C++11更新内容(2)--完美转发--默认移动构造/移动赋值--1116
1.完美转发
1.1万能引用
void Fun(int &x){ cout << "左值引用" << endl; }
void Fun(const int &x){ cout << "const 左值引用" << endl; }
void Fun(int &&x){ cout << "右值引用" << endl; }
void Fun(const int &&x){ cout << "const 右值引用" << endl; }
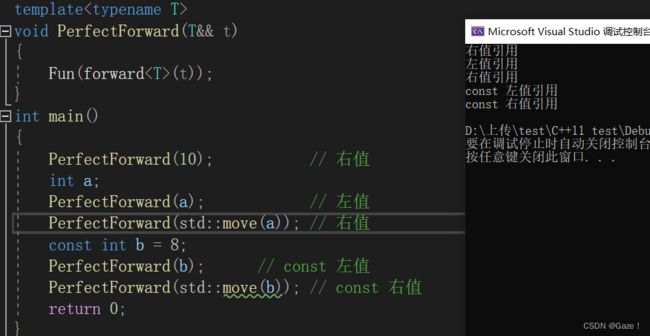
template
void PerfectForward(T&& t)
{
Fun(t);
}
模板中的&&不代表右值引用,而是万能引用,其既能接收左值又能接收右值。 模板的万能引用只是提供了能够接收同时接收左值引用和右值引用的能力。但是引用类型的唯一作用就是限制了接收的类型,后续使用中都退化成了左值。
如果希望能够在传递过程中保持它的左值或者右值的属性, 就需要用完美转发。
1.2 std::forward
template
void PerfectForward(T&& t)
{
Fun(std::forward(t));
}
2. 新的类功能
2.1 新的默认生成函数
原来C++类中,有6个默认成员函数:
1. 构造函数 2. 析构函数 3. 拷贝构造函数 4. 拷贝赋值重载 5. 取地址重载 6. const 取地址重载
2.1.1 新增1:默认的移动构造函数
如果没有实现移动构造函数,而且没实现 析构函数&&拷贝构造函数&&拷贝赋值重载
编译器会自动生成一个默认的移动构造函数。该构造函数对于内置类型成员进行逐字节拷贝,对于自定义类型,需要看其是否实现了移动构造函数。实现了就用其的移动构造函数,没实现就用拷贝构造函数。
2.1.2 新增2:默认的移动赋值重载函数
如果没有实现移动赋值重载函数,而且没有实现 析构函数&&拷贝构造函数&&拷贝赋值重载
编译器胡自动生成一个默认的移动赋值重载函数。对于内置类型逐字节拷贝。对于自定义类型,如果其实现了移动赋值重载,就调用。如有没有实现,就调用其拷贝构造函数。
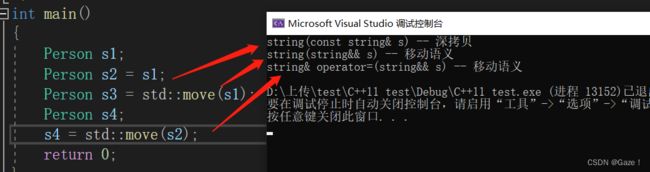
例如
class Person
{
public:
Person(const char* name = "", int age = 0)
:_name(name)
, _age(age)
{}
private:
chy::string _name;
int _age;
};
int main()
{
Person s1;
Person s2 = s1;
Person s3 = std::move(s1);
Person s4;
s4 = std::move(s2);
return 0;
}该类没有实现 析构、拷贝构造、拷贝赋值重载。且成员变量有自定义类型,即是上篇博客展示的非库中的string(主要是在 移动拷贝、移动赋值重载中添加了打印)
2.2 新增关键字
2.2.1强制生成默认函数的关键字default
使用default关键字指定生成某默认函数
Person(Person&& p) = default;
Person(const Person& p)=default;
2.2.2禁止生成默认函数的关键字delete
该语法指示编译器不生成对应函数的默认版本
Person(Person&& p) = delete;
Person(const Person& p)=delete;
2.2.3 final
声明该类是不能被继承的类,如果仍然被继承,编译时自动报错。
class A final
{
public:
A()
{}
protected:
int _a;
};
class B : public A
{
};2.2.4 override
检查派生类虚函数是否重写了基类某个虚函数,如果没有重写编译报错。
class Car{
public:
virtual void Drive(){}
};
class Benz :public Car {
public:
virtual void Drive() override {cout << "Benz-舒适" << endl;}
};3.可变参数模板
3.1参数包的使用
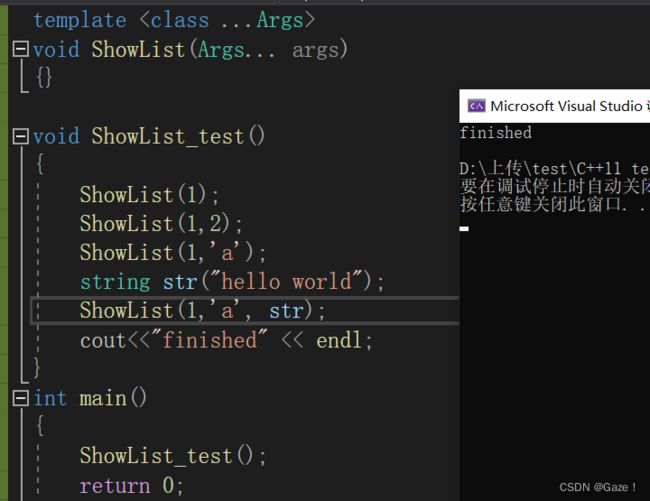
Args是一个模板参数包,args是一个函数形参参数包
声明一个参数包Args...args,这个参数包中可以包含0到任意个模板参数。
template
void ShowList(Args... args)
{}
3.1.1 递归函数方式展开参数包
template
void ShowList2(T value, Args... args)
{
