【Elasticsearch】Elasticsearch快速入门,掌握这些刚刚好!(官网入门案例)
文章目录
- 1. 简介
- 2. 相关概念
- 3. 安装
- 4. 集群状态查看
- 5. 索引操作
- 6. 文档操作
- 7. 数据搜索
-
- 数据准备
- 搜索入门(match_all)
- 条件搜索(match)
- 组合搜索(bool)
- 过滤搜索(filter)
- 搜索聚合(aggs)
- 8. 参考资料
本文的主要功能是带领从0到1入门Elasticsearch的基础使用,重点是Elasticsearch中的"数据搜索",即
_search
1. 简介
Elasticsearch是一个近乎实时的搜索平台。它提供了一个分布式的全文搜索引擎,提供了REST API接口与用户交互。Elasticsearch是用Java语言开发的,基于Apache协议的开源项目,是目前最受欢迎的企业搜索引擎。Elasticsearch广泛运用于云计算中,能够达到实时搜索,具有稳定,可靠,快速的特点。
如何与Elasticsearch交流,Elasticsearch提供了一个非常全面和强大的REST API,您可以使用它
- Check your cluster, node, and index health, status, and statistics
- Administer your cluster, node, and index data and metadata
- Perform CRUD (Create, Read, Update, and Delete) and search operations against your indexes
- Execute advanced search operations such as paging, sorting, filtering, scripting, aggregations, and many others
2. 相关概念
官网说明了以下概念。
- Near Realtime(近实时):Elasticsearch是一个近乎实时的搜索平台,这意味着从索引文档到可搜索文档之间只有一个轻微的延迟(通常是一秒钟)。
- Cluster(集群):群集是一个或多个节点的集合,它们一起保存整个数据,并提供跨所有节点的联合索引和搜索功能。每个群集都有自己的唯一群集名称,节点通过名称加入群集。
- Node(节点):节点是指属于集群的单个Elasticsearch实例,存储数据并参与集群的索引和搜索功能。
- Index(索引):Index相当于**“某类数据”**。索引是一些具有相似特征的文档集合。
- Document(文档):Document相当于Index中的**“某条数据”**。文档是可被索引的基本信息单位,以JSON形式表示
- Shards(分片):分片概念类似Kafka中的分区。分片机制赋予了索引水平扩容的能力,提高性能和吞吐量。
- Replicas(副本):副本在某些节点失效的情况下提供高可用性。
3. 安装
注:
尽管作者前面写过Docker安装Elasticsearch、Kibana的文章,但是后期分析Docker方式体验很差,这里并不适用Docker安装,没有给我们带来方便,所以这里不推荐Docker安装方式而是使用安装包方式。
Elasticsearch和Kibana的版本要求保持一致。
Elasticsearch是近乎实时的搜索平台,提供了REST API接口与用户交互,所以后面的案例本可以只安装Elasticsearch就够了。但是为了方便起见,我们选择多安装一个Elasticsearch的可视化平台Kibana来操作后面的案例。以Elasticsearch6.6.2为例:
- Elasticsearch下载安装
curl -L -O https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/elasticsearch/elasticsearch-6.6.2.tar.gz
tar -xvf elasticsearch-6.6.2.tar.gz
cd elasticsearch-6.6.2
./bin/elasticsearch
- 浏览器访问http://localhost:9200检查Elasticsearch是否安装成功
- Kibana下载安装
curl -O https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/kibana/kibana-6.6.2-darwin-x86_64.tar.gz
tar -xzf kibana-6.6.2-darwin-x86_64.tar.gz
cd kibana-6.6.2-darwin-x86_64/
./bin/kibana
- 浏览器访问http://localhost:5601检查Kibana是否安装成功
能正常点击左侧菜单就没有问题,zipkin是我测试zipkin时的索引,可忽略
- 使用Kibana的可视化平台操作界面,后续案例的操作都在这里进行
4. 集群状态查看
- 查看集群健康状态;
GET /_cat/health?v
- 查看节点状态;
GET /_cat/nodes?v
- 查看所有索引信息;
GET /_cat/indices?v
5. 索引操作
- 创建索引并查看;
PUT /customer
GET /_cat/indices?v
- 删除索引并查看;
DELETE /customer
GET /_cat/indices?v
6. 文档操作
- 在索引中添加文档;
PUT /customer/_doc/1
{
"name": "John Doe"
}
