(int pwm_A, int pwm_B, int duration)
{
set_motor_currents(pwm_A, pwm_B);
delay(duration);
}
代码说明:
Arduino代码相当简单。它不需要任何库即可工作。草图首先声明连接到 DRV8833 控制引脚的 Arduino 引脚。
// Define the control inputs
#define MOT_A1_PIN 10
#define MOT_A2_PIN 9
#define MOT_B1_PIN 6
#define MOT_B2_PIN 5
代码的设置部分初始化硬件。它将所有电机控制引脚配置为数字输出,并将其设置为低电平,以最初禁用两个电机。然后,它以 9600 的波特率初始化串行通信。
void setup(void){
// Set all the motor control inputs to OUTPUT
pinMode(MOT_A1_PIN, OUTPUT);
pinMode(MOT_A2_PIN, OUTPUT);
pinMode(MOT_B1_PIN, OUTPUT);
pinMode(MOT_B2_PIN, OUTPUT);
// Turn off motors - Initial state
digitalWrite(MOT_A1_PIN, LOW);
digitalWrite(MOT_A2_PIN, LOW);
digitalWrite(MOT_B1_PIN, LOW);
digitalWrite(MOT_B2_PIN, LOW);
// Initialize the serial UART at 9600 baud
Serial.begin(9600);
}
代码的循环部分生成一个固定的运动序列来演示电机模式。
它首先逐渐增加电机的速度,然后进入全速,再次减速并反转方向到全速,最后停止。
// Ramp speed up.
for (int i = 0; i < 11; i++) {
spin_and_wait(25*i, 25*i, 500);
}
// Full speed forward.
spin_and_wait(255,255,2000);
// Ramp speed into full reverse.
for (int i = 0; i < 21 ; i++) {
spin_and_wait(255 - 25*i, 255 - 25*i, 500);
}
// Full speed reverse.
spin_and_wait(-255,-255,2000);
// Stop.
spin_and_wait(0,0,2000);
停止后,它演示了两轮机器人底座的转弯操作,其中一个轮子向前移动,另一个轮子向后移动,导致机器人转动。在演示了所有这些动作之后,循环重复。
// Full speed, forward, turn, reverse, and turn for a two-wheeled base.
spin_and_wait(255, 255, 2000);
spin_and_wait(0, 0, 1000);
spin_and_wait(-255, 255, 2000);
spin_and_wait(0, 0, 1000);
spin_and_wait(-255, -255, 2000);
spin_and_wait(0, 0, 1000);
spin_and_wait(255, -255, 2000);
spin_and_wait(0, 0, 1000);
此草图中使用了三个用户定义的函数:
set_motor_pwm()set_motor_currents()spin_and_wait()
该功能使用 PWM 和方向逻辑设置电机通道上的电流。如果该值为负,则电机沿一个方向旋转。如果值为 0 或正,则电机停止或向另一个方向旋转。
set_motor_pwm()pwmpwm
void set_motor_pwm(int pwm, int IN1_PIN, int IN2_PIN)
{
if (pwm < 0) { // reverse speeds
analogWrite(IN1_PIN, -pwm);
digitalWrite(IN2_PIN, LOW);
} else { // stop or forward
digitalWrite(IN1_PIN, LOW);
analogWrite(IN2_PIN, pwm);
}
}
该函数使用前面的函数来设置两个电机上的电流。它将每个电机的当前PWM值打印到串行监视器。
set_motor_currents()
void set_motor_currents(int pwm_A, int pwm_B)
{
set_motor_pwm(pwm_A, MOT_A1_PIN, MOT_A2_PIN);
set_motor_pwm(pwm_B, MOT_B1_PIN, MOT_B2_PIN);
// Print a status message to the console.
Serial.print("Set motor A PWM = ");
Serial.print(pwm_A);
Serial.print(" motor B PWM = ");
Serial.println(pwm_B);
}
该函数设置速度并等待指定的时间量,然后再移动到下一个命令。它使用该函数为两个电机设置PWM值,然后等待指定的毫秒。
spin_and_wait()set_motor_currents()duration
void spin_and_wait(int pwm_A, int pwm_B, int duration)
{
set_motor_currents(pwm_A, pwm_B);
delay(duration);
}