ElasticSearch安装与介绍
Elastic Stack简介
如果没有听说过Elastic Stack,那你一定听说过ELK,实际上ELK是三款软件的简称,分别是Elasticsearch、 Logstash、Kibana组成,在发展的过程中,又有新成员Beats的加入,所以就形成了Elastic Stack。所以说,ELK是旧的称呼,Elastic Stack是新的名字。
全系的Elastic Stack技术栈包括:
Elasticsearch
Elasticsearch 基于java,是个开源分布式搜索引擎,它的特点有:分布式,零配置,自动发现,索引自动分片,索引副本机制,restful风格接口,多数据源,自动搜索负载等。
Logstash
Logstash 基于java,是一个开源的用于收集,分析和存储日志的工具。
Kibana
Kibana 基于nodejs,也是一个开源和免费的工具,Kibana可以为 Logstash 和 ElasticSearch 提供的日志分析友好的Web 界面,可以汇总、分析和搜索重要数据日志。
Beats
Beats是elastic公司开源的一款采集系统监控数据的代理agent,是在被监控服务器上以客户端形式运行的数据收集器的统称,可以直接把数据发送给Elasticsearch或者通过Logstash发送给Elasticsearch,然后进行后续的数据分析活动。Beats由如下组成:
-
Packetbeat:是一个网络数据包分析器,用于监控、收集网络流量信息,Packetbeat嗅探服务器之间的流量,解析应用层协议,并关联到消息的处理,其支 持ICMP (v4 and v6)、DNS、HTTP、Mysql、PostgreSQL、Redis、MongoDB、Memcache等协议;
-
Filebeat:用于监控、收集服务器日志文件,其已取代 logstash forwarder;
-
Metricbeat:可定期获取外部系统的监控指标信息,其可以监控、收集 Apache、HAProxy、MongoDB MySQL、Nginx、PostgreSQL、Redis、System、Zookeeper等服务;
Beats和Logstash其实都可以进行数据的采集,但是目前主流的是使用Beats进行数据采集,然后使用 Logstash进行数据的分割处理等,早期没有Beats的时候,使用的就是Logstash进行数据的采集。
ElasticSearch快速入门
简介
官网:Elasticsearch Platform — Find real-time answers at scale | Elastic
选择对应版本的数据,这里我使用的是Linux来进行安装,所以就先下载好ElasticSearch的Linux安装包
拉取Docker容器
因为我们需要部署在Linux下,为了以后迁移ElasticStack环境方便,我们就使用Docker来进行部署,首先我们拉取一个带有ssh的centos docker镜像
# 拉取镜像 docker pull moxi/centos_ssh # 制作容器 docker run --privileged -d -it -h ElasticStack --name ElasticStack -p 11122:22 -p 9200:9200 -p 5601:5601 -p 9300:9300 -v /etc/localtime:/etc/localtime:ro moxi/centos_ssh /usr/sbin/init
然后直接远程连接11122端口即可
单机版安装
因为ElasticSearch不支持Root用户直接操作,因此我们需要创建一个elsearch用户
# 添加新用户 useradd elsearch # 创建一个soft目录,存放下载的软件 mkdir /soft # 进入,然后通过xftp工具,将刚刚下载的文件拖动到该目录下 cd /soft # 解压缩 tar -zxvf elasticsearch-7.9.1-linux-x86_64.tar.gz #重命名 mv elasticsearch-7.9.1/ elsearch
因为刚刚我们是使用root用户操作的,所以我们还需要更改一下/soft文件夹的所属,改为elsearch用户
chown elsearch:elsearch /soft/ -R
然后在切换成elsearch用户进行操作
# 切换用户 su - elsearch
然后我们就可以对我们的配置文件进行修改了
# 进入到 elsearch下的config目录 cd /soft/elsearch/config
然后找到下面的配置
#打开配置文件 vim elasticsearch.yml #设置ip地址,任意网络均可访问 network.host: 0.0.0.0
在Elasticsearch中如果,network.host不是localhost或者127.0.0.1的话,就会认为是生产环境,会对环境的要求比较高,我们的测试环境不一定能够满足,一般情况下需要修改2处配置,如下:
# 修改jvm启动参数 vim conf/jvm.options #根据自己机器情况修改 -Xms128m -Xmx128m
然后在修改第二处的配置,这个配置要求我们到宿主机器上来进行配置
