剑指Offer(较难)
JZ19 顺时针打印矩阵
JZ19 顺时针打印矩阵
代码分析
public class Solution {
public ArrayList<Integer> printMatrix(int[][] matrix) {
ArrayList<Integer> ret = new ArrayList<>();
int r1 = 0, r2 = matrix.length - 1, c1 = 0, c2 = matrix[0].length - 1;
while (r1 <= r2 && c1 <= c2) {
// 上
for (int i = c1; i <= c2; i++)
ret.add(matrix[r1][i]);
// 右
for (int i = r1 + 1; i <= r2; i++)
ret.add(matrix[i][c2]);
if (r1 != r2){
// 下
for (int i = c2 - 1; i >= c1; i--)
ret.add(matrix[r2][i]);
}
if (c1 != c2){
// 左
for (int i = r2 - 1; i > r1; i--)
ret.add(matrix[i][c1]);
}
r1++; r2--; c1++; c2--;
}
return ret;
}
}
分析
特殊情况:只要一行的时候所以需要后面两个if判断。
Z25 复杂链表的复制
题目地址
方法一(map)
public class Solution {
public RandomListNode Clone(RandomListNode pHead) {
if(pHead == null) return null;
RandomListNode cur = pHead;
Map<RandomListNode, RandomListNode> map = new HashMap<>();
// 3. 复制各节点,并建立 “原节点 -> 新节点” 的 Map 映射
while(cur != null) {
map.put(cur, new RandomListNode(cur.label));
cur = cur.next;
}
cur = pHead;
// 4. 构建新链表的 next 和 random 指向
while(cur != null) {
map.get(cur).next = map.get(cur.next);
map.get(cur).random = map.get(cur.random);
cur = cur.next;
}
// 5. 返回新链表的头节点
return map.get(pHead);
}
}
算法流程:
- 若头节点 head 为空节点,直接返回 nullnull ;
- 初始化: 哈希表 map, 节点 cur 指向头节点;
- 复制链表:
- 建立新节点,并向 dic 添加键值对 (原 cur 节点, 新 cur 节点) ;
- cur 遍历至原链表下一节点;
- 构建新链表的引用指向:
- 构建新节点的 next 和 random 引用指向;
- cur 遍历至原链表下一节点;
- 返回值: 新链表的头节点 map[cur] ;
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
弄个字典对应新老节点,需要节点,从字典的值拿
方法二:拼接 + 拆分
public class Solution {
public RandomListNode Clone(RandomListNode pHead) {
if(pHead == null) return null;
RandomListNode cur = pHead;
// 1. 复制各节点,并构建拼接链表
while(cur != null) {
RandomListNode tmp = new RandomListNode(cur.label);
tmp.next = cur.next;
cur.next = tmp;
cur = tmp.next;
}
// 2. 构建各新节点的 random 指向
cur = pHead;
while(cur != null) {
if(cur.random != null)
cur.next.random = cur.random.next;
cur = cur.next.next;
}
// 3. 拆分两链表
cur = pHead.next;
RandomListNode pre = pHead;//老链表指针
RandomListNode res = pHead.next;//新链表指针
while(cur.next != null) {
pre.next = pre.next.next;
cur.next = cur.next.next;
pre = pre.next;
cur = cur.next;
}
pre.next = null; // 单独处理原链表尾节点
return res; // 返回新链表头节点
}
}
分析
wrong,cannot used original node of list(错误,不能使用列表的原始节点)
所以单独处理原链表尾节点
JZ64 滑动窗口的最大值
题目地址
暴力解法
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public ArrayList<Integer> maxInWindows(int [] num, int size) {
