string类
string类
- 1.string类的常用接口
- 2. string的插入
- 3. string的遍历
- 4. string的拼接
- 5. string的删除
- 6. string的查找
- 7. string的大小或容量
- 8. string中与迭代器相关的函数
- 9. string中运算符的使用
- 10. string中插入与替换
- 10. string中子字符串的提取
- 11. string转换为字符串
- 12. string中的getline函数
1.string类的常用接口
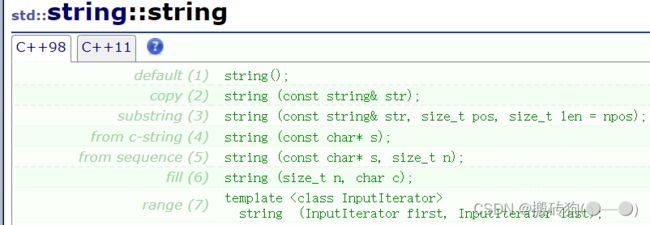
- string()
构造空的string类对象,即空字符串;- string(const string& str)
用C-string来构造string类对象;- string(const string& str, szie_t pos, szie_t len = npos)
赋值str字符串从pos位置开始,并且跨越len长度(如果字符串太长或者太短就直接到结尾);- string(const char * s)
复制以空结尾的字符串序列;- string(const char * s, size_t n)
复制s中指向的前n个字符;- string (size_t n, char c)
用字符c的n个连续副本填充字符串;
1 #include<iostream>
2 using namespace std;
3 void StringTest1()
4 {
5 string s1;
6 cout << s1 << endl;
7 string s2("hello");
8 cout << s2 << endl; //hello
9 string s3(s2);
10 cout << s3 << endl; //hello
11 string s4(s2, 2, 2);
12 string _s4(s2, 2);
13 cout << s4 << endl; //ll
14 cout << _s4 << endl; //llo
15 string s5("hello world", 5);
16 cout << s5 << endl; //hello
17 string s6(10,'x');
18 cout << s6 << endl; //xxxxxxxxxx
19 }
20 int main()
21 {
22 StringTest1();
23 }
2. string的插入
- void push_back
将字符c追加到字符串的末尾,使其长度增加1;
21 int main()
22 {
23 string s;
24 s.push_back('a');
25 s.push_back('b');
26 s.push_back('c');
27 s.push_back('d');
28 cout << s << endl; //abcd
29 return 0;
30 }
- insert
- string& insert (size_t pos, const string& str)
(在pos位置插入str副本)- string& insert (size_tpos, const char * s)
(在pos位置插入一个字符串)- iterator insert (iterator p, char c)
(pos位置插入字符c)
32 int main()
33 {
34 string s("hello ");
35 s.insert(6, "world");
36 cout << s << endl;//hello world
37
38 string s1("!!!");
39 s.insert(11, s1);
40 cout << s << endl;//hello world!!!
41
42 s.insert(s.end(), '@');
43 s.insert(s.begin(), '@');
44 cout << s << endl;//@hello world!!!@
45 return 0;
46 }
3. string的遍历
1.使用下标进行遍历
48 int main()
49 {
50 string s("hello");
51 size_t i = 0;
52 for(i = 0; i < s.size(); i++)
53 {
54 cout << s[i] << " ";//h e l l o
55 }
56 cout << endl;
57
58 for(i = 0; i < s.size(); i++)
59 {
60 s[i]++;
61 }
62 cout << s << endl;//ifmmp
63 return 0;
64 }
2.使用范围for进行遍历
49 int main()
50 {
51 string s("hello");
52 for(auto ch : s)
53 {
54 cout << ch;//hello
55 }
56 cout << endl;
57 for(auto& ch : s)
58 {
59 ch++;
60 }
61 cout << s << endl;//ifmmp
62 return 0;
63 }
4. string的拼接
- string& append (const string& str)
加一个str的副本- string& append (const char * s)
追加一个以NULL结尾的字符串- string& append (size_t n, char c)
追加n个字符c的连续副本
66 int main()
67 {
68 string s("hello");
69 s.append(" world");
70 cout << s << endl;//hello world
71
72 string s1("!!!");
73 s.append(s1);
74 cout << s << endl;//hello world!!!
