SpringBoot实现数据导出成Excel
SpringBoot实现数据导出成Excel
SpringBoot实现Excel读取在另一篇文章 文章地址:
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_45367825/article/details/111411691
这是本人写的一个SpringBoot对Excel写入的方法,实测能用,待提升的地方有很多,有不足之处请多多指点。
Excel2003版(后缀为.xls)最大行数是65536行,最大列数是256列。
Excel2007以上的版本(后缀为.xlsx)最大行数是1048576行,最大列数是16384列。
若数据量超出行数,需要进行脚页的控制,这一点没做,因为一般100W行已够用。
提供3种方法写入:
1.根据给定的实体类列List和列名数组arr[]进行Excel写入
2.根据给定的List和key的顺序数组key[]进行Excel写入
3.根据给定的List按顺序Excel写入,列名数组arr[]需要自行和数据列顺序进行一一对应
同名的Excel会被覆盖!!!
写入Excel所需要的几个类
1.在pom.xml加上依赖
dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.poigroupId>
<artifactId>poiartifactId>
<version>4.0.1version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.poigroupId>
<artifactId>poi-ooxmlartifactId>
<version>4.0.1version>
dependency>
dependencies>
2.ExcelPOJO实体类
package com.cly.utils.Excel;
/**
* @author : CLy
* @ClassName : ExcelPOJO
* @date : 2020/7/9 17:13
* 实体类所有成员变量都需要有GET,SET方法
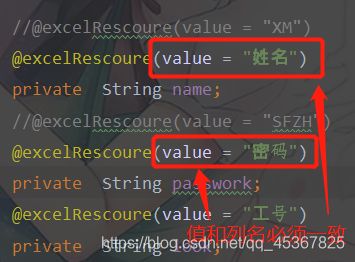
* 所有成员变量都要加上注解@excelRescoure(value = "?"),?为Excel真实列名,必须一一对应
* @excelRescoure(value = "?"),?可为空,需要用到才赋值
* 成员变量目前只允许String,Double,Interge,Float
**/
public class ExcelPOJO {
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getPasswork() {
return passwork;
}
public void setPasswork(String passwork) {
this.passwork = passwork;
}
public String getLook() {
return look;
}
public void setLook(String look) {
this.look = look;
}
@excelRescoure(value = "姓名")
private String name;
@excelRescoure(value = "密码")
private String passwork;
@excelRescoure(value = "工号")
private String look;
@Override
public String toString(){
return "name:"+this.getName()+",passwork:"+this.getPasswork()+",look:"+this.getLook();
}
public ExcelPOJO() {}
}
3.@interface自定义注解(用于实体类读取)
package com.cly.utils.Excel;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
/**
* @author : CLy
* @ClassName : myRescoure
* @date : 2020/7/10 9:31
**/
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface excelRescoure {
String value() default "";//默认为空
}
4.excelWrite类(写入Excel数据类)有很多冗余的代码,可抽离出来
package com.cly.utils.Excel;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.*;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFCellStyle;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFWorkbook;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.beans.IntrospectionException;
import java.beans.PropertyDescriptor;
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.net.URLEncoder;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.*;
/**
* @author : CLy
* @ClassName : excelWrite
* @date : 2020/7/17 17:01
**/
public class excelWrite {
//日志输出
private static Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(excelWrite.class);
/**
* 方法一:
* 实体类数据写入新建的excel
* @path:excel文件路径
* @array[]:文件首行数据列名,可为空,为空时不存在首行列名
* @list:实体类数据数列
*/
public static <T> String writeToExcelByPOJO(String path, String[] array, List<T> list) {
/* for (T t : list) {
System.out.println(t);
}*/
//创建工作薄
Workbook wb = new XSSFWorkbook();
/**标题和页码*/
CellStyle titleStyle = wb.createCellStyle();
// 设置单元格对齐方式
