用node.js搭建一个视频推流服务
由于业务中有不少视频使用的场景,今天来说说如何使用node完成一个视频推流服务。
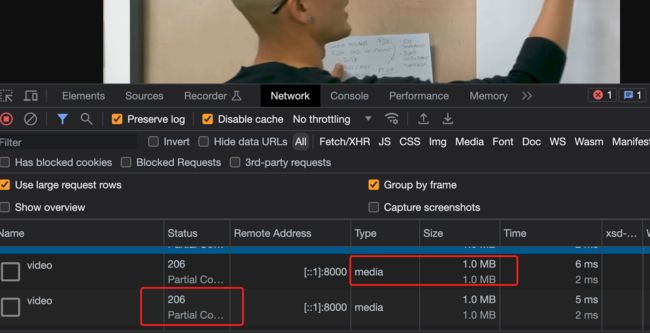
先看看效果:
这里的播放的视频是一个多个Partial Content组合起来的,每个Partial Content大小是1M。
一,项目搭建
(1)初始化项目,创建package.json
npm init
(2)安装express和nodemon
npm install --save express nodemon
(3)创建html文件
Video Streaming With Node
(4)创建index.js作为video接口服务
二,编写video接口
最终实现的效果如刚开始的实例,在浏览器中打开视频,会请求/video,该接口返回media类型的数据流片段。
首先引入express和fs。前者提供服务,后者操作文件系统,将视频文件序列化成流pipe出去。下面看看代码实现
const express = require("express");
const app = express();
const fs = require("fs");
app.get("/", function (req, res) {
res.sendFile(__dirname + "/index.html");
});
// more code will go in here just befor the listening function
app.listen(8000, function () {
console.log("Listening on port 8000!");
});
创建服务,serve Index.html文件。
app.get("/video", function (req, res) {
const range = req.headers.range;
if (!range) {
res.status(400).send("Requires Range header");
}
});保证request的header里面有range,没有range就无法判断需要把那一部分content写入response。
const videoPath = "Chris-Do.mp4";
const videoSize = fs.statSync("Chris-Do.mp4").size;还需要资源的路径和资源的大小,资源的大小会用来计算那一部分content要被send。这里简单放在相对index.js的位置。
const CHUNK_SIZE = 10 ** 6; // 1MB
const start = Number(range.replace(/\D/g, ""));这里规定每次返回1M的内容,开始位置从request的header里获取并将其转成Number类型。
const end = Math.min(start + CHUNK_SIZE, videoSize - 1);计算结束位置,这里取开始位置加上1M数据和结束位置两者之间的最小值。
三、创建Response headers。
在响应头里面我们需要返回Content的大小,Content-range,Accept-ranges,Content-type。
const headers = {
"Content-Range": `bytes ${start}-${end}/${videoSize}`,
"Accept-Ranges": "bytes",
"Content-Length": contentLength,
"Content-Type": "video/mp4",
};状态码设置为206表明我们返回的部分内容。
// HTTP Status 206 for Partial Content
res.writeHead(206, headers);四、创建Stream并返回。
这里需要使用fs来创建一个videoSteam,使用videoPath和start和end作为参数。这里只需要把videoStream pipe到response即可。
// create video read stream for this particular chunk
const videoStream = fs.createReadStream(videoPath, { start, end });
// Stream the video chunk to the client
videoStream.pipe(res);启动服务,看到视频被正常推流。好了,这里一个简易的视频推流服务就写好了。
-- End --