# 到宿主机上打开文件 vim /etc/sysctl.conf # 增加这样一条配置,一个进程在VMAs(虚拟内存区域)创建内存映射最大数量 vm.max_map_count=655360 # 让配置生效 sysctl -p
启动ElasticSearch
首先我们需要切换到 elsearch用户
su - elsearch
然后在到bin目录下,执行下面
# 进入bin目录 cd /soft/elsearch/bin # 后台启动 ./elasticsearch -d
启动成功后,访问下面的URL
http://202.193.56.222:9200/
如果出现了下面的信息,就表示已经成功启动了
如果你在启动的时候,遇到过问题,那么请参考下面的错误分析~
错误分析
错误情况1
如果出现下面的错误信息
java.lang.RuntimeException: can not run elasticsearch as root at org.elasticsearch.bootstrap.Bootstrap.initializeNatives(Bootstrap.java:111) at org.elasticsearch.bootstrap.Bootstrap.setup(Bootstrap.java:178) at org.elasticsearch.bootstrap.Bootstrap.init(Bootstrap.java:393) at org.elasticsearch.bootstrap.Elasticsearch.init(Elasticsearch.java:170) at org.elasticsearch.bootstrap.Elasticsearch.execute(Elasticsearch.java:161) at org.elasticsearch.cli.EnvironmentAwareCommand.execute(EnvironmentAwareCommand.java:86) at org.elasticsearch.cli.Command.mainWithoutErrorHandling(Command.java:127) at org.elasticsearch.cli.Command.main(Command.java:90) at org.elasticsearch.bootstrap.Elasticsearch.main(Elasticsearch.java:126) at org.elasticsearch.bootstrap.Elasticsearch.main(Elasticsearch.java:92) For complete error details, refer to the log at /soft/elsearch/logs/elasticsearch.log [root@e588039bc613 bin]# 2020-09-22 02:59:39,537121 UTC [536] ERROR CLogger.cc@310 Cannot log to named pipe /tmp/elasticsearch-5834501324803693929/controller_log_381 as it could not be opened for writing 2020-09-22 02:59:39,537263 UTC [536] INFO Main.cc@103 Parent process died - ML controller exiting
就说明你没有切换成 elsearch用户,因为不能使用root操作es
su - elsearch
错误情况2
[1]:max file descriptors [4096] for elasticsearch process is too low, increase to at least[65536]
解决方法:切换到root用户,编辑limits.conf添加如下内容
vi /etc/security/limits.conf # ElasticSearch添加如下内容: * soft nofile 65536 * hard nofile 131072 * soft nproc 2048 * hard nproc 4096
错误情况3
[2]: max number of threads [1024] for user [elsearch] is too low, increase to at least [4096]
也就是最大线程数设置的太低了,需要改成4096
#解决:切换到root用户,进入limits.d目录下修改配置文件。 vi /etc/security/limits.d/90-nproc.conf #修改如下内容: * soft nproc 1024 #修改为 * soft nproc 4096
错误情况4
[3]: system call filters failed to install; check the logs and fix your configuration or disable system call filters at your own risk
