搜索二叉树(二叉树进阶)
目录
1.二叉搜索树
1.1二叉搜索树概念
1.2二叉搜索树操作
2.3二叉搜索树的实现
2.4二叉搜索树的应用
2.5二叉搜索树的性能分析
1.二叉搜索树
1.1二叉搜索树概念
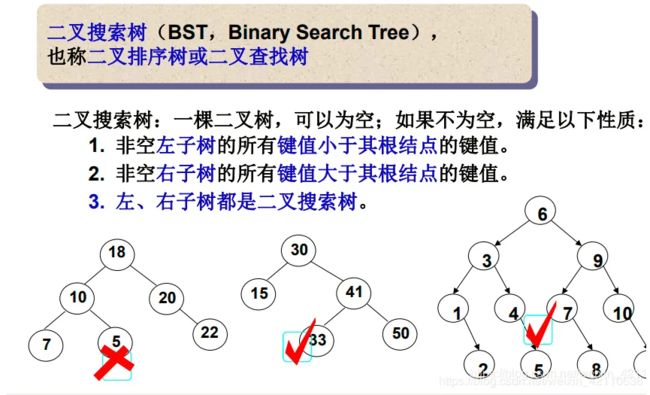
二叉搜索树又称二叉排序树,它或者是一颗空树,或者是具有以下性质的二叉树:
1.若它的左子树不为空,则左子树上所有节点的值都小于根节点的值
2.若它的右子树不为空,则右子树上所有节点的值都大于根节点的值
3.它的左右子树也分别为二叉搜索树
1.2二叉搜索树操作
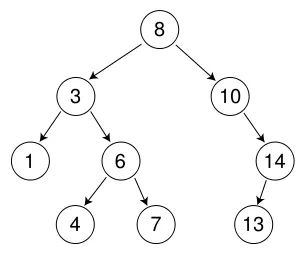
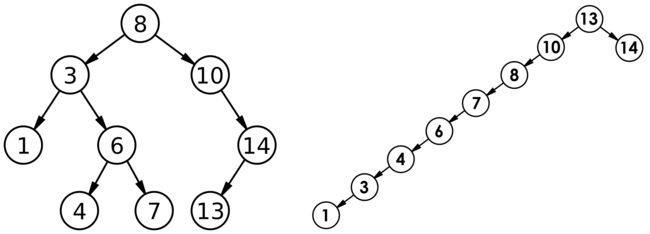
int a[] = {8, 3, 1, 10, 6, 4, 7, 14, 13};
1. 二叉搜索树的查找
a、从根开始比较,查找,比根大则往右边走查找,比根小则往左边走查找。
b、最多查找高度次,走到到空,还没找到,这个值不存在。(时间复杂度最坏是O(N),比如所有节点都在右子树或者左子树上面。)
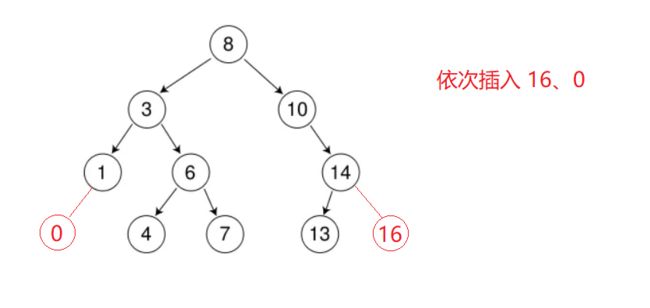
2. 二叉搜索树的插入
插入的具体过程如下:
a. 树为空,则直接新增节点,赋值给root指针
b. 树不空,按二叉搜索树性质查找插入位置,插入新节点
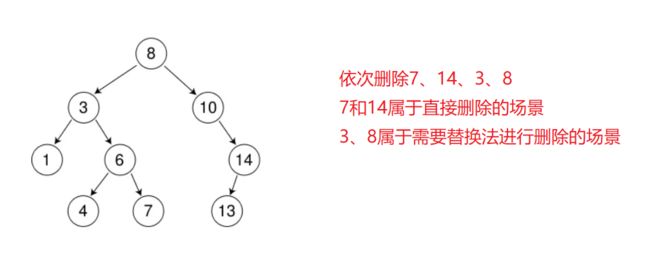
3.二叉搜索树的删除
首先查找元素是否在二叉搜索树中,如果不存在,则返回, 否则要删除的结点可能分下面四种情况:
a. 要删除的结点无孩子结点
b. 要删除的结点只有左孩子结点
c. 要删除的结点只有右孩子结点
d. 要删除的结点有左、右孩子结点
看起来有待删除节点有4中情况,实际情况a可以与情况b或者c合并起来,因此真正的删除过程如下:
情况b:删除该结点且使被删除节点的双亲结点指向被删除节点的左孩子结点--直接删除
情况c:删除该结点且使被删除节点的双亲结点指向被删除结点的右孩子结点--直接删除
情况d:在它的右子树中寻找中序下的第一个结点(关键码最小),用它的值填补到被删除节点中,再来处理该结点的删除问题--替换法删除
2.3二叉搜索树的实现
//BinarySearchTree.h
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include
#include
using namespace std;
template
struct BSTreeNode
{
BSTreeNode* _left;
BSTreeNode* _right;
K _key;
BSTreeNode(const K& key)
:_left(nullptr)
, _right(nullptr)
, _key(key)
{}
};
template
class BSTree
{
typedef BSTreeNode Node;
public:
BSTree()
:_root(nullptr)
{}
BSTree(const BSTree& t)
{
_root = Copy(t._root);
}
~BSTree()
{
Destroy(_root);
}
//现代写法:因为operator=是传值调用,过程中调用了拷贝构造形成了t
//然后通过swap交换他们的内部资源,最后引用返回延长了内部资源的生命周期。
//防止t出了作用域被销毁时把内部给释放了
BSTree& operator=(BSTree t)
{
swap(_root, t._root);
return *this;
}
bool Insert(const K& key)
{
if (_root == nullptr)
{
_root = new Node(key);
return true;
}
Node* cur = _root;
Node* parent = nullptr;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key < key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (cur->_key > key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
return false;
}
cur = new Node(key);
if (parent->_key < key)
parent->_right = cur;
else
parent->_left = cur;
return true;
}
bool Find(const K& key)
{
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key < key)
{
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (cur->_key > key)
{
cur = cur->_left;
}
else
{
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
bool Erase(const K& key)
{
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_key < key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (cur->_key > key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else //找到了
{
if (cur->_left == nullptr)//左为空
{
if (cur == _root)
_root = cur->_right;
else
{
if (parent->_right == cur)
parent->_right = cur->_right;
else
parent->_left = cur->_right;
}
}
else if (cur->_right == nullptr)//右为空
{
if (cur == _root)
_root = cur->_left;
else
{
if (parent->_right == cur)
parent->_right = cur->_left;
else
parent->_left = cur->_left;
}
}
else//左右不为空
{
Node* parent = cur;
//找替代节点 -- 左子树最大节点
Node* leftMax = cur->_left;
while (leftMax->_right)
{
parent = leftMax;
leftMax = leftMax->_right;
}
