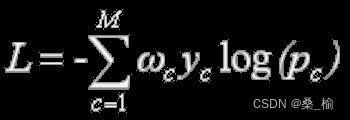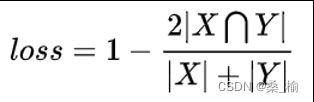图像分割场景中四种常见的损失函数(附代码)
图像分割场景中四种常见的损失函数
- 一 交叉熵损失
-
- 加权交叉熵
- BCELoss
- 二 Focal Loss
- 三 Dice系数
-
- DiceLoss
- IOULOSS
- 四 Jaccard系数
- 五 Tversky系数
- 六 Lovasz-SoftmaxLoss(有难度)
- 总结
一 交叉熵损失
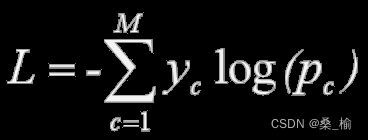
优点:交叉熵损失可以用在大多数语义分割场景中
缺点:对于只分割前景和背景的时候,当前景像素的数量远远小于背景像素的数量的时候,即y=0的数量远远大于y=1的数量,损失函数中的y=0成分就会占主导,使得模型严重偏向背景,导致效果不好
加权交叉熵
BCELoss
二 Focal Loss
源自目标检测(RetinaNet),是对标准交叉熵的一种改进,主要解决难易样本数量不平衡的问题,当正负样本数量不平衡时,可以通过在交叉熵中引入参数进行调节。
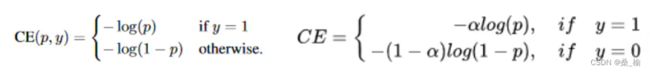
虽然以上公式平衡了正负样本的数量,但是,目标检测中大量的候选目标都是易分样本,这样样本的损失很低,但是由于数量极不平衡,易分样本的数量相对来讲太多,最终主导了总的损失。
因此,Focalloss认为易分样本对模型的提升效果非常小,模型应该主要关注那些难分样本。
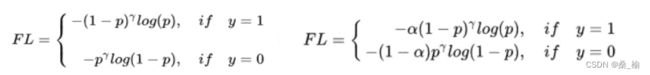
**参数P:**当p趋近于0的时候,调制因子1-p接近于1,损失不受影响,当p趋近于1的时候,1-p接近0,从而减小易分样本对总loss的损失
**参数gama:**当gama=0时,Focal就是传统的交叉熵,当它等于2时,易分样本loss就会很小,难分就会很大。
class FocalLoss(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, alpha=0.25, gamma=2, size_average=True, ignore_index=255):
super(FocalLoss, self).__init__()
self.alpha = alpha
self.gamma = gamma
self.ignore_index = ignore_index
self.size_average = size_average # 对batch里面的数据取均值/求和
def forward(self, inputs, targets):
ce_loss = F.cross_entropy(inputs, targets, ignore_index=self.ignore_index)
pt = torch.exp(-ce_loss)
focal_loss = self.alpha * (1-pt)**self.gamma * ce_loss
if self.size_average:
return focal_loss.mean()
else:
return focal_loss.sum()
三 Dice系数
是用来度量集合相似度的函数,通常用于计算两个样本之间的像素相似度

TP是真实为1预测也为1
FN是真实为1预测为0
FP是真实为0预测为1
TN是真实为0预测为0
DiceLoss适用于样本极度不平衡的情况,一般情况下使用DiceLoss会对反向传播不利,使得训练不稳定。
class DiceLoss(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, weight=None, size_average=True):
super(DiceLoss, self).__init__()
self.size_average = size_average
def forward(self, probs, labels):
"""
probs = [1, 12, 360, 480]
targets = [1, 12, 360, 480]
"""
targets = make_one_hot(labels.unsqueeze(0), 12)
num = targets.size(1) # num=12
smooth = 1
m1 = probs.view(num, -1) # m1 = 12, 172800
m2 = targets.view(num, -1) # m2 = 12, 172800
intersection = (m1 * m2) # intersection = 12,172800
score = 2. * (intersection.sum(1) + smooth) / (m1.sum(1) + m2.sum(1) + smooth)
dice_loss = 1 - score.sum() / num
if self.size_average:
return dice_loss.mean()
else:
return dice_loss.sum()
其中将mask变成独热编码的函数:
def make_one_hot(input, num_classes):
"""
input.shape = [1, 1, 360, 480]
num_classes = 12
output.shape = [1, 12, 360, 480]
"""
shape = np.array(input.shape) # shape = [1, 1, 352, 480]
shape[1] = num_classes # shape = [1, 12, 352, 480]
shape = tuple(shape)
result = torch.zeros(shape)
result = result.scatter_(1, input.cpu(), 1) # scatter_直接在原始Tensor上做修改
return result
scatter_()函数:scatter()和scatter_()的作用是一样的。scatter()不会直接修改原来的Tensor,而scatter_()会直接修改原来的Tensor
scatter(dim, index, src):
dim:沿着哪个维度进行索引
index:元素索引