解决:Centos6不支持SecComp,而ES5.2.0默认bootstrap.system_call_filter为true
vim config/elasticsearch.yml # 添加 bootstrap.system_call_filter: false bootstrap.memory_lock: false
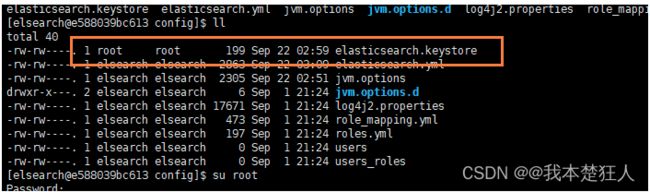
错误情况5
[elsearch@e588039bc613 bin]$ Exception in thread "main" org.elasticsearch.bootstrap.BootstrapException: java.nio.file.AccessDeniedException: /soft/elsearch/config/elasticsearch.keystore Likely root cause: java.nio.file.AccessDeniedException: /soft/elsearch/config/elasticsearch.keystore at java.base/sun.nio.fs.UnixException.translateToIOException(UnixException.java:90) at java.base/sun.nio.fs.UnixException.rethrowAsIOException(UnixException.java:111) at java.base/sun.nio.fs.UnixException.rethrowAsIOException(UnixException.java:116) at java.base/sun.nio.fs.UnixFileSystemProvider.newByteChannel(UnixFileSystemProvider.java:219) at java.base/java.nio.file.Files.newByteChannel(Files.java:375) at java.base/java.nio.file.Files.newByteChannel(Files.java:426) at org.apache.lucene.store.SimpleFSDirectory.openInput(SimpleFSDirectory.java:79) at org.elasticsearch.common.settings.KeyStoreWrapper.load(KeyStoreWrapper.java:220) at org.elasticsearch.bootstrap.Bootstrap.loadSecureSettings(Bootstrap.java:240) at org.elasticsearch.bootstrap.Bootstrap.init(Bootstrap.java:349) at org.elasticsearch.bootstrap.Elasticsearch.init(Elasticsearch.java:170) at org.elasticsearch.bootstrap.Elasticsearch.execute(Elasticsearch.java:161) at org.elasticsearch.cli.EnvironmentAwareCommand.execute(EnvironmentAwareCommand.java:86) at org.elasticsearch.cli.Command.mainWithoutErrorHandling(Command.java:127) at org.elasticsearch.cli.Command.main(Command.java:90) at org.elasticsearch.bootstrap.Elasticsearch.main(Elasticsearch.java:126) at org.elasticsearch.bootstrap.Elasticsearch.main(Elasticsearch.java:92)
我们通过排查,发现是因为 /soft/elsearch/config/elasticsearch.keystore 存在问题
也就是说该文件还是所属于root用户,而我们使用elsearch用户无法操作,所以需要把它变成elsearch
chown elsearch:elsearch elasticsearch.keystore
错误情况6
[1]: the default discovery settings are unsuitable for production use; at least one of [discovery.seed_hosts, discovery.seed_providers, cluster.initial_master_nodes] must be configured ERROR: Elasticsearch did not exit normally - check the logs at /soft/elsearch/logs/elasticsearch.log