ArrayList<Integer> list=new ArrayList<Integer>();
int max=0;
if(num.length == 0 || size > num.length || size==0){
return list;
}
for(int i=0;i <= num.length - size;i++){
max=num[i];
for(int j=i;j<size + i;j++){
if(max < num[j]){
max=num[j];
}
}
list.add(max);
}
return list;
}
}
单调队列
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public ArrayList<Integer> maxInWindows(int [] nums, int k) {
//单调队列
//下面是要注意的点:
//队列按从大到小放入
//如果首位值(即最大值)不在窗口区间,删除首位
//如果新增的值小于队列尾部值,加到队列尾部
//如果新增值大于队列尾部值,删除队列中比新增值小的值,如果在把新增值加入到队列中
//如果新增值大于队列中所有值,删除所有,然后把新增值放到队列首位,保证队列一直是从大到小
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
if(k <= 0|| k > nums.length)return list;
Deque<Integer> deque = new LinkedList<>();
//未形成窗口区间
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
//队列不为空时,当前值与队列尾部值比较,如果大于,删除队列尾部值
//一直循环删除到队列中的值都大于当前值,或者删到队列为空
while (!deque.isEmpty() && nums[i] > deque.peekLast()) deque.removeLast();
//执行完上面的循环后,队列中要么为空,要么值都比当前值大,然后就把当前值添加到队列中
deque.addLast(nums[i]);
}
//窗口区间刚形成后,把队列首位值添加到队列中
//因为窗口形成后,就需要把队列首位添加到数组中,而下面的循环是直接跳过这一步的,所以需要我们直接添加
list.add(deque.peekFirst());
//窗口区间形成
for (int i = k; i < nums.length; i++) {
//i-k是已经在区间外了,如果首位等于nums[i-k],那么说明此时首位值已经不再区间内了,需要删除
if (deque.peekFirst() == nums[i - k]) deque.removeFirst();
//删除队列中比当前值大的值
while (!deque.isEmpty() && nums[i] > deque.peekLast()) deque.removeLast();
//把当前值添加到队列中
deque.addLast(nums[i]);
//把队列的首位值添加到arr数组中
list.add(deque.peekFirst());
}
return list;
}
}
分析
最大值放在第一位
JZ56 删除链表中重复的结点
题目地址
递归
public class Solution {
public ListNode deleteDuplication(ListNode pHead) {
// 递归出口:当「输入节点为空」或者「不存在下一节点」,直接返回
if (pHead == null || pHead.next == null) return pHead;
if (pHead.val != pHead.next.val) {
// 若「当前节点」与「下一节点」值不同,则当前节点可以被保留
pHead.next = deleteDuplication(pHead.next);
return pHead;
} else {
// 若「当前节点」与「下一节点」相同,需要跳过「值相同的连续一段」
ListNode tmp = pHead;//用来对比
while (tmp != null && tmp.val == pHead.val) tmp = tmp.next;
return deleteDuplication(tmp);
}
}
}
非递归
public ListNode deleteDuplication(ListNode pHead) {
ListNode h = new ListNode(0), p = h;
h.next = pHead;
while (pHead != null) {
if (pHead.next != null && pHead.val == pHead.next.val) {
p.next = null;
} else if (pHead.next != null && p.next == null) {
p.next = pHead.next;
} else {
p = p.next;
}
pHead = pHead.next;
}
return h.next;
}
说明:
pHead为指针
p为指针
如果当前结点和下一个重复,则p.next没空,否则,如果p.next为空,则跳过当前结点(代表当前结点为同类重复结点的最后一个).