titleStyle.setAlignment(HorizontalAlignment.CENTER); // 水平居中
//titleStyle.setVerticalAlignment(); // 默认垂直居中
// 设置字体样式
Font titleFont = wb.createFont();
titleFont.setFontHeightInPoints((short) 12); // 字体高度
titleFont.setFontName("黑体"); // 字体样式
titleStyle.setFont(titleFont);
//创建sheet
Sheet sheet = wb.createSheet("第一页");
sheet.autoSizeColumn(0);// 自动设置宽度
// 在sheet中添加标题行
Row row = sheet.createRow((int) 0);// 行数从0开始
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
Cell cell = row.createCell(i);
cell.setCellValue(array[i]);
cell.setCellStyle(titleStyle);
}
/**数据样式*/
// 数据样式 因为标题和数据样式不同 需要分开设置 不然会覆盖
CellStyle dataStyle = wb.createCellStyle();
// 设置居中样式
dataStyle.setAlignment(HorizontalAlignment.CENTER); // 水平居中
/**处理实体类数据并写入*/
//获取当前的泛型对象
Object obj = list.get(0);
ArrayList arrayList = new ArrayList();
//LinkedHashMap保证顺序
LinkedHashMap<String, Object> POJOfields = getPOJOFieldAndValue(obj);
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
for (Map.Entry<String, Object> map : POJOfields.entrySet()) {
if (map.getKey().equals(array[i])) {
arrayList.add(map.getValue());
}
}
}
if (array.length != arrayList.size()) {
return "标题列数和实体类标记数不相同";
}
try {
//数据从序号1开始
int index = 1;
//利用迭代器,遍历集合数据,产生数据行
Iterator<T> it = list.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
row = sheet.createRow(index);// 默认的行数从0开始,为了统一格式设置从1开始,就是从excel的第二行开始
index++;
T t = (T) it.next();
//System.out.println("t:" + t);
for (int i = 0; i < arrayList.size(); i++) {
String fieldName = (String) arrayList.get(i);
//System.out.println(fieldName);
String getMethodName = "get" + fieldName.substring(0, 1).toUpperCase() + fieldName.substring(1);
//System.out.println(getMethodName);
Class<? extends Object> tCls = t.getClass();// 泛型为Object以及所有Object的子类
//System.out.println(tCls);
Method method = tCls.getMethod(getMethodName, new Class[]{});// 通过方法名得到对应的方法
//PropertyDescriptor pd = new PropertyDescriptor((String) arrayList.get(i), it.getClass());
//获取成员变量的get方法
//Method method = pd.getWriteMethod();
Object value = method.invoke(t, new Object[]{});// 动态调用方,得到属性值
//System.out.println(value.toString());
Cell cell = row.createCell(i);
if (value != null) {
if (value instanceof Date) {
SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd");
value = simpleDateFormat.format(value);
}
cell.setCellValue(value.toString());// 为当前列赋值
cell.setCellStyle(dataStyle);//设置数据的样式
}
}
}
FileOutputStream fileOut = new FileOutputStream(path);
wb.write(fileOut);
fileOut.flush();
wb.close();
fileOut.close();
return "success";
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "faile";
}
/**
* 获取对应的实体类成员
*/
private static LinkedHashMap<String, Object> getPOJOFieldAndValue(Object T) {
//声明返回结果集
LinkedHashMap<String, Object> result = new LinkedHashMap<>();
Field[] fields = T.getClass().getDeclaredFields();//获取属性名
if (fields != null) {
for (Field field : fields) {
excelRescoure Rescoure = field.getAnnotation(excelRescoure.class);
if (Rescoure.value() != null && !"".equals(Rescoure.value())) {
result.put(Rescoure.value(), field.getName());
}
}
} else {
logger.warn("实体类:" + T + "不存在成员变量");
