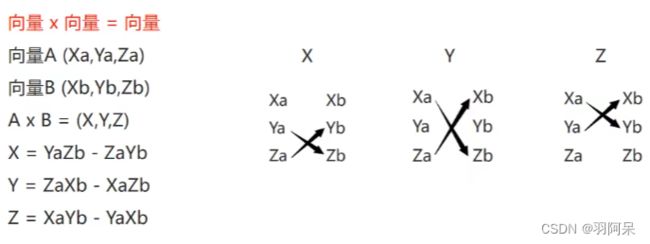Unity 基础函数
Mathf:
//1.π-PI
print(Mathf.PI);
//2.取绝对值-Abs
print(Mathf.Abs(-10));
print(Mathf.Abs(-20));
print(Mathf.Abs(1));
//3.向上取整-Ce il To In t
float f = 1.3f;
int i = (int)f;
print(i);
print(Mathf.CeilToInt(f));
print(Mathf.CeilToInt(1.00001f));
//4.向下取整-FloorToInt
print(Mathf.FloorToInt(9.6f));
//5.钳制函数-clamp 限制大小
print(Mathf.Clamp(10, 11, 20));//10
print(Mathf.Clamp(22, 11, 20));//20
print(Mathf.Clamp(15, 11, 20));//15
//6.获取最大值-Max
print(Mathf.Max(10, 11, 20));//取最大数
//7.获取最小值-Min
print(Mathf.Pow(10, 2));//10的2次方
//8.一个数的n次幕-Pow
print(Mathf.FloorToInt(9.6f));
//9.四舍五入-RoundToInt
print(Mathf.RoundToInt(9.6f));
//10.返回一个数的平方根-Sqrt
print(Mathf.Sqrt(4f));//2
//11.判断一个数是否是2的n次方-IsPowerofTwo
print(Mathf.IsPowerOfTwo(9));//false
//12.判断正负数-Sign
print(Mathf.Sign(9.6f));//正数返回1
三角函数:
// 弧度转角度
float rad = 1;
float anger = rad * Mathf.Rad2Deg;
print(anger);
// 角度转弧度
anger = 1;
rad = anger * Mathf.Deg2Rad;
print(rad);
//注意:Mathf中的三角函数相关函数,传入的参数需要时弧度值
print(Mathf.Sin(30 * Mathf.Deg2Rad));
print(Mathf.Cos(60 * Mathf.Deg2Rad));
//注意:反三角函数得到的结果是正弦或者余弦值对应的弧度
rad = Mathf.Asin(0.5f);
print(rad * Mathf.Rad2Deg);
rad = Mathf.Acos(0.5f);
print(rad * Mathf.Rad2Deg);
坐标系转换:
//世界坐标系
//目前学习的和世界坐标系相关的
//this.transform.position;
//this.transform.rotation;
//this.transform.eulerAngles;
//this.transform.lossyScale;
//修改他们会是相对世界坐标系的变化
//相对坐标系
//相对父对象的物体坐标系的位置本地坐标相对坐标
//this.transform.localPosition;
//this.transform.localEulerAngles;
//this.transform.localRotation;
//this.transform.localscale;
//修改他们会是相对父对象物体坐标系的变化
//三屏幕坐标系
//Input.mouse Position
//screen.width;
//screen.height;
//坐标转换相关
//世界转本地
//this.transform.InverseTransformDirection
//this.transform.InverseTransformPoint
//this.transform.InverseTransformVector
//本地转世界
//this.transform.TransformDirection
//this.transform.TransformPoint
//this.transform.TransformVector
//世界转屏幕
//Camera.main.WorldToscreenPoint
//屏幕转世界
//Camera.main.ScreenToworldPoint;
//世界转视口
//Camera.main.WorldToViewportPoint
//视口转世界
//Camera.main.ViewportToworldPoint
//视口转屏幕
//Camera.main.ViewportToScreenPoint
