图像 检测 - PETR: Position Embedding Transformation for Multi-View 3D Object Detection (ECCV 2022)
图像 检测 - PETR: Position Embedding Transformation for Multi-View 3D Object Detection - 用于多视图3D目标检测的位置嵌入变换(ECCV 2022)
- 摘要
- 1. 引言
- 2. 相关工作
-
- 2.1 基于transformer的目标检测
- 2.2 基于视觉的3D目标检测
- 2.3 隐式神经表示
- 3. 方法
-
- 3.1 总体架构
- References
声明:此翻译仅为个人学习记录
文章信息
- 标题:PETR: Position Embedding Transformation for Multi-View 3D Object Detection (ECCV 2022)
- 作者:Yingfei Liu*, Tiancai Wang*, Xiangyu Zhang, Jian Sun (* Equal contribution)
- 文章链接:https://arxiv.org/pdf/2203.05625.pdf
- 文章代码:https://github.com/megvii-research/PETR
摘要
在本文中,我们开发了用于多视图3D目标检测的位置嵌入变换(PETR)。PETR将3D坐标的位置信息编码为图像特征,产生3D位置感知特征。目标查询可以感知3D位置感知特征并执行端到端的目标检测。PETR在标准nuScenes数据集上实现了最先进的性能(50.4%的NDS和44.1%的mAP),并在基准测试中排名第一。它可以作为未来研究的一个简单而有力的基线。代码在https://github.com/megvii-research/PETR.
关键词:位置嵌入,transformer,3D目标检测
1. 引言
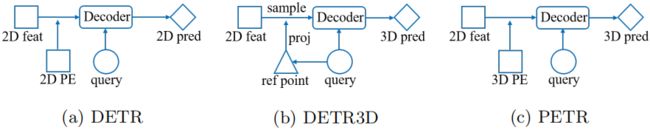
在自动驾驶系统中,基于多视角图像的3D目标检测由于其低成本而备受关注。以前的工作[6,33,49,34,48]主要从单目目标检测的角度解决了这个问题。近年来,DETR[4]因其在端到端目标检测方面的贡献而受到关注。在DETR[4]中,每个目标查询表示一个目标,并与transformer解码器中的2D特征交互以产生预测(见图1(a))。DETR3D[51]简单地从DETR[4]框架扩展而来,为端到端3D目标检测提供了直观的解决方案。通过目标查询预测的3D参考点通过相机参数投影回图像空间,并用于对所有相机视图中的2D特征进行采样(见图1(b))。解码器将采样特征和查询作为输入,并更新目标查询的表示。
然而,DETR3D[51]中的这种2D到3D转换可能会引入几个问题。首先,参考点的预测坐标可能不那么准确,使得采样的特征超出了目标区域。其次,只收集投影点的图像特征,无法从全局角度进行表示学习。此外,复杂的特征采样过程将阻碍检测器的实际应用。因此,在没有在线2D到3D转换和特征采样的情况下构建端到端的3D目标检测框架仍然是一个遗留问题。
图1. DETR、DETR3D和我们提出的PETR的比较。(a) 在DETR中,目标查询与2D特征交互以执行2D检测。(b) DETR3D将生成的3D参考点重复投影到图像平面中,并对2D特征进行采样以与解码器中的目标查询交互。(c) PETR通过将3D位置嵌入(3D PE)编码为2D图像特征来生成3D位置感知特征。目标查询直接与3D位置感知特征交互并输出3D检测结果。
在本文中,我们的目标是开发一个基于DETR[4]的用于3D目标检测的简单而优雅的框架。我们想知道是否有可能将2D特征从多视图转换为3D感知特征。通过这种方式,可以在3D环境下直接更新目标查询。我们的工作受到了内隐神经表示[17,8,32]的这些进步的启发。在MetaSR[17]和LIFF[8]中,通过将HR坐标信息编码到LR特征中,从低分辨率(LR)输入生成高分辨率(HR)RGB值。在本文中,我们试图通过对3D位置嵌入进行编码,将多视图图像的2D特征转换为3D表示(见图1(c))。
为了实现这一目标,首先将不同视图共享的相机截头体空间离散为网格坐标。然后通过不同的相机参数对坐标进行变换以获得3D世界空间的坐标。然后,从主干和3D坐标提取的2D图像特征被输入到简单的3D位置编码器以产生3D位置感知特征。3D位置感知特征将与transformer解码器中的目标查询交互,并且更新的目标查询进一步用于预测目标类和3D边界框。
与DETR3D[51]相比,所提出的PETR架构带来了许多优点。它保持了原始DETR[4]的端到端精神,同时避免了复杂的2D到3D投影和特征采样。在推断时间期间,3D位置坐标可以以离线方式生成,并用作额外的输入位置嵌入。它在实际应用中相对容易。
总之,我们的贡献是:
-
我们提出了一个简单而优雅的框架,称为PETR,用于多视图3D目标检测。通过对3D坐标进行编码,将多视图特征转换到3D域中。可以通过与3D位置感知特征交互来更新目标查询并生成3D预测。
-
引入了一种新的3D位置感知表示,用于多视图3D目标检测。引入了一个简单的隐式函数,将3D位置信息编码为二维多视图特征。
-
实验表明,PETR在标准nuScenes数据集上实现了最先进的性能(50.4%的NDS和44.1%的mAP),并在3D目标检测排行榜上排名第一。
2. 相关工作
2.1 基于transformer的目标检测
Transformer[47]是一个广泛应用于对长期依赖性建模的注意力块。在transformer中,特征通常与位置嵌入一起添加,位置嵌入提供图像[13,53,27]、序列[15,47,11,10,54]和视频[1,24,52]的位置信息。Transformer XL[10]使用相对位置嵌入来对成对令牌的相对距离进行编码。ViT[13]将学习的位置嵌入添加到对不同块的距离进行编码的块表示中。MViT[24]分解相对位置嵌入的距离计算,并对时空结构进行建模。
最近,DETR[4]将transformer引入到用于端到端检测的2D目标检测任务中。在DETR[4]中,每个目标被表示为目标查询,该目标查询通过transformer解码器与2D图像特征交互。然而,DETR[4]的收敛速度较慢。[44]将缓慢收敛归因于交叉注意力机制,并设计了仅编码器的DETR。此外,许多工作通过添加位置先验来加速收敛。SMAC[14]预测2D类高斯权重图作为每个查询的空间先验。可变形DETR[58]将目标查询与2D参考点相关联,并提出可变形交叉注意力以执行稀疏交互。[50,30,26]从锚点或使用位置先验的锚点生成目标查询,以实现快速收敛。SOLQ[12]从DETR[58]扩展而来,使用目标查询同时执行分类、框回归和实例分割。
2.2 基于视觉的3D目标检测