- 查看索引中的文档;
GET /customer/_doc/1
- 替换索引中的文档
PUT /customer/_doc/1?pretty
{
"name": "John Doe"
}
- 修改索引中的文档:
POST /customer/_doc/1/_update?pretty
{
"doc": { "name": "Jane Doe" }
}
POST /customer/_doc/1/_update?pretty
{
"doc": { "name": "Jane Doe", "age": 20 }
}
POST /customer/_doc/1/_update?pretty
{
"script" : "ctx._source.age += 5"
}
修改跟替换是不同的
- 删除索引中的文档;
DELETE /customer/doc/1
- 对索引中的文档执行批量操作
POST /customer/doc/_bulk
{"index":{"_id":"1"}}
{"name": "John Doe" }
{"index":{"_id":"2"}}
{"name": "Jane Doe" }
7. 数据搜索
查询表达式(Query DSL)是一种非常灵活又富有表现力的查询语言,Elasticsearch使用它可以以简单的JSON接口来实现丰富的搜索功能,下面的搜索操作都将使用它。
数据搜索才是Elasticsearch的重点内容。
数据准备
- 首先我们需要导入一定量的数据用于搜索,使用的是银行账户表的例子,数据结构schema如下:
{
"account_number": 0,
"balance": 16623,
"firstname": "Bradshaw",
"lastname": "Mckenzie",
"age": 29,
"gender": "F",
"address": "244 Columbus Place",
"employer": "Euron",
"email": "[email protected]",
"city": "Hobucken",
"state": "CO"
}
- 下载官方准备好的数据数据,数据地址:https://github.com/elastic/elasticsearch/blob/6.6/docs/src/test/resources/accounts.json。备用地址:https://gitee.com/firefish985/article-list/blob/master/%E5%A4%A7%E6%95%B0%E6%8D%AE/Elasticsearch/accounts.json
- 导入数据到Elasticsearch
可以在当前目录用命令导入
curl -H "Content-Type: application/json" -XPOST "localhost:9200/bank/_doc/_bulk?pretty&refresh" --data-binary "@accounts.json"
也可以在Kibana的Dev Tools中批量导入。
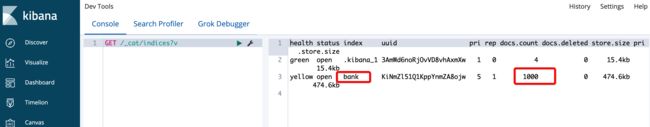
- 导入完成后查看索引信息,可以发现
bank索引中已经创建了1000条文档
GET /_cat/indices?v
搜索入门(match_all)
- 最简单的搜索,使用
match_all来表示,例如搜索全部;
GET /bank/_search
{
"query": { "match_all": {} }
}
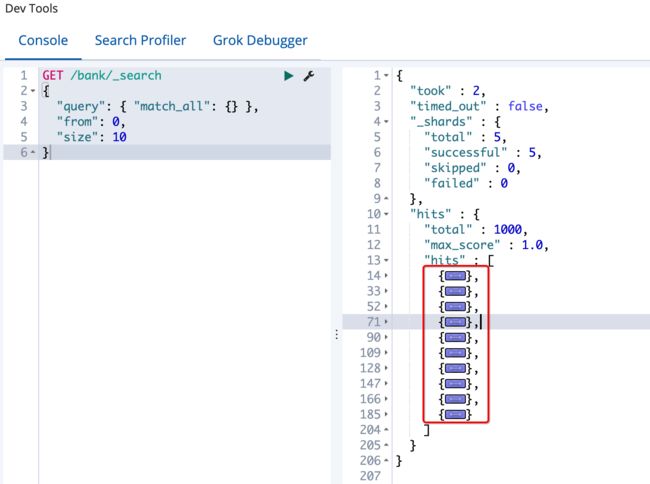
- 分页搜索,
from表示偏移量,从0开始,size表示每页显示的数量;
GET /bank/_search
{
"query": { "match_all": {} },
"from": 0,
"size": 10
}
- 搜索排序,使用
sort表示,例如按balance字段降序排列;
GET /bank/_search
{
"query": { "match_all": {} },
"sort": { "balance": { "order": "desc" } }
}
- 搜索并返回指定字段内容,使用
_source表示,例如只返回account_number和balance两个字段内容:
GET /bank/_search
{
"query": { "match_all": {} },
"_source": ["account_number", "balance"]
}
条件搜索(match)
- 条件搜索,使用
match表示匹配条件,例如搜索出account_number为20的文档:
GET /bank/_search
{
"query": { "match": { "account_number": 20 } }
}
- 文本类型字段的条件搜索,例如搜索
address字段中包含mill的文档,对比上一条搜索可以发现,对于数值类型match操作使用的是精确匹配,对于文本类型使用的是模糊匹配;
GET /bank/_search
{
"query": { "match": { "address": "mill" } },
"_source": ["address", "account_number"]
}
- 短语匹配搜索,使用
match_phrase表示,例如搜索address字段中包含mill lane的文档
GET /bank/_search
{
"query": { "match_phrase": { "address": "mill lane" } }
}
组合搜索(bool)
- 组合搜索,使用
