LeetCode-Java(05)
19. 删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点
两个方法,方法一是先走一遍链表得出链表长度,再走第二遍,找到倒数第n个数。方法二是双指针,首先快指针就比慢指针多走n步,然后这俩指针同步走,快指针走到头了,慢指针也就指向目标节点了。
方法一:
class Solution {
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0, head);
int length = getLength(head);
ListNode cur = dummy;
for (int i = 1; i < length - n + 1; ++i) {
cur = cur.next;
}
cur.next = cur.next.next;
ListNode ans = dummy.next;
return ans;
}
public int getLength(ListNode head) {
int length = 0;
while (head != null) {
++length;
head = head.next;
}
return length;
}
}方法二:
class Solution {
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0, head);
ListNode first = head;
ListNode second = dummy;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
first = first.next;
}
while (first != null) {
first = first.next;
second = second.next;
}
second.next = second.next.next;
ListNode ans = dummy.next;
return ans;
}
}
20. 有效的括号 ⭐
括号匹配,肯定用栈啊
class Solution {
public boolean isValid(String s) {
if(s.isEmpty())
return true;
Stack stack=new Stack();
for(char c:s.toCharArray()){
if(c=='(')
stack.push(')');
else if(c=='{')
stack.push('}');
else if(c=='[')
stack.push(']');
else if(stack.empty()||c!=stack.pop())
return false;
}
return stack.empty();
}
} 给定的字符串s = "{([])()}"
- 遇到'{'时,将对应的右括号'}'压入栈中。 栈内变化:}
- 遇到'('时,将对应的右括号')'压入栈中。 栈内变化:},)
- 遇到'['时,将对应的右括号']'压入栈中。 栈内变化:},),]
- 遇到']'时,检查栈顶元素是否为']',如果不是则返回false,否则将栈顶元素弹出。 栈内变化:},)
- 遇到')'时,检查栈顶元素是否为')',如果不是则返回false,否则将栈顶元素弹出。 栈内变化:}
- 遇到'('时,将对应的右括号')'压入栈中。 栈内变化:},)
- 遇到')'时,检查栈顶元素是否为')',如果不是则返回false,否则将栈顶元素弹出。 栈内变化:}
- 遇到'}'时,检查栈顶元素是否为'}',如果不是则返回false,否则将栈顶元素弹出。 栈内变化:empty
- 当遍历完所有字符后,如果栈为空,则说明括号是合法的,返回true;否则返回false
21. 合并两个有序链表
递归写法就是比较大小
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
if(list1 == null){
return list2;
}
if(list2 == null){
return list1;
}
if(list1.val <= list2.val){
list1.next = mergeTwoLists(list1.next, list2);
return list1;
}else{
list2.next = mergeTwoLists(list1, list2.next);
return list2;
}
}
}
非递归:首先判断特殊情况(为空时),定义一个newhead=初始值最小的那个,然后h1或者h2向后移位,每次比较h1和h2的大小,谁小就连谁。最后当有一个连完了,直接把另一个整个接上就行。
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode pHead1, ListNode pHead2) {
if (pHead1 == null) return pHead2;
else if (pHead2 == null) return pHead1;
else {
ListNode newhead=new ListNode(-1);
ListNode p = newhead;
while (pHead1 != null && pHead2 != null) {
if (pHead1.val < pHead2.val) {
p.next = pHead1;
p=p.next;
pHead1 = pHead1.next;
} else {
p.next = pHead2;
p=p.next;
pHead2 = pHead2.next;
}
}
if(pHead1==null) p.next=pHead2;
else p.next=pHead1;
return newhead.next;
}
}
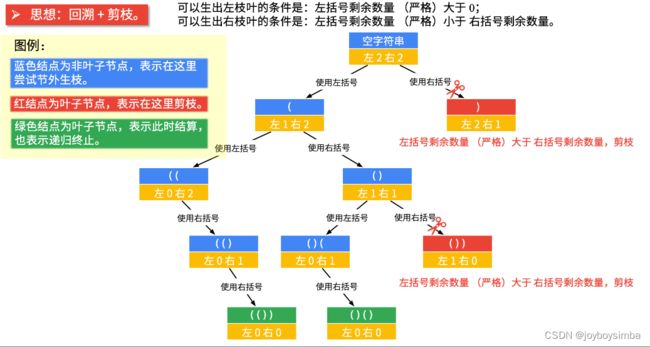
}22. 括号生成 ⭐⭐
- 当前左右括号都有大于 000 个可以使用的时候,才产生分支;
- 产生左分支的时候,只看当前是否还有左括号可以使用;
- 产生右分支的时候,还受到左分支的限制,右边剩余可以使用的括号数量一定得在严格大于左边剩余的数量的时候,才可以产生分支;
- 在左边和右边剩余的括号数都等于 000 的时候结算。
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class Solution {
// 做加法
public List generateParenthesis(int n) {
List res = new ArrayList<>();
// 特判
if (n == 0) {
return res;
}
dfs("", 0, 0, n, res);
return res;
}
/**
* @param curStr 当前递归得到的结果
* @param left 左括号已经用了几个
* @param right 右括号已经用了几个
* @param n 左括号、右括号一共得用几个
* @param res 结果集
*/
private void dfs(String curStr, int left, int right, int n, List res) {
if (left == n && right == n) {
res.add(curStr);
return;
}
// 剪枝
if (left < right) {
return;
}
if (left < n) {
dfs(curStr + "(", left + 1, right, n, res);
}
if (right < n) {
dfs(curStr + ")", left, right + 1, n, res);
}
}
} 优化一下
class Solution {
public List generateParenthesis(int n) {
List res = new ArrayList<>();
backtracking(res, new StringBuilder(), 0, 0, n);
return res;
}
public void backtracking(List res, StringBuilder cur, int open, int close, int max) {
if (cur.length() == max*2) {
res.add(cur.toString());
return;
}
if (open < max) {
cur.append('(');
backtracking(res, cur, open+1, close, max);
cur.deleteCharAt(cur.length()-1);
}
if (close < open) {
cur.append(')');
backtracking(res, cur, open, close+1, max);
cur.deleteCharAt(cur.length()-1);
}
}
}