mybatis — 执行流程解析
mybatis常见面试题:
1、MyBatis框架适用场合:
(1)MyBatis专注于SQL本身,是一个足够灵活的DAO层解决方案。
(2)对性能的要求很高,或者需求变化较多的项目,如互联网项目,MyBatis将是不错的选择。
2、MyBatis与Hibernate有哪些不同?
(1)Mybatis和hibernate不同,它不完全是一个ORM框架,因为MyBatis需要程序员自己编写Sql语句。
(2)Mybatis直接编写原生态sql,可以严格控制sql执行性能,灵活度高,非常适合对关系数据模型要求不高的软件开发,因为这类软件需求变化频繁,一但需求变化要求迅速输出成果。但是灵活的前提是mybatis无法做到数据库无关性,如果需要实现支持多种数据库的软件,则需要自定义多套sql映射文件,工作量大。
(3)Hibernate对象/关系映射能力强,数据库无关性好,对于关系模型要求高的软件,如果用hibernate开发可以节省很多代码,提高效率。
3、#{}和${}的区别是什么?
#{}是预编译处理,$ {}是字符串替换。
Mybatis在处理#{}时,会将sql中的#{}替换为?号,调用PreparedStatement的set方法来赋值;
Mybatis在处理${}时,就是把${}替换成变量的值。
使用#{}可以有效的防止SQL注入,提高系统安全性。
4、Mybatis是如何进行分页的?分页插件的原理是什么?
Mybatis使用RowBounds对象进行分页,它是针对ResultSet结果集执行的内存分页,而非物理分页。可以在sql内直接书写带有物理分页的参数来完成物理分页功能,也可以使用分页插件来完成物理分页。
分页插件的基本原理是使用Mybatis提供的插件接口,实现自定义插件,在插件的拦截方法内拦截待执行的sql,然后重写sql,根据dialect方言,添加对应的物理分页语句和物理分页参数。
5、Mybatis是如何将sql执行结果封装为目标对象并返回的?都有哪些映射形式?
第一种是使用标签,逐一定义数据库列名和对象属性名之间的映射关系。
第二种是使用sql列的别名功能,将列的别名书写为对象属性名。
有了列名与属性名的映射关系后,Mybatis通过反射创建对象,同时使用反射给对象的属性逐一赋值并返回,那些找不到映射关系的属性,是无法完成赋值的。
1、Mybatis 插件介绍
Mybatis作为一个应用广泛的优秀的ORM框架,这个框架具有强大的灵活性,在四大组件(Executor、StatementHandler、ParameterHandler、ResultSetHandler)处提供了简单易用的插件扩展机制。Mybatis对持久层的操作就是借助于四大核心对象。MyBatis支持用插件对四大核心对象进行拦截,对mybatis来说插件就是拦截器,用来增强核心对象的功能,增强功能本质上是借助于底层的动态代理实现的,换句话说,MyBatis中的四大对象都是代理对象。
MyBatis 所允许拦截的方法如下:
- 执行器Executor [update、query、commit、rollback]
- SQL语法构建器StatementHandler[prepare、parameterize、batch、update、query]
- 参数处理器ParameterHandler[gerParameterObject、setParameters方法]
- 结果集处理器ResultSetHandler[handleResultSets、handleOutputParameters等方法]
自定义插件
- 创建自定义插件类实现Interceptor接口
- 重写Intercept()方法
- 然后给插件编写注解,指定需要拦截 的接口和方法
- 在mybatis配置文件中配置所写的插件类
2、MyBatis 执行流程
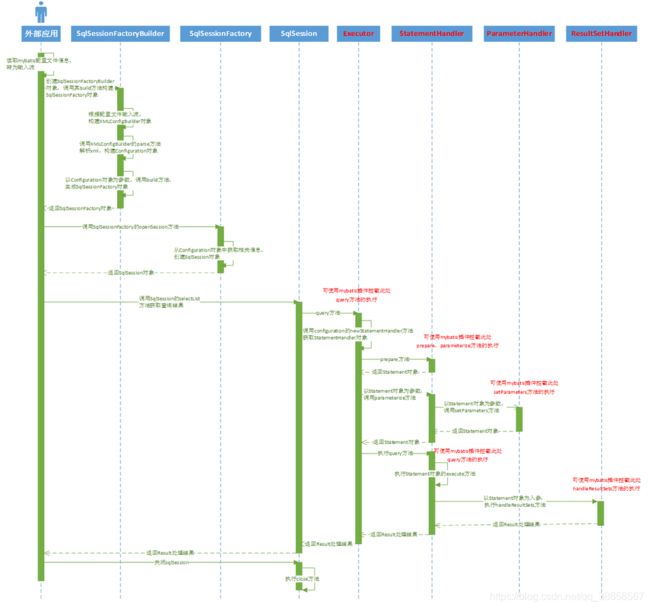
2.1、SqlSessionFactoryBuilder
