NLP之NLTK、spacy、jieba(中文)的使用
一、NLTK库的基本使用
import nltk #pip install nltk
nltk.download() # 下载语言模型
from nltk.tokenize import word_tokenize # 把句子转成一个一个词
from nltk.text import Text
input_str = "Today's weather is good, very windy and sunny, we have no classes in the afternoon,We have to play basketball tomorrow."
tokens = word_tokenize(input_str)
# 查看词库中前5个词
tokens = [word.lower() for word in tokens]
print(tokens[:5])from nltk.tokenize import word_tokenize # 把句子转成一个一个词
from nltk.text import Text
input_str = "Today's weather is good, very windy and sunny, we have no classes in the afternoon,We have to play basketball tomorrow."
tokens = word_tokenize(input_str)
t = Text(tokens) # 创建一个TEXT对象, 可以计算某一个词的个数和索引,也可以画图
print(t.count('good')) # 1
print(t.index('good')) # 4
t.plot(8)"""
停用词的使用
"""
from nltk.corpus import stopwords
print(stopwords.readme().replace('\n', ' ')) # 停用词的介绍
print(stopwords.fileids()) # 各个组国家的停用词
print(stopwords.raw('english').replace('\n',' ')) # 查看某个国家的停用词
"""
词性标注
"""
nltk.download() # 下载第三个
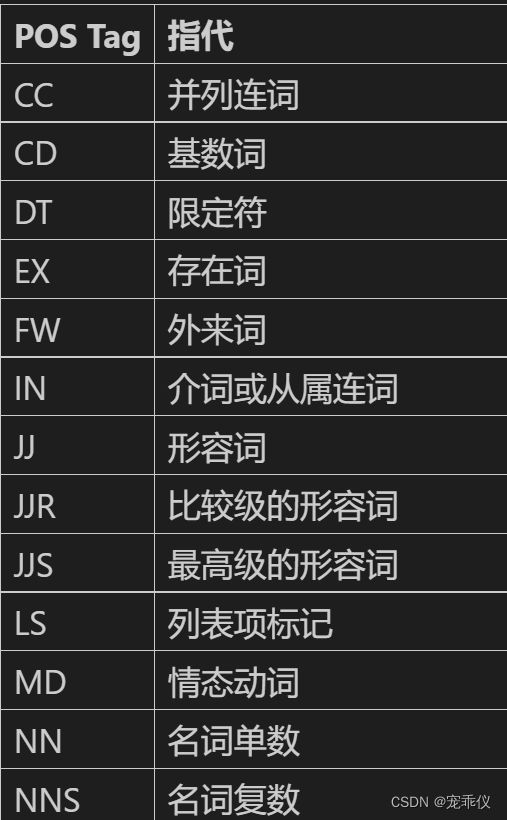
from nltk import pos_tag
tags = pos_tag(tokens)
print(tags) """
分块
"""
from nltk.chunk import RegexpParser
entence = [('the','DT'),('little','JJ'),('yellow','JJ'),('dog','NN'),('died','VBD')]
grammer = "MY_NP: {?*}"
cp = nltk.RegexpParser(grammer) #生成规则
result = cp.parse(sentence) #进行分块
print(result)
result.draw() #调用matplotlib库画出来 import nltk
nltk.download()
#maxent_ne_chunke
#words
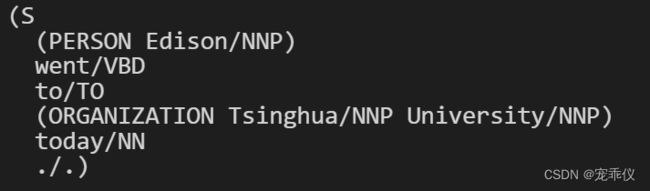
from nltk import ne_chunk
sentence = "Edison went to Tsinghua University today."
print(ne_chunk(pos_tag(word_tokenize(sentence))))数据清洗示例
def txt_data_clean(text):
cache_english_stopwords = stopwords.words('english')
# print('原始数据:', text, '\n')
# 去掉HTML标签(e.g. &)
text_no_special_entities = re.sub(r'\&\w*;|#\w*|@\w*', '', text)
# print('去掉特殊标签后的:', text_no_special_entities, '\n')
# 去掉一些价值符号
text_no_tickers = re.sub(r'\$\w*', '', text_no_special_entities)
# print('去掉价值符号后的:', text_no_tickers, '\n')
# 去掉超链接
text_no_hyperlinks = re.sub(r'https?:\/\/.*\/\w*', '', text_no_tickers)
# print('去掉超链接后的:', text_no_hyperlinks, '\n')
# 去掉一些专门名词缩写,简单来说就是字母比较少的词
text_no_small_words = re.sub(r'\b\w{1,2}\b', '', text_no_hyperlinks)
# print('去掉专门名词缩写后:', text_no_small_words, '\n')
# 去掉多余的空格
text_no_whitespace = re.sub(r'\s\s+', ' ', text_no_small_words)
text_no_whitespace = text_no_whitespace.lstrip(' ')
# print('去掉空格后的:', text_no_whitespace, '\n')
# 分词
tokens = word_tokenize(text_no_whitespace)
# print('分词结果:', tokens, '\n')
# 去停用词
list_no_stopwords = [i for i in tokens if i not in cache_english_stopwords]
# print('去停用词后结果:', list_no_stopwords, '\n')
# 过滤后结果
text_filtered = ' '.join(list_no_stopwords) # ''.join() would join without spaces between words.