src:源元素,可以是一个标量或一个张量
官方文档举例:三维向量
self[index[i][j][k]][j][k] = src[i][j][k] # if dim == 0
self[i][index[i][j][k]][k] = src[i][j][k] # if dim == 1
self[i][j][index[i][j][k]] = src[i][j][k] # if dim == 2
mask_batch = mask_tensor.unsqueeze(0).unsqueeze(0)
mask_one_hot = make_one_hot(mask_batch, 12)
print("原标签尺寸:\n", mask_tensor.shape, '\n')
print("先增加一维batchsize,再增加一维通道后标签尺寸:\n", mask_batch.shape, '\n')
print("经过独热编码后尺寸:\n", mask_one_hot.shape, '\n')
print("经过独热编码后某一维标签尺寸:\n", mask_one_hot[:,1,:,:], '\n')
原标签尺寸:
torch.Size([360, 480])
先增加一维batchsize,再增加一维通道后标签尺寸:
torch.Size([1, 1, 360, 480])
经过独热编码后尺寸:
torch.Size([1, 12, 360, 480])
经过独热编码后某一维标签尺寸:
tensor([[[1., 1., 1., …, 0., 0., 0.],
[1., 1., 1., …, 0., 0., 0.],
[1., 1., 1., …, 0., 0., 0.],
…,
[0., 0., 0., …, 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., …, 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., …, 0., 0., 0.]]])
DiceLoss
IOULOSS
四 Jaccard系数
五 Tversky系数
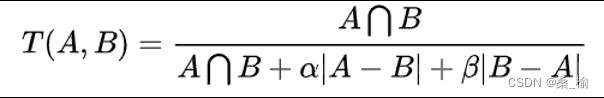
当alpha和bata都是0.5时,这个就是Dice系数,当都为1时,就是Jaccard系数
六 Lovasz-SoftmaxLoss(有难度)
class LovaszSoftmax(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, ignore=None, size_average=True):
super(LovaszSoftmax, self).__init__()
"""
Multi-class Lovasz-Softmax loss
probas: [B, C, H, W] Variable, class probabilities at each prediction (between 0 and 1).
Interpreted as binary (sigmoid) output with outputs of size [B, H, W].
labels: [B, H, W] Tensor, ground truth labels (between 0 and C - 1)
ignore: void class labels
"""
"""
probas.shape = [1, 3, 4, 4]
labels.shape = [1, 4, 4]
"""
self.size_average = size_average
self.ignore = ignore
def forward(self, probas, labels):
loss = lovasz_softmax_flat(*flatten_probas(probas, labels, self.ignore))
return loss
def flatten_probas(probas, labels, ignore=None):
"""
Flattens predictions in the batch
"""
B, C, H, W = probas.size() # 1, 3, 4, 4
probas = probas.permute(0, 2, 3, 1).contiguous().view(-1, C) # 1, 4, 4, 3 --> 16, 3
labels = labels.view(-1) # 16
if ignore is None:
return probas, labels
valid = (labels != ignore)
vprobas = probas[valid.nonzero().squeeze()]
vlabels = labels[valid]
return vprobas, vlabels
def lovasz_softmax_flat(probas, labels):
"""
Multi-class Lovasz-Softmax loss
probas: [P, C] Variable, class probabilities at each prediction (between 0 and 1)
labels: [P] Tensor, ground truth labels (between 0 and C - 1)
"""
"""
probas.shape = [16, 3]
labels.shape = [16]
labels = [1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 0, 2, 2, 2, 0, 2, 2, 1, 1, 0, 1]
"""
C = probas.size(1) # C = 3
losses = []
class_to_sum = list(range(C)) # class_to_sum = [0, 1, 2]
for c in class_to_sum:
fg = (labels == c).float() # δ
class_pred = probas[:, c]
"""
c = 0:
fg = [0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 1., 0., 0., 0., 1., 0., 0., 0., 0., 1., 0.]