从名称长可以看出来使用的建造者设计模式(Builder),用于构建SqlSessionFactory对象
- 解析mybatis的xml配置文件,然后创建Configuration对象(对应标签)
- 根据创建的Configuration对象,创建SqlSessionFactory(默认使用DefaultSqlSessionFactory)
2.2、SqlSessionFactory
从名称上可以看出使用的工厂模式(Factory),用于创建并初始化SqlSession对象(数据库会话)
- 调用openSession方法,创建SqlSession对象,可以将SqlSession理解为数据库连接(会话)
- openSession方法有多个重载,可以创建SqlSession关闭自动提交、指定ExecutorType、指定数据库事务隔离级别等
public interface SqlSessionFactory {
/**
* 使用默认配置
* 1.默认不开启自动提交
* 2.执行器Executor默认使用SIMPLE
* 3.使用数据库默认的事务隔离级别
*/
SqlSession openSession();
/**
* 指定是否开启自动提交
* @param autoCommit 是否开启自动提交
*/
SqlSession openSession(boolean autoCommit);
/**
* 根据已有的数据库连接创建会话(事务)
* @param connection 数据库连接
*/
SqlSession openSession(Connection connection);
/**
* 创建连接时,指定数据库事务隔离级别
* @param level 事务隔离界别
*/
SqlSession openSession(TransactionIsolationLevel level);
/**
* 创建连接时,指定执行器类型
* @param execType 执行器
*/
SqlSession openSession(ExecutorType execType);
SqlSession openSession(ExecutorType execType, boolean autoCommit);
SqlSession openSession(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level);
SqlSession openSession(ExecutorType execType, Connection connection);
/**
* 获取Configuration对象,也就是解析xml配置文件中的标签后的数据
*/
Configuration getConfiguration();
}
2.3、SqlSession
session,译为“会话、会议”,数据的有效时间范围是在会话期间(会议期间),会话(会议)结束后,数据就清除了。也可以将SqlSession理解为一个数据库连接。SqlSession是一个接口,定义了很多操作数据库的方法声明:
public interface SqlSession extends Closeable {
/* 获取数据库连接 */
Connection getConnection();
/* 数据库的增删改查 */
<T> T selectOne(String statement);
<E> List<E> selectList(String statement);
int update(String statement, Object parameter);
int delete(String statement, Object parameter);
/* 事务回滚与提交 */
void rollback();
void commit();
/* 清除一级缓存 */
void clearCache();
//....