swap(cur->_key, leftMax->_key);
if (parent->_left == leftMax)
parent->_left = leftMax->_left;
else
parent->_right = leftMax->_left;
cur = leftMax;
}
delete cur;
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
//二叉搜索树中序遍历出来是有序的
void InOrder()
{
_InOrder(_root);
cout << endl;
}
//以下是递归版本
bool FindR(const K& key)
{
return _FindR(_root, key);
}
bool InsertR(const K& key)
{
return _InsertR(_root, key);
}
bool EraseR(const K& key)
{
return _EraseR(_root, key);
}
private:
Node* Copy(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return nullptr;
Node* copyroot = new Node(root->_key);
copyroot->_left = Copy(root->_left);
copyroot->_right = Copy(root->_right);
return copyroot;
}
void Destroy(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return;
Destroy(root->_left);
Destroy(root->_right);
delete root;
root = nullptr;
}
bool _EraseR(Node*& root, const K& key)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return false;
if (root->_key < key)
return _EraseR(root->_right, key);
else if (root->_key > key)
return _EraseR(root->_left, key);
else
{
Node* del = root;
if (root->_left == nullptr)//左为空
root = root->_right;
else if (root->_right == nullptr)//右为空
root = root->_left;
else//左右不为空
{
Node* leftMax = root->_left;
while (leftMax->_right)
{
leftMax = leftMax->_right;
}
swap(root->_key, leftMax->_key);
return _EraseR(root->_left, key);
}
delete del;
return true;
}
}
bool _InsertR(Node*& root, const K& key)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
root = new Node(key);
return true;
}
if (root->_key < key)
{
return _InsertR(root->_right, key);
}
else if (root->_key > key)
{
return _InsertR(root->_left, key);
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
bool _FindR(Node* root, const K& key)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return false;
if (root->_key < key)
{
return _FindR(root->_right, key);
}
else if (root->_key > key)
{
return _FindR(root->_left, key);
}
else
{
return true;
}
}
void _InOrder(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return;
}
_InOrder(root->_left);
cout << root->_key << " ";
_InOrder(root->_right);
}
private:
Node* _root;
}; //main.cpp
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include"BinarySearchTree.h"
//迭代版
void TestBSTree1()
{
int a[] = { 8,3,1,10,6,4,7,14,13 };
BSTree t;
for (auto e : a)
{
t.Insert(e);
}
BSTree t1;
t1 = t;
t.InOrder();
t.Erase(4);
t.InOrder();
t.Erase(6);
t.InOrder();
t.Erase(7);
t.InOrder();
t.Erase(3);
t.InOrder();
for (auto e : a)
{
t.Erase(e);
t.InOrder();
}
}
//递归版
void TestBSTree2()
{
int a[] = { 8,3,1,10,6,4,7,14,13 };
BSTree t;
for (auto e : a)
{
t.InsertR(e);
}
BSTree t1(t);
t1 = t;
t.InOrder();
t1.InOrder();
t.EraseR(4);
t.InOrder();
}
int main()
{
TestBSTree1();
return 0;
} 2.4二叉搜索树的应用
1. K模型(key的搜索模型):K模型即只有key作为关键码,结构中只需要存储Key即可,关键码即为需要搜索到的值。
比如:给一个单词word,判断该单词是否拼写正确,具体方式如下:
以词库中所有单词集合中的每个单词作为key,构建一棵二叉搜索树
在二叉搜索树中检索该单词是否存在,存在则拼写正确,不存在则拼写错误。
//main.cpp
void TestBSTree1()
{
bit::BSTree dict;
dict.InsertR("insert", "插入");
dict.InsertR("sort", "排序");
dict.InsertR("right", "右边");
