Android 串口开发(二) 支持设置奇偶校验、数据位、停止位
谷歌官网提供的串口库的奇偶校验位数据位停止位都是默认的,如果有项目需要配置固定的参数的时候,很显然谷歌官网提供的是不可行的,但是是可参考的谷歌开源串口库,下面这边文章也仅仅是作为自己的一个踩过的坑的记录,本篇文章主要参考了一位简书上的大哥的文章,Android 串口通信
在上一篇已经讲解了谷歌开源的串口库的一些东西,所以在这篇里面就不过多口舌了
项目结构
看过我上篇文章的笔友会发现其实和上篇的东西大差不差,项目结构以及类的划分基本一致,主要改动还是java向jni文件里传值多了三个参数,这个native方法就是用来和jni里面的C通信的,比谷歌提供的又新增了三个参数
/**
* 打开串口
*
* @param device 串口设备文件
* @param baudRate 波特率
* @param parity 奇偶校验,0 None(默认); 1 Odd; 2 Even
* @param dataBits 数据位,5 ~ 8 (默认8)
* @param stopBit 停止位,1 或 2 (默认 1)
* @param flags 标记 0(默认)
* @throws SecurityException
* @throws IOException
*/
private native static FileDescriptor open(String path, int baudRate, int parity, int dataBits,
int stopBit, int flags);同样修改后发现居然运行不起来,百度上找了一大堆文章都没能解决问题,想起来之前一位同事说简书要比csdn上的可靠,所以一大早来到公司就上简书搜索,果然不出所料,才看了两篇就找到想要的答案了,就是上面参考的那位大哥的文章,文章不繁琐,结构清晰,做过硬件开发的Android或者玩过串口的朋友一看就知道怎么回事,好了废话不多说,在这里还有两个文件没有贴出来,下面贴一下serial-port.cpp代码
//
// Created by Administrator on 2019\1\29 0029.
//
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include "android/log.h"
static const char *TAG="serial_port";
#define LOGI(fmt, args...) __android_log_print(ANDROID_LOG_INFO, TAG, fmt, ##args)
#define LOGD(fmt, args...) __android_log_print(ANDROID_LOG_DEBUG, TAG, fmt, ##args)
#define LOGE(fmt, args...) __android_log_print(ANDROID_LOG_ERROR, TAG, fmt, ##args)
static speed_t getBaudrate(jint baudrate)
{
switch(baudrate) {
case 0: return B0;
case 50: return B50;
case 75: return B75;
case 110: return B110;
case 134: return B134;
case 150: return B150;
case 200: return B200;
case 300: return B300;
case 600: return B600;
case 1200: return B1200;
case 1800: return B1800;
case 2400: return B2400;
case 4800: return B4800;
case 9600: return B9600;
case 19200: return B19200;
case 38400: return B38400;
case 57600: return B57600;
case 115200: return B115200;
case 230400: return B230400;
case 460800: return B460800;
case 500000: return B500000;
case 576000: return B576000;
case 921600: return B921600;
case 1000000: return B1000000;
case 1152000: return B1152000;
case 1500000: return B1500000;
case 2000000: return B2000000;
case 2500000: return B2500000;
case 3000000: return B3000000;
case 3500000: return B3500000;
case 4000000: return B4000000;
default: return -1;
}
}
static void throwException(JNIEnv *env, const char *name, const char *msg)
{
jclass cls = env->FindClass(name);
/* if cls is NULL, an exception has already been thrown */
if (cls != NULL) {
env->ThrowNew(cls, msg);
}
/* free the local ref */
env->DeleteLocalRef(cls);
}
extern "C"
JNIEXPORT jobject JNICALL
Java_com_deemons_serialportlib_SerialPort_open
(JNIEnv *env, jobject instance, jstring path, jint baudrate,jint parity, jint dataBits, jint stopBit, jint flags)
{
int fd;
speed_t speed;
jobject mFileDescriptor;
/* Check arguments */
{
speed = getBaudrate(baudrate);
if (speed == -1) {
throwException(env, "java/lang/IllegalArgumentException", "Invalid baudrate");
return NULL;
}
if (parity <0 || parity>2) {
throwException(env, "java/lang/IllegalArgumentException", "Invalid parity");
return NULL;
}
if (dataBits <5 || dataBits>8) {
throwException(env, "java/lang/IllegalArgumentException", "Invalid dataBits");
return NULL;
}
if (stopBit <1 || stopBit>2) {
throwException(env, "java/lang/IllegalArgumentException", "Invalid stopBit");
return NULL;
}
}
/* Opening device */
{
jboolean iscopy;
const char *path_utf = env->GetStringUTFChars(path, &iscopy);
LOGD("Opening serial port %s with flags 0x%x", path_utf, O_RDWR | flags);
fd = open(path_utf, O_RDWR | flags);
LOGD("open() fd = %d", fd);
env->ReleaseStringUTFChars(path, path_utf);
if (fd == -1)
{