非递归二
class Solution {
public ListNode deleteDuplication(ListNode pHead) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode tail = dummy;
while (pHead != null) {
// 进入循环时,确保了 pHead 不会与上一节点相同
if (pHead.next == null || pHead.next.val != pHead.val) {
tail.next = pHead;
tail = pHead;
}
// 如果 pHead 与下一节点相同,跳过相同节点(到达「连续相同一段」的最后一位)
while (pHead.next != null && pHead.val == pHead.next.val) pHead = pHead.next;
pHead = pHead.next;
}
tail.next = null;
return dummy.next;
}
}
说明:
dummy :哑节点,保存正确头节点
tail :连接正确节点
pHead:试错的
什么时候用哑节点
可以起到避免处理头节点为空的边界问题的作用,减少代码执行异常的可能性。
通过这样完美解决一旦头结点被删除无法返回元素的问题。
哑节点一般用来保存头结点的,所以遇到一些问题可能导致头结点不在的非递归问题,用到他。
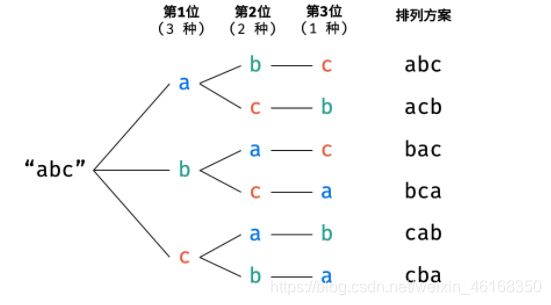
JZ27 字符串的排列
题目地址
递归
public ArrayList<String> Permutation(String s) {
c = s.toCharArray();
//从第一层开始递归
dfs(0);
//将字符串数组ArrayList转化为String类型数组
return list1;
}
public void dfs(int x) {
//递归出口,最后只有一个字符,不需要交换
if (x == c.length - 1) {
//将字符数组转换为字符串
list1.add(String.valueOf(c));
return;
}
//为了防止同一层递归出现重复元素
HashSet<Character> set = new HashSet<>();
//这里就很巧妙了,第一层可以是a,b,c那么就有三种情况,这里i = x,正巧dfs(0),正好i = 0开始
// 当第二层只有两种情况,dfs(1)i = 1开始
for (int i = x; i < c.length; i++) {
//发生剪枝,当包含这个元素的时候,直接跳过
if (set.contains(c[i])) {
continue;
}
set.add(c[i]);
//交换元素,这里很是巧妙,当在第二层dfs(1),x = 1,那么i = 1或者 2, 不是交换1和1,要就是交换1和2
swap(i, x);
//进入下一层递归
dfs(x + 1);
swap(i, x);
}
}
public void swap(int i, int x) {
char temp = c[i];
c[i] = c[x];
c[x] = temp;
}
第一层是 a b c,第一个for循环。
(x == c.length - 1)递归结束条件
每一层会有个set的存储,所以每一层的第一个元素都不可能重复,
遍历递归
第一个swap(i, x):负责把后面的分别和每一层第一个元素替换
dfs(x + 1);会进入下一层:x就是层数
第二个swap:用以使得字符数组的顺序回到进入递归前的状态,这样才不会影响外部的遍历顺序。因为在第一次交换后进入递归运算的时候,字符数组的顺序改变了。
下一个排列
public ArrayList<String> Permutation2(String str) {
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();
if (str == null || str.length() == 0) {
return list;
}
char[] chars = str.toCharArray();
Arrays.sort(chars);
list.add(String.valueOf(chars));
int len = chars.length;
while (true) {
int l = len - 1;
int r;
while (l >= 1 && chars[l - 1] >= chars[l]) {
l--;
}
if (l == 0)
break;
r = l;
while (r < len && chars[r] > chars[l - 1]) {
r++;
}
swap(chars, l - 1, r - 1);
reverse(chars, l);
list.add(String.valueOf(chars));
}
return list;
}
private void swap(char[] cs, int i, int j) {
char temp = cs[i];
cs[i] = cs[j];
cs[j] = temp;
}
private void reverse(char[] chars, int k) {
if (chars == null || chars.length <= k)
return;
int len = chars.length;
for (int i = 0; i < (len - k) / 2; i++) {
int m = k + i;
int n = len - 1 - i;
if (m <= n) {
swap(chars, m, n);
}
}
}
分析
一个全排列可看做一个字符串,字符串可有前缀、后缀。
生成给定全排列的下一个排列.所谓一个的下一个就是这一个与下一个之间没有其他的。
这就要求这一个与下一个有尽可能长的共同前缀,也即变化限制在尽可能短的后缀上。