}
SqlSession只是定义了执行sql的一些方法,而具体的实现由子类来完成,比如SqlSession有一个接口实现类DefaultSqlSession。
MyBatis中通过Executor来执行sql的,在创建SqlSession的时候(openSession),同时会创建一个Executor对象,如下:
@Override
public SqlSession openSession() {
return openSessionFromDataSource(configuration.getDefaultExecutorType(), null, false);
}
private SqlSession openSessionFromDataSource(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit) {
Transaction tx = null;
try {
final Environment environment = configuration.getEnvironment();
final TransactionFactory transactionFactory = getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(environment);
tx = transactionFactory.newTransaction(environment.getDataSource(), level, autoCommit);
// 利用传入的参数,创建executor对象
final Executor executor = configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType);
return new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor, autoCommit);
} catch (Exception e) {
closeTransaction(tx); // may have fetched a connection so lets call close()
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error opening session. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
2.4、Executor
Executor(人称“执行器”)是一个接口,定义了对JDBC的封装;
MyBatis中提供了多种执行器,如下:

Executor只有三种类型:
public enum ExecutorType {
SIMPLE, // 简单
REUSE, // 复用
BATCH; // 批量
}
CacheExecutor其实是一个Executor代理类,包含一个delegate,需要创建时手动传入(要入simple、reuse、batch三者之一);
ClosedExecutor,所有接口都会抛出异常,表示一个已经关闭的Executor;
创建SqlSession时,默认使用的是SimpleExecutor;
下面是创建Executor的代码:org.apache.ibatis.session.Configuration#newExecutor()
public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction) {
return newExecutor(transaction, defaultExecutorType);
}
public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction, ExecutorType executorType) {
//Executor默认是simple
executorType = executorType == null ? defaultExecutorType : executorType;
executorType = executorType == null ? ExecutorType.SIMPLE : executorType;
Executor executor;
//根据传入的ExecutorType,创建对应的Executor
if (ExecutorType.BATCH == executorType) {
executor = new BatchExecutor(this, transaction);
} else if (ExecutorType.REUSE == executorType) {
executor = new ReuseExecutor(this, transaction);
} else {
executor = new SimpleExecutor(this, transaction);
}
//如果开启一级缓存,则创建CachingExecutor
if (cacheEnabled) {
executor = new CachingExecutor(executor);
}
//拦截器,加载插件
executor = (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor);
return executor;
}
Executor是对JDBC的封装。当我们使用JDBC来执行sql时,一般会先预处理sql,也就是conn.prepareStatement(sql),获取返回的PreparedStatement对象(实现了Statement接口),再调用statement的executeXxx()来执行sql。
也就是说,Executor在执行sql的时候也是需要创建Statement对象的,下面以SimpleExecutor为例:
public class SimpleExecutor extends BaseExecutor {
public SimpleExecutor(Configuration configuration, Transaction transaction) {
super(configuration, transaction);
}
@Override
public <E> List<E> doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt = null;
try {
Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(wrapper, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog());
return handler.query(stmt, resultHandler);
} finally {
closeStatement(stmt);
}
}
private Statement prepareStatement(StatementHandler handler, Log statementLog) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt;
Connection connection = getConnection(statementLog);
stmt = handler.prepare(connection, transaction.getTimeout());
handler.parameterize(stmt);
return stmt;
}
// ......