dict.InsertR("date", "日期");
string str;
while (cin >> str)
{
bit::BSTreeNode* ret = dict.FindR(str);
if (ret)
{
cout << ret->_value << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "无此单词" << endl;
}
}
} 2. KV模型(key/value的搜索模型):每一个关键码key,都有与之对应的值Value,即
比如英汉词典就是英文与中文的对应关系,通过英文可以快速找到与其对应的中文,英文单词与其对应的中文
再比如统计单词次数,统计成功后,给定单词就可快速找到其出现的次数,单词与其出现次数就是
//main.cpp
void TestBSTree2()
{
string arr[] = { "苹果", "西瓜", "苹果", "西瓜", "苹果", "苹果", "西瓜","苹果", "香蕉", "苹果", "香蕉", };
bit::BSTree countTree;
for (auto& str : arr)
{
auto ret = countTree.FindR(str);
if (ret == nullptr)
{
countTree.InsertR(str, 1);
}
else
{
ret->_value++;
}
}
countTree.InOrder();
} 使用递归或者迭代写的二叉搜索树进行以下修改:
//BinarySearchTree.h
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#pragma once
#include
#include
using namespace std;
namespace bit
{
template
struct BSTreeNode
{
BSTreeNode* _left;
BSTreeNode* _right;
K _key;
V _value;//添加一个成员,所以要多加一个模板参数
BSTreeNode(const K& key, const V& value)
:_left(nullptr)
, _right(nullptr)
, _key(key)
, _value(value)
{}
};
template
class BSTree
{
typedef BSTreeNode Node;
public:
BSTree()
:_root(nullptr)
{}
//二叉搜索树中序遍历出来是有序的
void InOrder()
{
_InOrder(_root);
cout << endl;
}
Node* FindR(const K& key)
{
return _FindR(_root, key);
}
bool InsertR(const K& key, const V& value)
{
return _InsertR(_root, key, value);
}
bool EraseR(const K& key)
{
return _EraseR(_root, key);
}
private:
bool _EraseR(Node*& root, const K& key)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return false;
if (root->_key < key)
{
return _EraseR(root->_right, key);
}
else if (root->_key > key)
{
return _EraseR(root->_left, key);
}
else
{
Node* del = root;
if (root->_left == nullptr)//左为空
{
root = root->_right;
}
else if (root->_right == nullptr)//右为空
{
root = root->_left;
}
else//左右不为空
{
Node* leftMax = root->_left;
while (leftMax->_right)
{
leftMax = leftMax->_right;
}
swap(root->_key, leftMax->_key);
return _EraseR(root->_left, key);
}
delete del;
return true;
}
}
bool _InsertR(Node*& root, const K& key, const V& value)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
root = new Node(key, value);
return true;
}
if (root->_key < key)
{
return _InsertR(root->_right, key, value);
}
else if (root->_key > key)
{
return _InsertR(root->_left, key, value);
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
Node* _FindR(Node* root, const K& key)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return nullptr;
if (root->_key < key)
{
return _FindR(root->_right, key);
}
else if (root->_key > key)
{
return _FindR(root->_left, key);
}
else
{
return root;
}
}
void _InOrder(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
return;
}
_InOrder(root->_left);
cout << root->_key << ":" << root->_value << endl;
_InOrder(root->_right);
}
private:
Node* _root;
};
} 2.5二叉搜索树的性能分析
插入和删除操作都必须先查找,查找效率代表了二叉搜索树中各个操作的性能。
对有n个结点的二叉搜索树,若每个元素查找的概率相等,则二叉搜索树平均查找长度是结点在二叉搜索树的深度的函数,即结点越深,则比较次数越多。但对于同一个关键码集合,如果各关键码插入的次序不同,可能得到不同结构的二叉搜索树:
最优情况下,二叉搜索树为完全二叉树(或者接近完全二叉树),其平均比较次数为:O(logN)
最差情况下,二叉搜索树退化为单支树(或者类似单支),其平均比较次数为:O(N)