75
76 s.append(3, '@');
77 cout << s << endl;//hello world!!!@@@
78 return 0;
79 }
5. string的删除
- void pop_back
删掉最后一个字符,长度减1;
83 int main()
84 {
85 string s("hello");
86 s.pop_back();
87 cout << s << endl;//hell
88 s.pop_back();
89 cout << s << endl;//hel
90 return 0;
91 }
- erase
- string& erase (size_t pos = 0, size_t len = npos)
从pos位置删除长度为len的字符串- iterator erase (iterator p)
删除p位置的字符- iterator erase (iterator first, iterator last)
删除[first, last)范围内的字符
93 int main()
94 {
95 string s("hello_world");
96 s.erase(0,6);
97 cout << s << endl;//world
98
99 s.erase(s.end()-1);
100 cout << s << endl;//worl
101
102 s.erase(s.begin()+1,s.end()-1);
103 cout << s <<endl;//wl
104 return 0;
105 }
6. string的查找
- find
- size_t find (const string& str, size_t pos = 0) const
正向搜索与str对象所匹配的第一个位置- size_t find (const char * s, size_t pos = 0) const
正向搜索与字符串s对象所匹配的第一个位置- size_t find (char c, size_t pos = 0) const
正向搜索与字符char对象所匹配的第一个位置
136 int main()
137 {
138 string s1("https://legacy.cplusplus.com/reference/string/string/find/");
139
140 string s2("cplusplus.com");
141 size_t pos1 = s1.find(s2);
142 cout << pos1 << endl;//15
143
144 size_t pos2 = s1.find("reference");
145 cout << pos2 <<endl;//29
146
147 size_t pos3 = s1.find(':');
148 cout << pos3 <<endl;//5
149 return 0;
150 }
- rfind()
- size_t rfind (const string& str, size_t pos = npos) const
反向搜索与str对象所匹配的第一个位置- size_t rfind (const char * s, size_t pos = npos) const
反向搜索与字符串s对象所匹配的第一个位置- size_t rfind (char c, size_t pos = npos) const
反向搜索与字符char对象所匹配的第一个位置
152 int main()
153 {
154
155 string s1("https://legacy.cplusplus.com/reference/string/string/find/");
156
157 string s2("string");
158 size_t pos1 = s1.rfind(s2);
159 cout << pos1 << endl;//46
160
161 size_t pos2 = s1.rfind("reference");
162 cout << pos2 <<endl;//29
163
164 size_t pos3 = s1.rfind('/');
165 cout << pos3 <<endl;//57
166 return 0;
167 }
7. string的大小或容量
- size_t size() const
- size_t length() const
107 int main()
108 {
109 string s("hello");
110 cout << s.size() << endl;//5
111 cout << s.length() << endl;//5
112 return 0;
113 }
- size_t max_size() const
115 int main()
116 {
117 string s("hello");
118 cout << s.max_size() <<endl;//4611686018427387897(Linux环境下)
119 return 0;
120 }
- size_t capacity() const
133 int main()
134 {
135 string s("hello");
136 size_t sz = s.capacity();
137 cout << sz << endl;//5
138 return 0;
139 }
8. string中与迭代器相关的函数
1、与正向迭代器相关的函数
begin:返回一个指向字符串末尾后的字符的迭代器。
iterator end();
const_iterator end() const;
end:返回一个指向字符串末尾后的字符的迭代器。
iterator end();
const_iterator end() const;
122 int main()
123 {
124 string s("hello world");
125 string::iterator it = s.begin();
126 while(it != s.end())
127 {
128 cout << *it;
129 it++;
130 }
131 cout << endl;//hello world
132 return 0;
133 }
2、与反向迭代器相关的函数
rbegin:返回一个指向字符串最后一个字符的反向迭代器(即它的反向开头)。
reverse_iterator rbegin();
const_reverse_iterator rbegin() const;
rend:返回一个反向迭代器,指向字符串第一个字符前面的理论元素(被认为是字符串的反向结束)。
reverse_iterator rend();
const_reverse_iterator rend() const;
191 int main()
192 {
193 string s("hello world");
194
195 string::reverse_iterator rit = s.rbegin();
196 while(rit != s.rend())
197 {
198 cout << *rit;//dlrow olleh
199 rit++;
200 }
201 cout << endl;
202 return 0;
203 }
9. string中运算符的使用
- operator=
- string& operator= (const string& str)
替换当前内容为str对象- string& operator= (const char * s)
替换当前内容为s字符串- string& operator= (char c)
替换当前内容为字符char
205 int main()
206 {
207 string s1("hello");
208 string s2("world");
209
210 s1 = s2;
211 cout << s1 << endl;//world
212
213 s1 = "linux";
214 cout << s1 << endl;//linux
215
216 s1 = 'c';
217 cout << s1 << endl;//c
218 return 0;
219 }
- operator+=
- string& operator+= (const string& str)
在当前字符串末尾追加一个str对象- string& operator+= (const char * s)
在当前字符串末尾追加一个s字符串- string& operator+= (char c)
在当前字符串末尾追加一个char字符
221 int main()
222 {
223 string s("hello");
224 string s1(" world");
225
226 s += s1;
227 cout << s << endl;//hello world
228
229 s += "!!!";
230 cout << s << endl;//hello world!!!