bool来进行组合,must表示同时满足,例如搜索address字段中同时包含mill和lane的文档;
GET /bank/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{ "match": { "address": "mill" } },
{ "match": { "address": "lane" } }
]
}
}
}
- 组合搜索,
should表示满足其中任意一个,搜索address字段中包含mill或者lane的文档;
GET /bank/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"should": [
{ "match": { "address": "mill" } },
{ "match": { "address": "lane" } }
]
}
}
}
- 组合搜索,
must_not表示同时不满足,例如搜索address字段中不包含mill且不包含lane的文档;
GET /bank/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must_not": [
{ "match": { "address": "mill" } },
{ "match": { "address": "lane" } }
]
}
}
}
- 组合搜索,组合
must和must_not,例如搜索age字段等于40且state字段不包含ID的文档;
GET /bank/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{ "match": { "age": "40" } }
],
"must_not": [
{ "match": { "state": "ID" } }
]
}
}
}
过滤搜索(filter)
- 搜索过滤,使用
filter来表示,例如过滤出balance字段在20000~30000的文档;
GET /bank/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": { "match_all": {} },
"filter": {
"range": {
"balance": {
"gte": 20000,
"lte": 30000
}
}
}
}
}
}
搜索聚合(aggs)
- 对搜索结果进行聚合,使用
aggs来表示,类似于MySql中的group by,例如对state字段进行聚合,统计出相同state的文档数量;
GET /bank/_search
{
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"group_by_state": {
"terms": {
"field": "state.keyword"
}
}
}
}
类似于SQL语句中的
SELECT state, COUNT(*) FROM bank GROUP BY state ORDER BY COUNT(*) DESC LIMIT 10;
"size": 0只要聚合结果
- 嵌套聚合,例如对
state字段进行聚合,统计出相同state的文档数量,再统计出balance的平均值;
GET /bank/_search
{
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"group_by_state": {
"terms": {
"field": "state.keyword"
},
"aggs": {
"average_balance": {
"avg": {
"field": "balance"
}
}
}
}
}
}
- 对聚合搜索的结果进行排序,例如按
balance的平均值降序排列;
GET /bank/_search
{
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"group_by_state": {
"terms": {
"field": "state.keyword",
"order": {
"average_balance": "desc"
}
},
"aggs": {
"average_balance": {
"avg": {
"field": "balance"
}
}
}
}
}
}
- 按字段值的范围进行分段聚合,例如分段范围为
age字段的[20,30][30,40][40,50],之后按gender统计文档个数和balance的平均值;
GET /bank/_search
{
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"group_by_age": {
"range": {
"field": "age",
"ranges": [
{
"from": 20,
"to": 30
},
{
"from": 30,
"to": 40
},
{
"from": 40,
"to": 50
}
]
},
"aggs": {
"group_by_gender": {
"terms": {
"field": "gender.keyword"
},
"aggs": {
"average_balance": {
"avg": {
"field": "balance"
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
8. 参考资料
官网入门案例:https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/6.6/getting-started.html