return null;
}
return result;
}
/**---------------------===================================================---------------------------**/
/**
* 方法2:
* HashMap数据写入新建的excel
* @path:excel文件路径
* @array[]:文件首行数据列名,可为空,为空时不存在首行列名
* @List>:HashMap数据数列
* @key:hashmap里面的key值,需要一一对应列名的顺序
* */
public static String writeToExcelByHashMap (String path, String[] array, List<HashMap> list,String[] key){
//创建工作薄
Workbook wb = new XSSFWorkbook();
/**标题和页码*/
CellStyle titleStyle = wb.createCellStyle();
// 设置单元格对齐方式
titleStyle.setAlignment(HorizontalAlignment.CENTER); // 水平居中
//titleStyle.setVerticalAlignment(); // 默认垂直居中
// 设置字体样式
Font titleFont = wb.createFont();
titleFont.setFontHeightInPoints((short) 12); // 字体高度
titleFont.setFontName("黑体"); // 字体样式
titleStyle.setFont(titleFont);
//创建sheet
Sheet sheet = wb.createSheet("第一页");
sheet.autoSizeColumn(0);// 自动设置宽度
// 在sheet中添加标题行
Row row = sheet.createRow((int) 0);// 行数从0开始
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
Cell cell = row.createCell(i);
cell.setCellValue(array[i]);
cell.setCellStyle(titleStyle);
}
/**数据样式*/
// 数据样式 因为标题和数据样式不同 需要分开设置 不然会覆盖
CellStyle dataStyle = wb.createCellStyle();
// 设置居中样式
dataStyle.setAlignment(HorizontalAlignment.CENTER); // 水平居中
/**数据写入*/
//数据从序号1开始
try {
int index = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
row = sheet.createRow(index);// 默认的行数从0开始,为了统一格式设置从1开始,就是从excel的第二行开始
index++;
HashMap hashMap= list.get(i);
for (int j = 0; j < key.length; j++) {
Cell cell = row.createCell(j);
cell.setCellValue(hashMap.get(key[j]).toString());// 为当前列赋值
cell.setCellStyle(dataStyle);//设置数据的样式
}
}
FileOutputStream fileOut = new FileOutputStream(path);
wb.write(fileOut);
fileOut.flush();
wb.close();
fileOut.close();
return "success";
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "faile";
}
/**------------------===========================================================------------------------------------------------------*/
/**
* 方法3:
* HashMap数据写入新建的excel
* @path:excel文件路径
* @array[]:文件首行数据列名,可为空,为空时不存在首行列名,列名需要和数列的数据顺序一一对应
* @List:数列数据数列
*
* */
public static String writeToExcelByList(String path, String[] array, List<List> list){
//创建工作薄
Workbook wb = new XSSFWorkbook();
/**标题和页码*/
CellStyle titleStyle = wb.createCellStyle();
// 设置单元格对齐方式
titleStyle.setAlignment(HorizontalAlignment.CENTER); // 水平居中
//titleStyle.setVerticalAlignment(); // 默认垂直居中
// 设置字体样式
Font titleFont = wb.createFont();
titleFont.setFontHeightInPoints((short) 12); // 字体高度
titleFont.setFontName("黑体"); // 字体样式
titleStyle.setFont(titleFont);
//创建sheet
Sheet sheet = wb.createSheet("第一页");
sheet.autoSizeColumn(0);// 自动设置宽度
// 在sheet中添加标题行
Row row = sheet.createRow((int) 0);// 行数从0开始
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
Cell cell = row.createCell(i);
cell.setCellValue(array[i]);
cell.setCellStyle(titleStyle);
}
/**数据样式*/
// 数据样式 因为标题和数据样式不同 需要分开设置 不然会覆盖
CellStyle dataStyle = wb.createCellStyle();
// 设置居中样式
dataStyle.setAlignment(HorizontalAlignment.CENTER); // 水平居中
/**数据写入*/
//数据从序号1开始
try {
int index = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