throwException(env, "java/io/IOException", "Cannot open port");
return NULL;
}
}
/* Configure device */
{
struct termios cfg;
LOGD("Configuring serial port");
if (tcgetattr(fd, &cfg))
{
LOGE("tcgetattr() failed");
close(fd);
throwException(env, "java/io/IOException", "tcgetattr() failed");
return NULL;
}
cfmakeraw(&cfg);
cfsetispeed(&cfg, speed);
cfsetospeed(&cfg, speed);
/* More attribute set */
switch (parity) {
case 0: break;
case 1: cfg.c_cflag |= PARENB; break;
case 2: cfg.c_cflag &= ~PARODD; break;
}
switch (dataBits) {
case 5: cfg.c_cflag |= CS5; break;
case 6: cfg.c_cflag |= CS6; break;
case 7: cfg.c_cflag |= CS7; break;
case 8: cfg.c_cflag |= CS8; break;
}
switch (stopBit) {
case 1: cfg.c_cflag &= ~CSTOPB; break;
case 2: cfg.c_cflag |= CSTOPB; break;
}
if (tcsetattr(fd, TCSANOW, &cfg))
{
LOGE("tcsetattr() failed");
close(fd);
/* TODO: throw an exception */
return NULL;
}
}
/* Create a corresponding file descriptor */
{
jclass cFileDescriptor = env->FindClass("java/io/FileDescriptor");
jmethodID iFileDescriptor = env->GetMethodID(cFileDescriptor, "", "()V");
jfieldID descriptorID = env->GetFieldID(cFileDescriptor, "descriptor", "I");
mFileDescriptor = env->NewObject(cFileDescriptor, iFileDescriptor);
env->SetIntField(mFileDescriptor, descriptorID, (jint)fd);
}
return mFileDescriptor;
}
/*
* Class: cedric_serial_SerialPort
* Method: close
* Signature: ()V
*/
JNIEXPORT void JNICALL Java_com_deemons_serialportlib_SerialPort_close
(JNIEnv *env, jobject thiz)
{
jclass SerialPortClass = env->GetObjectClass( thiz);
jclass FileDescriptorClass = env->FindClass( "java/io/FileDescriptor");
jfieldID mFdID = env->GetFieldID(SerialPortClass, "mFd", "Ljava/io/FileDescriptor;");
jfieldID descriptorID = env->GetFieldID(FileDescriptorClass, "descriptor", "I");
jobject mFd = env->GetObjectField(thiz, mFdID);
jint descriptor = env->GetIntField(mFd, descriptorID);
LOGD("close(fd = %d)", descriptor);
close(descriptor);
} 完了以后呢,还有一个CMakeLists.txt文件需要配置一下,具体有什么用呢,我也不太清楚,也是第一次看这样配置
# For more information about using CMake with Android Studio, read the
# documentation: https://d.android.com/studio/projects/add-native-code.html
# Sets the minimum version of CMake required to build the native library.
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.4.1)
# Creates and names a library, sets it as either STATIC
# or SHARED, and provides the relative paths to its source code.
# You can define multiple libraries, and CMake builds them for you.
# Gradle automatically packages shared libraries with your APK.
add_library( # Sets the name of the library.
serial-port
# Sets the library as a shared library.
SHARED
# Provides a relative path to your source file(s).
src/main/cpp/serial-port.cpp
)
# Searches for a specified prebuilt library and stores the path as a
# variable. Because CMake includes system libraries in the search path by
# default, you only need to specify the name of the public NDK library
# you want to add. CMake verifies that the library exists before
# completing its build.
find_library( # Sets the name of the path variable.
log-lib
# Specifies the name of the NDK library that
# you want CMake to locate.
log )
# Specifies libraries CMake should link to your target library. You
# can link multiple libraries, such as libraries you define in this
# build script, prebuilt third-party libraries, or system libraries.
target_link_libraries( # Specifies the target library.
serial-port
# Links the target library to the log library
# included in the NDK.
${log-lib} )
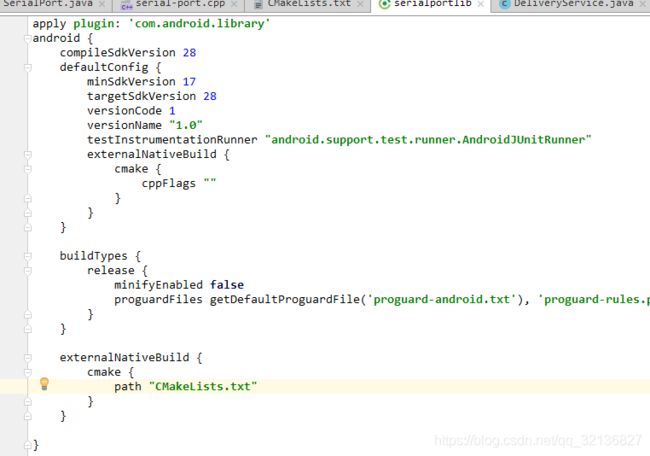
最后在build.gradle里面再添加一下配置
致辞结束,还是非常感谢这位仁兄,帮助我解决了一大难题
上一篇 Android 串口开发(一) 串口读写操作