基于视觉的3D目标检测是从摄像机图像中检测3D边界框。许多以前的工作[6,33,20,21,41,19,2,49,48]在图像视图中执行3D目标检测。M3D-RPN[2]引入了深度感知卷积,该卷积学习用于3D目标检测的位置感知特征。FCOS3D[49]将3D真值转换为图像视图,并扩展FCOS[46]以预测3D长方体参数。PGD[48]遵循FCOS3D[49],并使用概率表示来捕捉深度的不确定性。它极大地缓解了深度估计问题,同时引入了更多的计算预算和更大的推理延迟。DD3D[34]表明,在大规模深度数据集上进行深度预训练可以显著提高3D目标检测的性能。
最近,一些工作试图在3D世界空间中进行3D目标检测。OFT[39]和CaDDN[38]将单目图像特征映射到鸟瞰图(BEV)中,并检测BEV空间中的3D目标。ImVoxelNet[40]在3D世界空间中构建3D体积,并对多视图特征进行采样以获得体素表示。然后使用3D卷积和特定领域的头部来检测室内和室外场景中的目标。与CaDDN[38]类似,BEVDet[18]采用Lift Splat Shoot[37]将2D多视图特征转换为BEV表示。对于BEV表示,CenterPoint[55]头用于以直观的方式检测3D目标。在DETR[4]之后,DETR3D[51]将3D目标表示为目标查询。从目标查询生成的3D参照点会重复投影回所有摄影机视图,并对二维特征进行采样。
基于BEV的方法往往会引入Z轴误差,导致其他3D感知任务(例如,3D车道检测)的性能较差。基于DETR的方法可以从具有更多训练增强的端到端建模中获得更多好处。我们的方法是基于DETR的,以简单有效的方式检测3D目标。我们将3D位置信息编码为2D特征,产生3D位置感知特征。目标查询可以在没有投影误差的情况下直接与这种3D位置感知表示交互。
2.3 隐式神经表示
隐式神经表示(INR)通常通过多层感知器(MLP)将坐标映射到视觉信号。这是一种对3D目标[35,9,31]、3D场景[32,43,36]和2D图像[17,8,45,42]进行建模的高效方法。NeRF[32]采用完全连接的网络来表示特定场景。为了合成新的视图,沿着相机光线的5D坐标被输入到网络作为查询,并输出体积密度和与视图相关的发射辐射。在MetaSR[17]和LIFF[8]中,HR坐标被编码到LR特征中,并且可以生成任意大小的HR图像。我们的方法可以看作是INR在3D目标检测中的扩展。用3D坐标对2D图像进行编码以获得3D位置感知特征。3D空间中的锚点由MLP转换为目标查询,并且进一步与3D位置感知特征交互以预测对应的3D目标。
3. 方法
3.1 总体架构
图2显示了拟议的PETR的总体架构。
图2. 所提出的PETR范式的架构。多视图图像被输入到骨干网络(例如ResNet)以提取多视图2D图像特征。在3D坐标生成器中,将所有视图共享的相机截头体空间离散为3D网格。网格坐标通过不同的相机参数进行变换,得到3D世界空间中的坐标。然后将2D图像特征和3D坐标注入到所提出的3D位置编码器以生成3D位置感知特征。由查询生成器生成的目标查询通过与transformer解码器中的3D位置感知特征的交互进行更新。更新后的查询进一步用于预测3D边界框和目标类。
References
- Bertasius, G., Wang, H., Torresani, L.: Is space-time attention all you need for video understanding. arXiv preprint arXiv:2102.05095 2(3), 4 (2021) 3
- Brazil, G., Liu, X.: M3d-rpn: Monocular 3d region proposal network for object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. pp. 9287–9296 (2019) 3
- Caesar, H., Bankiti, V., Lang, A.H., Vora, S., Liong, V.E., Xu, Q., Krishnan, A., Pan, Y., Baldan, G., Beijbom, O.: nuscenes: A multimodal dataset for autonomous driving. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. pp. 11621–11631 (2020) 8
- Carion, N., Massa, F., Synnaeve, G., Usunier, N., Kirillov, A., Zagoruyko, S.: End-to-end object detection with transformers. In: European conference on computer vision. pp. 213–229. Springer (2020) 1, 2, 3, 4, 7
- Chabra, R., Lenssen, J.E., Ilg, E., Schmidt, T., Straub, J., Lovegrove, S., Newcombe, R.: Deep local shapes: Learning local sdf priors for detailed 3d reconstruction. In: European Conference on Computer Vision. pp. 608–625. Springer (2020) 4
- Chen, X., Kundu, K., Zhang, Z., Ma, H., Fidler, S., Urtasun, R.: Monocular 3d object detection for autonomous driving. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. pp. 2147–2156 (2016) 1, 3
- Chen, Y., Liu, S., Shen, X., Jia, J.: Dsgn: Deep stereo geometry network for 3d object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. pp. 12536–12545 (2020) 5
- Chen, Y., Liu, S., Wang, X.: Learning continuous image representation with local implicit image function. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. pp. 8628–8638 (2021) 2, 4
- Chen, Z., Zhang, H.: Learning implicit fields for generative shape modeling. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. pp. 5939–5948 (2019) 4