class_pred = [0.6565, 0.8674, 0.8831, 0.4174, 0.4845, 0.1666, 0.2379, 0.4416, 0.5015,
0.9657, 0.4523, 0.2172, 0.3103, 0.5980, 0.7919, 0.4523]
c = 1
fg = [1., 1., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 1., 1., 0., 1.]
class_pred = [0.8110, 0.4605, 0.9819, 0.3185, 0.7950, 0.1819, 0.7492, 0.7690, 0.8270,
0.3137, 0.0826, 0.8931, 0.9237, 0.3156, 0.6388, 0.6351]
c = 2
fg = [0., 0., 1., 1., 1., 0., 1., 1., 1., 0., 1., 1., 0., 0., 0., 0.]
class_pred = [0.0658, 0.8870, 0.9484, 0.2572, 0.4305, 0.2031, 0.3526, 0.3824, 0.4131,
0.4258, 0.0298, 0.3857, 0.8182, 0.7671, 0.5974, 0.1790]
"""
errors = (Variable(fg) - class_pred).abs() # m
errors_sorted, perm = torch.sort(errors, 0, descending=True) # π
perm = perm.data
fg_sorted = fg[perm]
"""
c = 0:
errors = [0.6565, 0.8674, 0.8831, 0.4174, 0.4845, 0.8334, 0.2379, 0.4416, 0.5015,
0.0343, 0.4523, 0.2172, 0.3103, 0.5980, 0.2081, 0.4523]
errors_sorted = [0.8831, 0.8674, 0.8334, 0.6565, 0.5980, 0.5015, 0.4845, 0.4523, 0.4523,
0.4416, 0.4174, 0.3103, 0.2379, 0.2172, 0.2081, 0.0343]
perm = [ 2, 1, 5, 0, 13, 8, 4, 10, 15, 7, 3, 12, 6, 11, 14, 9]
fg_sorted = [0., 0., 1., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 1., 1.]
"""
losses.append(torch.dot(errors_sorted, Variable(lovasz_grad(fg_sorted)))) # torch.dot():一维向量对应位置相乘再相加
return mean(losses)
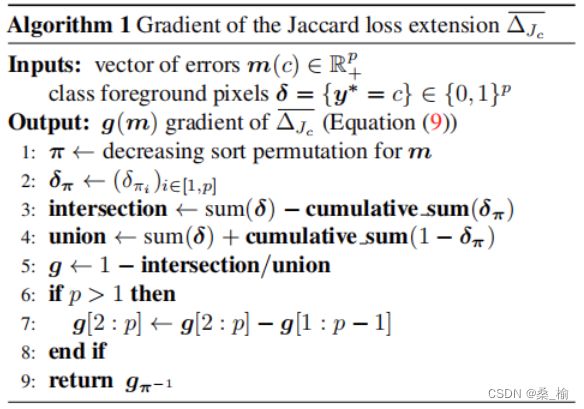
def lovasz_grad(gt_sorted):
p = len(gt_sorted) # p = 16
gts = gt_sorted.sum() # 4
intersection = gts - gt_sorted.float().cumsum(0)
union = gts + (1 - gt_sorted).float().cumsum(0)
jaccard = 1. - intersection / union
if p > 1: # cover 1-pixel case
jaccard[1:p] = jaccard[1:p] - jaccard[0:-1]
return jaccard
def isnan(x):
return x != x
def mean(l, ignore_nan=False, empty=0):
"""
nanmean compatible with generators.
"""
l = iter(l)
if ignore_nan:
l = ifilterfalse(isnan, l)
try:
n = 1
acc = next(l)
except StopIteration:
if empty == 'raise':
raise ValueError('Empty mean')
return empty
for n, v in enumerate(l, 2):
acc += v
if n == 1:
return acc
return acc / n
总结
BCELoss + DiceLoss :将两者进行组合,在数据较为均衡情况下有所改善,但是在数据极度不平衡的情况下交叉熵会在迭代几个Epoch之后远小于DiceLoss,这个组合Loss会退化为DiceLoss
Focal Loss + DiceLoss:论文提出来解决小器官分割问题