}
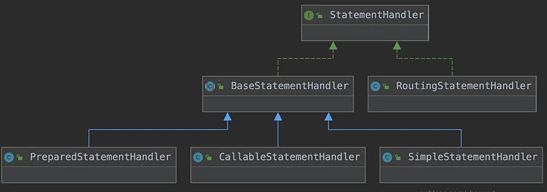
2.5、StatementHandler
在JDBC中,是调用Statement.executeXxx()来执行sql;
在MyBatis,也是调用Statement.executeXxx()来执行sql,此时就不得不提StatementHandler:
- 对sql进行预处理;
- 调用statement.executeXxx()执行sql;
- 将数据库返回的结果集进行对象转换(ORM);
public interface StatementHandler {
/**
* 获取预处理对象
*/
Statement prepare(Connection connection, Integer transactionTimeout) throws SQLException;
/**
* 进行预处理
*/
void parameterize(Statement statement) throws SQLException;
/**
* 批量sql(内部调用statement.addBatch)
*/
void batch(Statement statement) throws SQLException;
/**
* 执行更新操作
* @return 修改的记录数
*/
int update(Statement statement) throws SQLException;
/**
* 执行查询操作
* @param statement sql生成的statement
* @param resultHandler 结果集的处理逻辑
* @return 查询结果
*/
<E> List<E> query(Statement statement, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException;
<E> Cursor<E> queryCursor(Statement statement) throws SQLException;
BoundSql getBoundSql();
ParameterHandler getParameterHandler();
}
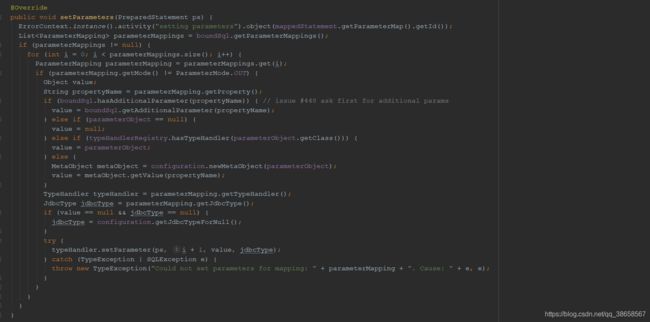
2.6、ParameterHandler
ParameterHandler的功能就是sql预处理后,进行设置参数:
public interface ParameterHandler {
Object getParameterObject();
void setParameters(PreparedStatement ps) throws SQLException;
}
ParamterHandler有一个DefaultParameterHandler,下面是其重写setParameters的代码:
2.7、ResultSetHandler
当执行statement.execute()后,就可以通过statement.getResultSet()来获取结果集,获取到结果集之后,MyBatis会使用ResultSetHandler来将结果集的数据转换为Java对象(ORM映射)。
public interface ResultSetHandler {
/**
* 从statement中获取结果集,并将结果集的数据库属性字段映射到Java对象属性
* @param stmt 已经execute的statement,调用state.getResultSet()获取结果集
* @return 转换后的数据
*/
<E> List<E> handleResultSets(Statement stmt) throws SQLException;
<E> Cursor<E> handleCursorResultSets(Statement stmt) throws SQLException;
void handleOutputParameters(CallableStatement cs) throws SQLException;
}
2.8、TypeHandler
TypeHandler主要用在两个地方:
- 参数绑定,发生在ParameterHandler.setParamenters()中。
MyBatis中,可以使用来定义结果的映射关系,包括每一个字段的类型,比如下面这样:
<resultMap id="baseMap" type="com.demo.model.User">
<id column="uid" property="id" jdbcType="INTEGER" />
<result column="uname" property="name" jdbcType="VARCHAR" />
</resultMap>
TypeHandler,可以对某个字段按照xml中配置的类型进行设置值,比如设置sql的uid参数时,类型为INTEGER(jdbcType)。
- 获取结果集中的字段值,发生在ResultSetHandler处理结果集的过程中。
TypeHandler的定义如下:
public interface TypeHandler<T> {
/**
* 设置预处理参数
*
* @param ps 预处理statement
* @param i 参数位置
* @param parameter 参数值
* @param jdbcType 参数的jdbc类型
*/
void setParameter(PreparedStatement ps, int i, T parameter, JdbcType jdbcType) throws SQLException;
/**
* 获取一条结果集的某个字段值
*
* @param rs 一条结果集
* @param columnName 列名(字段名称)
* @return 字段值
*/
T getResult(ResultSet rs, String columnName) throws SQLException;
/**
* 获取一条结果集的某个字段值(按照字段的顺序获取)
*
* @param rs 一条结果集
* @param columnIndex 字段列的顺序
* @return 字段值
*/
T getResult(ResultSet rs, int columnIndex) throws SQLException;
T getResult(CallableStatement cs, int columnIndex) throws SQLException;
}