- Dai, Z., Yang, Z., Yang, Y., Carbonell, J., Le, Q.V., Salakhutdinov, R.: Transformer-xl: Attentive language models beyond a fixed-length context. arXiv preprint arXiv:1901.02860 (2019) 3
- Devlin, J., Chang, M.W., Lee, K., Toutanova, K.: Bert: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. arXiv preprint arXiv:1810.04805 (2018) 3
- Dong, B., Zeng, F., Wang, T., Zhang, X., Wei, Y.: Solq: Segmenting objects by learning queries. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 34 (2021) 3
- Dosovitskiy, A., Beyer, L., Kolesnikov, A., Weissenborn, D., Zhai, X., Unterthiner, T., Dehghani, M., Minderer, M., Heigold, G., Gelly, S., et al.: An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv preprint arXiv:2010.11929 (2020) 3
- Gao, P., Zheng, M., Wang, X., Dai, J., Li, H.: Fast convergence of detr with spatially modulated co-attention. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. pp. 3621–3630 (2021) 3
- Gehring, J., Auli, M., Grangier, D., Yarats, D., Dauphin, Y.N.: Convolutional sequence to sequence learning. In: International Conference on Machine Learning. pp. 1243–1252. PMLR (2017) 3
- He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. pp. 770–778 (2016) 4, 8, 9
- Hu, X., Mu, H., Zhang, X., Wang, Z., Tan, T., Sun, J.: Meta-sr: A magnification-arbitrary network for super-resolution. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. pp. 1575–1584 (2019) 2, 4, 6
- Huang, J., Huang, G., Zhu, Z., Du, D.: Bevdet: High-performance multi-camera 3d object detection in bird-eye-view. arXiv preprint arXiv:2112.11790 (2021) 4, 9, 10
- J¨orgensen, E., Zach, C., Kahl, F.: Monocular 3d object detection and box fitting trained end-to-end using intersection-over-union loss. arXiv preprint arXiv:1906.08070 (2019) 3
- Kehl, W., Manhardt, F., Tombari, F., Ilic, S., Navab, N.: Ssd-6d: Making rgb-based 3d detection and 6d pose estimation great again. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision. pp. 1521–1529 (2017) 3
- Ku, J., Pon, A.D., Waslander, S.L.: Monocular 3d object detection leveraging accurate proposals and shape reconstruction. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. pp. 11867–11876 (2019) 3
- Kuhn, H.W.: The hungarian method for the assignment problem. Naval research logistics quarterly 2(1-2), 83–97 (1955) 8
- Lee, Y., Park, J.: Centermask: Real-time anchor-free instance segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. pp. 13906–13915 (2020) 8, 9
- Li, Y., Wu, C.Y., Fan, H., Mangalam, K., Xiong, B., Malik, J., Feichtenhofer, C.: Improved multiscale vision transformers for classification and detection. arXiv preprint arXiv:2112.01526 (2021) 3
- Lin, T.Y., Goyal, P., Girshick, R., He, K., Doll´ar, P.: Focal loss for dense object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision. pp. 2980–2988 (2017) 8
- Liu, S., Li, F., Zhang, H., Yang, X., Qi, X., Su, H., Zhu, J., Zhang, L.: Dab-detr: Dynamic anchor boxes are better queries for detr. arXiv preprint arXiv:2201.12329 (2022) 3