231
232 s += '@';
233 cout << s << endl;//hello world!!!@
234 return 0;
235 }
- operator>>
- operator<<
- istream& operator>> (istream& is, string& str)
从输入流中提取一个字符串,将序列存储在str中,该序列被覆盖(str的先前值被替换)。- ostream& operator<< (ostream& os, const string& str)
将符合 str 值的字符序列插入到 ostream。
238 int main()
239 {
240 string s;
241 cin >> s;
242 cout << s << endl;
243 return 0;
244 }
10. string中插入与替换
方法1:
246 int main()
247 {
248 string s("wo lai le");
249 for(size_t i = 0; i < s.size(); i++)
250 {
251 if(s[i] == ' ')
252 {
253 s.insert(i, "20%");
254 i += 4;
255 }
256 }
257
258 for(size_t i = 0; i < s.size(); i++)
259 {
260 if(s[i] == ' ')
261 {
262 s.erase(i, 1);
263 }
264 }
265 cout << s << endl;//wo20%lai20%le
266 return 0;
267 }
方法2:
270 int main()
271 {
272 string s("wo lai le");
273
274 string news;
275
276 for(size_t i = 0; i < s.size(); i++)
277 {
278 if(s[i] == ' ')
279 {
280 news += "20%";
281 }
282 else
283 {
284 news += s[i];
285 }
286 }
287 cout << news << endl;//wo20%lai20%le
288 return 0;
289 }
10. string中子字符串的提取
- substr
- string substr (size_t pos = 0, size_t len = npos) const
返回一个新构造的字符串对象,其值初始化为此对象的子字符串的副本
291 int main()
292 {
293 string s("I am process");
294 string s1 = s.substr(2, 3);
295 cout << s1 << endl;//am
296 return 0;
297 }
- 使用copy函数
size_t copy (char * s, size_t len, size_t pos = 0) const
将字符串对象当前值的子字符串复制到s所指向的数组中。该子字符串包含从位置pos开始的len个字符
300 int main()
301 {
302 string s("I am process");
303 char ch[20];
304
305 size_t length = s.copy(ch, 2, 2);
306 ch[length] = '\0';
307
308 cout << ch << endl;//am
309 return 0;
310 }
11. string转换为字符串
- const char c_str() const*
312 int main()
313 {
314 string s("hello world");
315 const char* str = s.c_str();
316 cout << str << endl;//hello world
317 return 0;
318 }
12. string中的getline函数
我们平时使用>>操作符是,遇见空格就会停止读取。
320 int main()
321 {
322 string s;
323 cin >> s;//hello world
324 cout << s << endl;//hello
325 return 0;
326 }
此时我们使用getline函数就可以很好的解决这个问题了
- istream& getline (istream& is, string& str, char delim)
- istream& getline (istream& is, string& str)
320 int main()
321 {
322 string s;
323 getline(cin, s);
324 cout << s << endl;
325 return 0;
326 }