[例]839647521是1–9的排列。1—9的排列最前面的是123456789,最后面的987654321,
从右向左扫描若都是增的,就到了987654321,也就没有下一个了。否则找出第一次出现下降的位置。
【例】 如何得到346987521的下一个
-
从尾部往前找第一个P(i-1) < P(i)的位置
3 4 6 <- 9 <- 8 <- 7 <- 5 <- 2 <- 1
最终找到6是第一个变小的数字,记录下6的位置i-1 -
从i位置往后找到最后一个大于6的数: chars[r] > chars[l - 1] ,因为是while,r-1才满足条件
3 4 6 -> 9 -> 8 -> 7 5 2 1
最终找到7的位置,记录位置为m -
交换位置i-1和m的值
3 4 7 9 8 6 5 2 1 -
倒序i位置后的所有数据
3 4 7 1 2 5 6 8 9
则347125689为346987521的下一个排列
while (true) {
int i = chars.length - 1;
int j = chars.length - 1;
while (i > 0 && chars[i-1] >= chars[i ]) {//为了保证不越界,而且最大也能判断得到,只能
i--;
}
if (i==0){
break;
}
while (j > i && chars[i-1] >= chars[j]) {
j--;
}
swap(chars, i-1, j);
reverse(chars, i );
list.add(String.valueOf(chars));
}
第二步也可以从后往前查找第一个大于i的数
while (i > 0 && chars[i-1] >= chars[i ]) {//为了保证不越界,而且最大也能判断得到,只能chars[i-1] >= chars[i]
下一个排列
public char[] nextPermutation(String str) {
char[] nums = str.toCharArray();
int i = nums.length - 1;
while (i > 0 && nums[i-1] >= nums[i ]) {
i--;
}
if (i > 0) {
int j = nums.length - 1;
while (j >= 0 && nums[i] >= nums[j]) {
j--;
}
swap(nums, i, j);
}
reverse(nums, i );
return nums;
}
为了321能变成123,所以i有个边界值0,。
矩阵中的路径
题目地址
代码分析
public boolean hasPath (char[][] board, String word) {
// write code here
char[] words = word.toCharArray();
for(int i = 0; i < board.length; i++) {// 遍历board,将所有的元素都看作起始节点开始搜寻
for(int j = 0; j < board[0].length; j++) {
if(dfs(board, words, i, j, 0)) return true;// 如果找到一次则直接返回true
}
}
return false;// 找不到返回 false
}
boolean dfs(char[][] board, char[] word, int i, int j, int k) {
//如果数组下标越界或者 board[i][j] != word[depth] ,则不匹配,返回false;
if(i >= board.length || i < 0 || j >= board[0].length || j < 0 || board[i][j] != word[k]) return false;
if(k == word.length-1 ) return true;//说明已经全部匹配完
board[i][j] = '\0'; // 即表示空字符,单词中永远不会走到
//递归
boolean res = dfs(board, word, i + 1, j, k + 1) || dfs(board, word, i - 1, j, k + 1) ||
dfs(board, word, i, j + 1, k + 1) || dfs(board, word, i , j - 1, k + 1);
board[i][j] = word[k];// 回溯: 将标记位复原
return res;
}
JZ33 丑数
题目地址
代码
public class Solution {
public int GetUglyNumber_Solution(int n) {
if(n==0) return 0;
int a = 0, b = 0, c = 0;//初始化三个指向三个潜在成为最小丑数的位置
int[] dp = new int[n];
dp[0] = 1;// 第一个丑数为 1
for(int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
int n2 = dp[a] * 2, n3 = dp[b] * 3, n5 = dp[c] * 5;
// 得到下一个丑数,三者中最小的
dp[i] = Math.min(Math.min(n2, n3), n5);
if(dp[i] == n2) a++;//下一个丑数可以由dp[i]*2得到,则a指针后移
if(dp[i] == n3) b++;//下一个丑数可以由dp[i]*3得到,则b指针后移
if(dp[i] == n5) c++;//下一个丑数可以由dp[i]*5得到,则c指针后移
//此处不能写if -else ,因为可能存在dp[a]*2==dp[b]*3这种情况
//那么在下一次循环中,dp[b]*3就会被再次选中,这样就会造成dp中有重复元素出现
}
return dp[n - 1];
}
}