- Liu, Z., Lin, Y., Cao, Y., Hu, H., Wei, Y., Zhang, Z., Lin, S., Guo, B.: Swin transformer: Hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. pp. 10012–10022 (2021) 3, 8
- Loshchilov, I., Hutter, F.: Sgdr: Stochastic gradient descent with warm restarts. arXiv preprint arXiv:1608.03983 (2016) 8
- Loshchilov, I., Hutter, F.: Decoupled weight decay regularization. arXiv preprint arXiv:1711.05101 (2017) 8
- Meng, D., Chen, X., Fan, Z., Zeng, G., Li, H., Yuan, Y., Sun, L., Wang, J.: Conditional detr for fast training convergence. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. pp. 3651–3660 (2021) 3
- Mescheder, L., Oechsle, M., Niemeyer, M., Nowozin, S., Geiger, A.: Occupancy networks: Learning 3d reconstruction in function space. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. pp. 4460–4470 (2019) 4
- Mildenhall, B., Srinivasan, P.P., Tancik, M., Barron, J.T., Ramamoorthi, R., Ng, R.: Nerf: Representing scenes as neural radiance fields for view synthesis. In: European conference on computer vision. pp. 405–421. Springer (2020) 2, 4
- Mousavian, A., Anguelov, D., Flynn, J., Kosecka, J.: 3d bounding box estimation using deep learning and geometry. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. pp. 7074–7082 (2017) 1, 3
- Park, D., Ambrus, R., Guizilini, V., Li, J., Gaidon, A.: Is pseudo-lidar needed for monocular 3d object detection? In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. pp. 3142–3152 (2021) 1, 3
- Park, J.J., Florence, P., Straub, J., Newcombe, R., Lovegrove, S.: Deepsdf: Learning continuous signed distance functions for shape representation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. pp. 165–174 (2019) 4
- Peng, S., Niemeyer, M., Mescheder, L., Pollefeys, M., Geiger, A.: Convolutional occupancy networks. In: European Conference on Computer Vision. pp. 523–540. Springer (2020) 4
- Philion, J., Fidler, S.: Lift, splat, shoot: Encoding images from arbitrary camera rigs by implicitly unprojecting to 3d. In: European Conference on Computer Vision. pp. 194–210. Springer (2020) 4
- Reading, C., Harakeh, A., Chae, J., Waslander, S.L.: Categorical depth distribution network for monocular 3d object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. pp. 8555–8564 (2021) 3, 4, 8
- Roddick, T., Kendall, A., Cipolla, R.: Orthographic feature transform for monocular 3d object detection. arXiv preprint arXiv:1811.08188 (2018) 3
- Rukhovich, D., Vorontsova, A., Konushin, A.: Imvoxelnet: Image to voxels projection for monocular and multi-view general-purpose 3d object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision. pp. 2397–2406 (2022) 3
- Simonelli, A., Bulo, S.R., Porzi, L., L´opez-Antequera, M., Kontschieder, P.: Disentangling monocular 3d object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. pp. 1991–1999 (2019) 3
- Sitzmann, V., Martel, J., Bergman, A., Lindell, D., Wetzstein, G.: Implicit neural representations with periodic activation functions. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 33, 7462–7473 (2020) 4