row = sheet.createRow(index);// 默认的行数从0开始,为了统一格式设置从1开始,就是从excel的第二行开始
index++;
List data= list.get(i);
for (int j = 0; j < data.size(); j++) {
Cell cell = row.createCell(j);
cell.setCellValue(data.get(j).toString());// 为当前列赋值
cell.setCellStyle(dataStyle);//设置数据的样式
}
}
FileOutputStream fileOut = new FileOutputStream(path);
wb.write(fileOut);
fileOut.flush();
wb.close();
fileOut.close();
return "success";
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "faile";
}
}
5.测试类,同名的Excel会被覆盖
package com.cly.utils.Excel;
import java.util.*;
/**
* @author : CLy
* @ClassName : WriteTest
* @date : 2020/7/31 15:26
**/
public class WriteTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
/**实体类测试
* writeToExcelByPOJO(String path, String[] array, List list)
* @path:excel文件路径
* @array[]:文件首行数据列名,可为空,为空时不存在首行列名
* @list:实体类数据数列
* 注意同名的Excel会被覆盖,请写好文件名字和对应的后缀
*/
ExcelPOJO excelPOJO = new ExcelPOJO();
excelPOJO.setName("name");
excelPOJO.setPasswork("pass");
excelPOJO.setLook("look");
ExcelPOJO POJO2 = new ExcelPOJO();
POJO2.setName("name2");
POJO2.setPasswork("pass2");
POJO2.setLook("look2");
ExcelPOJO POJO3 = new ExcelPOJO();
POJO3.setName("name3");
POJO3.setPasswork("pass3");
POJO3.setLook("look3");
List<ExcelPOJO> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(excelPOJO);
list.add(POJO2);
list.add(POJO3);
/**列名对应实体类中成员变量@excelRescoure的值,只需要写入要的列明,不必全部成员变量都写上*/
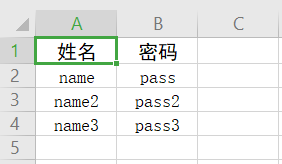
String[] arr = {"姓名", "密码"};
String s = excelWrite.writeToExcelByPOJO("D:\\123.xls", arr, list);
System.out.println(s);
/**HashMap测试
* writeToExcelByHashMap (String path, String[] array, List list,String[] key)
* @path:excel文件路径
* @array[]:文件首行数据列名,可为空,为空时不存在首行列名
* @List>:HashMap数据数列
* @key:hashmap里面的key值,需要一一对应列名的顺序
* 注意同名的Excel会被覆盖,请写好文件名字和对应的后缀
*/
HashMap hashMap= new HashMap<>();
hashMap.put("1","q");
hashMap.put("0","w");
hashMap.put("5","e");
hashMap.put("2","r");
HashMap hashMap2= new HashMap<>();
hashMap2.put("1","q2");
hashMap2.put("0","w2");
hashMap2.put("5","e2");
hashMap2.put("2","r2");
/**列名顺序*/
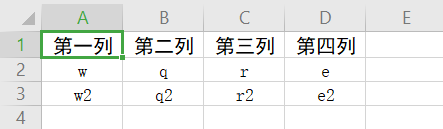
String[] arr2 = {"第一列","第二列","第三列","第四列"};
/**HashMap中的数据KEY对应列名顺序,不存在列名或顺序要求可随意,但该数组数据必须要*/
String[] key = {"0","1","2","5"};
List list = new ArrayList();
list.add(hashMap);
list.add(hashMap2);
String s = excelWrite.writeToExcelByHashMap("D:\\123.xls", arr2, list,key);
System.out.println(s);
/**List测试
* writeToExcelByList(String path, String[] array, List list)
* @path:excel文件路径
* @array[]:文件首行数据列名,可为空,为空时不存在首行列名,列名需要和数列的数据顺序一一对应
* @List:数列数据数列
* 注意同名的Excel会被覆盖,请写好文件名字和对应的后缀
*/
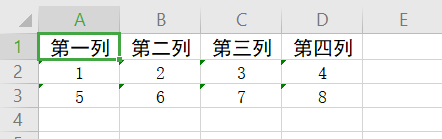
String[] arr3 = {"第一列","第二列","第三列","第四列"};
List data = new ArrayList();
data.add("1");
data.add("2");
data.add("3");
data.add("4");
List data2 = new ArrayList();
data2.add("5");
data2.add("6");
data2.add("7");
data2.add("8");
List<List> list1 = new ArrayList();
list1.add(data);
list1.add(data2);
String s = excelWrite.writeToExcelByList("D:\\123.xls", arr3, list1);
System.out.println(s);
}
}
6.运行结果和说明
1.实体类测试结果
2.HashMap测试
3.List测试
还有很多不足的地方,请多多指点,希望能给你带来帮助。