# print('过滤后:', text_filtered)
return text_filtered二、spacy的基本使用
# 导入工具包和英文模型
# python -m spacy download en 用管理员身份打开CMD
import spacy
nlp = spacy.load('en')"""
分词,分句,词性,命名实体识别
"""
import spacy
nlp = spacy.load('en')
str_ = 'Weather is good, very windy and sunny. We have no classes in the afternoon.'
doc = nlp(str_)
print(doc) # 分词
print(doc.sents) # 分句
for token in doc:
print ('{}-{}'.format(token,token.pos_)) # 查看每个词的词性
for ent in doc.ents:
print ('{}-{}'.format(ent,ent.label_)) # 命名实体识别
# 命名实体识别可视化展示
from spacy import displacy
doc = nlp('I went to Paris where I met my old friend Jack from uni.')
displacy.render(doc,style='ent',jupyter=False) # jupyter 是否在jupyternotebook上面展示
from collections import Counter # 用于计数
c = Counter()
print(c.most_common(10)) # 查看前10个
三、jieba使用(针对的是中文)
import jieba
seg_list = jieba.cut("我来到北京清华大学", cut_all=True)
print("全模式: " + "/ ".join(seg_list)) # 全模式 会输出所有可能性
# 全模式: 我/ 来到/ 北京/ 清华/ 清华大学/ 华大/ 大学
seg_list = jieba.cut("他来到了网易杭研大厦") # 默认是精确模式
print(", ".join(seg_list))
# 他, 来到, 了, 网易, 杭研, 大厦"""
自定义词典
"""
import jieba
jieba.load_userdict("./data/mydict.txt") #需UTF-8,可以在另存为里面设置
#也可以用jieba.add_word("乾清宫")
text = "故宫的著名景点包括乾清宫、太和殿和黄琉璃瓦等"
# 全模式
seg_list = jieba.cut(text, cut_all=True)
print(u"[全模式]: ", "/ ".join(seg_list))
# [全模式]: 故宫/ 的/ 著名/ 著名景点/ 景点/ 包括/ 乾清宫/ 清宫/ / / 太和/ 太和殿/ 和/ 黄琉璃瓦/ 琉璃/ 琉璃瓦/ 等
# 精确模式
seg_list = jieba.cut(text, cut_all=False)
print(u"[精确模式]: ", "/ ".join(seg_list))
# [精确模式]: 故宫/ 的/ 著名景点/ 包括/ 乾清宫/ 、/ 太和殿/ 和/ 黄琉璃瓦/ 等
3、词性标注
"""
关键词 抽取 越少的越稀有
"""
import jieba.analyse
import jieba
seg_list = jieba.cut(text, cut_all=False)
print (u"分词结果:")
print ("/".join(seg_list)) # 故宫/的/著名景点/包括/乾清宫/、/太和殿/和/黄琉璃瓦/等
#获取关键词
tags = jieba.analyse.extract_tags(text, topK=5, withWeight=True)
print (u"关键词:")
print (" ".join(tags)) # 著名景点 乾清宫 黄琉璃瓦 太和殿 故宫
for word, weight in tags:
print(word, weight)
# 著名景点 2.3167796086666668
# 乾清宫 1.9924612504833332
# 黄琉璃瓦 1.9924612504833332
# 太和殿 1.6938346722833335
# 故宫 1.54111955030333354、词性标注
import jieba.posseg as pseg
words = pseg.cut("我爱北京天安门")
for word, flag in words:
print("%s %s" % (word, flag))
# 我 r
# 爱 v
# 北京 ns
# 天安门 ns5、词云展示
import jieba
from wordcloud import WordCloud
from scipy.misc import imread
from collections import Counter
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
data={}
text_file = open('./data/19Congress.txt','r',encoding='utf-8')
text = text_file.read()
with open('./data/stopwords.txt',encoding='utf-8') as file:
stopwords = {line.strip() for line in file}
seg_list = jieba.cut(text, cut_all=False)
for word in seg_list:
if len(word)>=2:
if not data.__contains__(word):
data[word]=0
data[word]+=1
#print(data)
my_wordcloud = WordCloud(
background_color='white', #设置背景颜色
max_words=400, #设置最大实现的字数
font_path=r'./data/SimHei.ttf', #设置字体格式,如不设置显示不了中文
mask=imread('./data/mapofChina.jpg'), #指定在什么图片上画
width=1000,
height=1000,
stopwords = stopwords
).generate_from_frequencies(data)
plt.figure(figsize=(18,16))
plt.imshow(my_wordcloud)
plt.axis('off')
plt.show() # 展示词云
my_wordcloud.to_file('result.jpg')
text_file.close()