//屏幕转视口
//Camera.main.ScreenToViewportPoint;
向量:
//知识点一向量
//三维向量-Vector3
//Vector3有两种几何意义
//1.位置一代表一个点
print(this.transform.position);
//2.方向一代表一个方向
print(this.transform.forward);
print(this.transform.up);
//知识点二两点决定一向量
//A和B此时几何意义是两个点
Vector3 A = new Vector3(1, 2, 3);
Vector3 B = new Vector3(5, 1, 5);
//求向量
//此时AB和BA他们的几何意义是两个向量
Vector3 AB = B - A;
Vector3 BA = A - B;
//知识点三零向量和负向量
print(Vector3.zero);
print(Vector3.forward);
print(Vector3.forward);
//知识点四向量的模长
//Vector3中提供了获取向量模长的成员属性
//magnitude
print(AB.magnitude);
Vector3 c = new Vector3(5, 6, 7);
print(c.magnitude);
//知识点五单位向量
print(AB.normalized);
//向量加法
//this.transform.position += new Vector3(1, 2, 3);
this.transform.Translate(Vector3.forward * 5);
//向量减法
//this.transform.position -= new Vector3(1, 2, 3);
this.transform.Translate(-Vector3.forward * 5);
//向量乘除标量
this.transform.localScale *= 2;
this.transform.localScale /= 2;
//补充知识调试画线
//画线段
//前两个参数分别是起点终点
Debug.DrawLine(this.transform.position, this.transform.position + this.transform.forward, Color.red);
//画射线
// 前两个参数分别是起点方向
Debug.DrawRay(this.transform.position,transform.right, Color.green);
//通过点乘判断对象方位
//Vector3提供了计算点乘的方法
Debug.DrawRay(this.transform.position, this.transform.forward, Color.red);
//得到两个向量的点乘结果
//向量a点乘AB的结果
float dotResult = Vector3.Dot(this.transform.forward, target.position - this.transform.position);
if (dotResult >= 0)
print("它在我前方");
else
print("它在我后方");
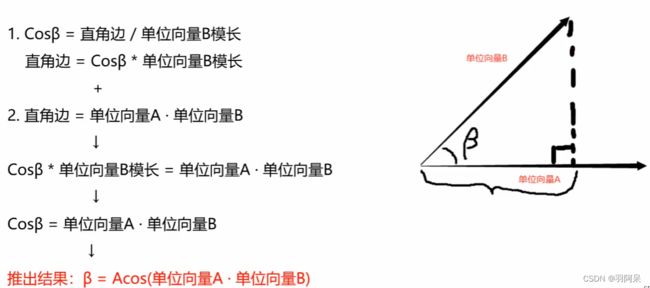
//通过点乘推导公式算出夹角
//步骤
//1.用单位向量算出点乘结果
//dot Result = Vector3.Dot(this.transform.forward, (target.position - this.transform.position).normalized);
//2.用反三角函数得出角度
print("角度" + Mathf.Acos(dotResult) * Mathf.Rad2Deg);
//Vector3中提供了得到两个向量之间夹角的方法
print("角度2" + Vector3.Angle(this.transform.forward, target.position - this.transform.position));//叉乘计算
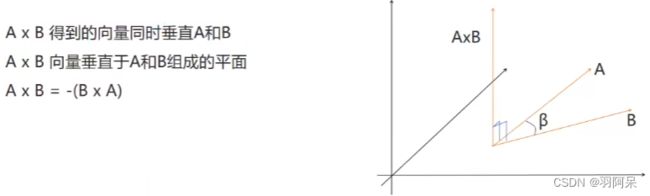
print(Vector3.Cross(AA.position, BB.position));
//叉乘几何意义
//假设向量A和B都在X Z平面上
//向量A叉乘向量B
//y大于0证明B在A右侧
//y小于0证明B在A左侧
Vector3 vec = Vector3.Cross(BB.position, AA.position);
if (vec.y > 0)
print("AA在BB的右侧");
else
print("AA在BB的左侧");