- Sitzmann, V., Zollh¨ofer, M., Wetzstein, G.: Scene representation networks: Continuous 3d-structure-aware neural scene representations. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 32 (2019) 4
- Sun, Z., Cao, S., Yang, Y., Kitani, K.M.: Rethinking transformer-based set prediction for object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. pp. 3611–3620 (2021) 3
- Tancik, M., Srinivasan, P., Mildenhall, B., Fridovich-Keil, S., Raghavan, N., Singhal, U., Ramamoorthi, R., Barron, J., Ng, R.: Fourier features let networks learn high frequency functions in low dimensional domains. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 33, 7537–7547 (2020) 4
- Tian, Z., Shen, C., Chen, H., He, T.: Fcos: Fully convolutional one-stage object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision. pp. 9627–9636 (2019) 3
- Vaswani, A., Shazeer, N., Parmar, N., Uszkoreit, J., Jones, L., Gomez, A.N., Kaiser, L., Polosukhin, I.: Attention is all you need. Advances in neural information processing systems 30 (2017) 3
- Wang, T., Xinge, Z., Pang, J., Lin, D.: Probabilistic and geometric depth: Detecting objects in perspective. In: Conference on Robot Learning. pp. 1475–1485. PMLR (2022) 1, 3, 9
- Wang, T., Zhu, X., Pang, J., Lin, D.: Fcos3d: Fully convolutional one-stage monocular 3d object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. pp. 913–922 (2021) 1, 3, 9
- Wang, Y., Zhang, X., Yang, T., Sun, J.: Anchor detr: Query design for transformer-based detector. arXiv preprint arXiv:2109.07107 (2021) 3, 7
- Wang, Y., Vitor Campagnolo, G., Zhang, T., Zhao, H., Solomon, J.: Detr3d: 3d object detection from multi-view images via 3d-to-2d queries. In: In Conference on Robot Learning. pp. 180–191 (2022) 1, 2, 4, 7, 8, 9, 10
- Wu, C.Y., Li, Y., Mangalam, K., Fan, H., Xiong, B., Malik, J., Feichtenhofer, C.: Memvit: Memory-augmented multiscale vision transformer for efficient long-term video recognition. arXiv preprint arXiv:2201.08383 (2022) 3
- Wu, K., Peng, H., Chen, M., Fu, J., Chao, H.: Rethinking and improving relative position encoding for vision transformer. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. pp. 10033–10041 (2021) 3
- Yang, Z., Dai, Z., Yang, Y., Carbonell, J., Salakhutdinov, R.R., Le, Q.V.: Xlnet: Generalized autoregressive pretraining for language understanding. Advances in neural information processing systems 32 (2019) 3
- Yin, T., Zhou, X., Krahenbuhl, P.: Center-based 3d object detection and tracking. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. pp. 11784–11793 (2021) 4, 8
- Zhou, X., Wang, D., Kr¨ahenb¨uhl, P.: Objects as points. arXiv preprint arXiv:1904.07850 (2019) 9
- Zhu, B., Jiang, Z., Zhou, X., Li, Z., Yu, G.: Class-balanced grouping and sampling for point cloud 3d object detection. arXiv preprint arXiv:1908.09492 (2019) 9, 11
- Zhu, X., Su, W., Lu, L., Li, B., Wang, X., Dai, J.: Deformable detr: Deformable transformers for end-to-end object detection. arXiv preprint arXiv:2010.04159 (2020) 3, 7