cout << value << " ";
ShowList2(args...);
} 相当于每次都用剩余的参数列表去调用该函数。参数列表的一个,当做value。
因为是递归,所以需要终止条件。
// 递归终止函数
template
void ShowList2(const T& t)
{
cout << t << endl;
} 3.1.2 逗号表达式展开参数包
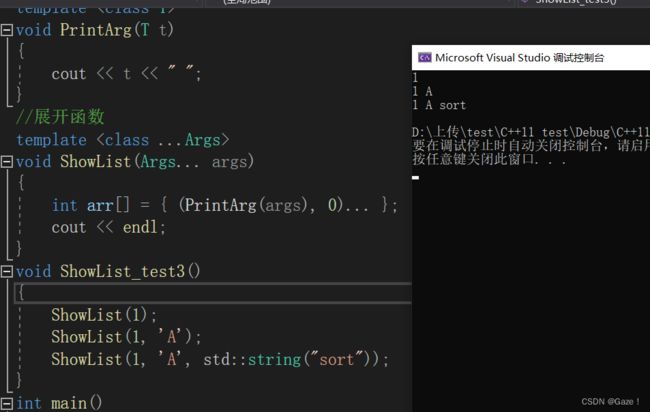
template
void PrintArg(T t)
{
cout << t << " ";
}
//展开函数
template
void ShowList(Args... args)
{
int arr[] = { (PrintArg(args), 0)... };
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
ShowList(1);
ShowList(1, 'A');
ShowList(1, 'A', std::string("sort"));
return 0;
} 3.2 empalce
template
void emplace_back (Args&&... args);
void emplace_test()
{
list lt1;//这里演示的需要 之前实现的几个类 这里不贴出来了
//我们这里的list在拷贝构造和 构造中分别添加了一句打印
lt1.push_back(Date(2022,11,16));
lt1.emplace_back(2022,11,16);
} 发现在list中 使用emplace_back可以少调用一次拷贝构造。
3.3 lambda
想要对一个数据集合中的元素进行排序,可以使用sort方法
sort(array, array+sizeof(array)/sizeof(array[0]));
如果需要从大到小排序
sort(array, array + sizeof(array) / sizeof(array[0]), greater()); //仿函数
bool cmp(int& a1, int& a2){ return a1>a2;}
sort(array, array + sizeof(array) / sizeof(array[0]), cmp);//这里是自己写的比较函数
如果需要排序的是自定义类型,需要我们去实现对应的仿函数。
int main()
{
vector v = { { "苹果", 2.1, 5 }, { "香蕉", 3, 4 }, { "橙子", 2.2,
3 }, { "菠萝", 1.5, 4 } };
sort(v.begin(), v.end(), ComparePriceLess());//这里都是仿函数
sort(v.begin(), v.end(), ComparePriceGreater());//仿函数
return 0;
}
由于每次写仿函数都需要创建一个结构体/类,在C++11语法中出现了Lambda表达式。
3.3.1 Lambda表达式
lambda表达式书写格式:[捕捉列表] (参数列表) mutable -> 返回值类型 { 比较的方法 }
int main()
{
// 两个数相加的lambda
auto add1 = [](int a, int b)->int{return a + b; };
cout << add1(1, 2) << endl;
// 省略返回值
auto add2 = [](int a, int b){return a + b; };
cout << add2(1, 2) << endl;
// 交换变量的lambda
int x = 0, y = 1;
auto swap1 = [](int& x1, int& x2)->void{int tmp = x1; x1 = x2; x2 = tmp; };
swap1(x, y);
cout << x << ":" << y << endl;
auto swap2 = [](int& x1, int& x2)
{
int tmp = x1;
x1 = x2;
x2 = tmp;
};
swap2(x, y);
cout << x << ":" << y << endl;
// 不传参数交换x y的lambda -- 捕捉列表
// 默认捕捉的对象不能修改
/*auto swap3 = [x, y]()mutable
{
int tmp = x;
x = y;
y = tmp;
};
swap3();
cout << x << ":" << y << endl;*/
auto swap3 = [&x, &y]
{
int tmp = x;
x = y;
y = tmp;
};
swap3();
cout << x << ":" << y << endl;
return 0;
}