继续修改配置 elasticsearch.yaml
# 取消注释,并保留一个节点 node.name: node-1 cluster.initial_master_nodes: ["node-1"]
ElasticSearchHead可视化工具
由于ES官方没有给ES提供可视化管理工具,仅仅是提供了后台的服务,elasticsearch-head是一个为ES开发的一个页面客户端工具,其源码托管于Github,地址为 传送门
head提供了以下安装方式
-
源码安装,通过npm run start启动(不推荐)
-
通过docker安装(推荐)
-
通过chrome插件安装(推荐)
-
通过ES的plugin方式安装(不推荐)
通过Docker方式安装
#拉取镜像 docker pull mobz/elasticsearch-head:5 #创建容器 docker create --name elasticsearch-head -p 9100:9100 mobz/elasticsearch-head:5 #启动容器 docker start elasticsearch-head
通过浏览器进行访问:
注意: 由于前后端分离开发,所以会存在跨域问题,需要在服务端做CORS的配置,如下:
vim elasticsearch.yml http.cors.enabled: true http.cors.allow-origin: "*"
通过chrome插件的方式安装不存在该问题
通过Chrome插件安装
打开chrome的应用商店,即可安装
https://chrome.google.com/webstore/detail/elasticsearch-head/ffmkiejjmecolpfloofpjologoblkegm
建议:推荐使用chrome插件的方式安装,如果网络环境不允许,就采用其它方式安装。
ElasticSearch中的基本概念
索引
-
索引(index)是Elasticsearch对逻辑数据的逻辑存储,所以它可以分为更小的部分。
-
可以把索引看成关系型数据库的表,索引的结构是为快速有效的全文索引准备的,特别是它不存储原始值。
-
Elasticsearch可以把索引存放在一台机器或者分散在多台服务器上,每个索引有一或多个分片(shard),每个分片可以有多个副本(replica)。
文档
-
存储在Elasticsearch中的主要实体叫文档(document)。用关系型数据库来类比的话,一个文档相当于数据库表中的一行记录。
-
Elasticsearch和MongoDB中的文档类似,都可以有不同的结构,但Elasticsearch的文档中,相同字段必须有相同类型。
-
文档由多个字段组成,每个字段可能多次出现在一个文档里,这样的字段叫多值字段(multivalued)。 每个字段的类型,可以是文本、数值、日期等。字段类型也可以是复杂类型,一个字段包含其他子文档或者数 组。
映射
所有文档写进索引之前都会先进行分析,如何将输入的文本分割为词条、哪些词条又会被过滤,这种行为叫做 映射(mapping)。一般由用户自己定义规则。
文档类型
-
在Elasticsearch中,一个索引对象可以存储很多不同用途的对象。例如,一个博客应用程序可以保存文章和评 论。
-
每个文档可以有不同的结构。
-
不同的文档类型不能为相同的属性设置不同的类型。例如,在同一索引中的所有文档类型中,一个叫title的字段必须具有相同的类型。
RESTful API
在Elasticsearch中,提供了功能丰富的RESTful API的操作,包括基本的CRUD、创建索引、删除索引等操作。
创建非结构化索引
在Lucene中,创建索引是需要定义字段名称以及字段的类型的,在Elasticsearch中提供了非结构化的索引,就是不需要创建索引结构,即可写入数据到索引中,实际上在Elasticsearch底层会进行结构化操作,此操作对用户是透明的。
创建空索引
PUT /haoke
{
"settings": {
"index": {
"number_of_shards": "2", #分片数
"number_of_replicas": "0" #副本数
}
}
}
删除索引
#删除索引
DELETE /haoke
{
"acknowledged": true
}
插入数据
URL规则: POST /{索引}/{类型}/{id}
POST /haoke/user/1001
#数据
{
"id":1001,
"name":"张三",
"age":20,
"sex":"男"
}
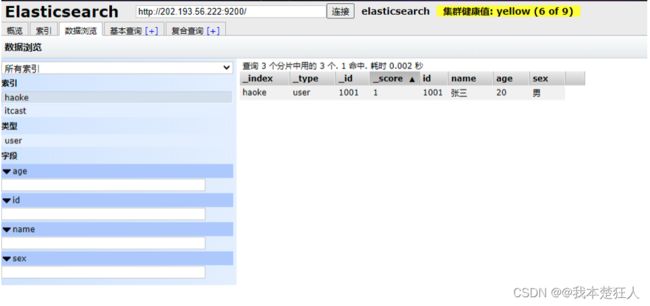
使用postman操作成功后
我们通过ElasticSearchHead进行数据预览就能够看到我们刚刚插入的数据了
更新数据
在Elasticsearch中,文档数据是不为修改的,但是可以通过覆盖的方式进行更新。
PUT /haoke/user/1001
{
"id":1001,
"name":"张三",
"age":21,
"sex":"女"
}
更新结果如下:
可以看到数据已经被覆盖了。问题来了,可以局部更新吗? -- 可以的。前面不是说,文档数据不能更新吗? 其实是这样的:在内部,依然会查询到这个文档数据,然后进行覆盖操作,步骤如下:
-
从旧文档中检索JSON
-
修改它
-
删除旧文档
-
索引新文档
#注意:这里多了_update标识
POST /haoke/user/1001/_update
{
"doc":{
"age":23
}
}
删除一个文档也不会立即从磁盘上移除,它只是被标记成已删除。Elasticsearch将会在你之后添加更多索引的时候才会在后台进行删除内容的清理。【相当于批量操作】
搜索数据
根据id搜索数据
GET /haoke/user/BbPe_WcB9cFOnF3uebvr
#返回的数据如下
{
"_index": "haoke",
"_type": "user",
"_id": "BbPe_WcB9cFOnF3uebvr",
"_version": 8,
"found": true,
"_source": { #原始数据在这里
"id": 1002,
"name": "李四",
"age": 40,
"sex": "男"
}
}
搜索全部数据
GET 1 /haoke/user/_search
注意,使用查询全部数据的时候,默认只会返回10条
关键字搜索数据
#查询年龄等于20的用户 GET /haoke/user/_search?q=age:20
结果如下:
DSL搜索
Elasticsearch提供丰富且灵活的查询语言叫做DSL查询(Query DSL),它允许你构建更加复杂、强大的查询。 DSL(Domain Specific Language特定领域语言)以JSON请求体的形式出现。
POST /haoke/user/_search
#请求体
{
"query" : {
"match" : { #match只是查询的一种
"age" : 20
}
}
}
实现:查询年龄大于30岁的男性用户。
POST /haoke/user/_search
#请求数据
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"filter": {
"range": {
"age": {
"gt": 30
}
}
},
"must": {
"match": {
"sex": "男"
}
}
}
}
}
查询出来的结果
全文搜索
POST /haoke/user/_search
#请求数据
{
"query": {
"match": {
"name": "张三 李四"
}
}
}
高亮显示,只需要在添加一个 highlight即可
POST /haoke/user/_search
#请求数据
{
"query": {
"match": {
"name": "张三 李四"
}
}
"highlight": {
"fields": {
"name": {}
}
}
}
聚合
在Elasticsearch中,支持聚合操作,类似SQL中的group by操作。
POST /haoke/user/_search
{
"aggs": {
"all_interests": {
"terms": {
"field": "age"
}
}
}
}
结果如下,我们通过年龄进行聚合
从结果可以看出,年龄30的有2条数据,20的有一条,40的一条。
ElasticSearch核心详解
文档
在Elasticsearch中,文档以JSON格式进行存储,可以是复杂的结构,如:
{
"_index": "haoke",
"_type": "user",
"_id": "1005",
"_version": 1,
"_score": 1,
"_source": {
"id": 1005,
"name": "孙七",
"age": 37,
"sex": "女",
"card": {
"card_number": "123456789"
}
}
}
其中,card是一个复杂对象,嵌套的Card对象
元数据(metadata)
一个文档不只有数据。它还包含了元数据(metadata)——关于文档的信息。三个必须的元数据节点是:
指定响应字段
在响应的数据中,如果我们不需要全部的字段,可以指定某些需要的字段进行返回。通过添加 _source
GET /haoke/user/1005?_source=id,name
#响应
{
"_index": "haoke",
"_type": "user",
"_id": "1005",
"_version": 1,
"found": true,
"_source": {
"name": "孙七",
"id": 1005
}
}
如不需要返回元数据,仅仅返回原始数据,可以这样:
GET /haoke/1 user/1005/_source
当然,这只表示你在查询的那一刻文档不存在,但并不表示几毫秒后依旧不存在。另一个进程在这期间可能创建新文档。
批量操作
有些情况下可以通过批量操作以减少网络请求。如:批量查询、批量插入数据。
批量查询
POST /haoke/user/_mget
{
"ids" : [ "1001", "1003" ]
}
结果:
如果,某一条数据不存在,不影响整体响应,需要通过found的值进行判断是否查询到数据。
POST /haoke/user/_mget
{
"ids" : [ "1001", "1006" ]
}
结果:
也就是说,一个数据的存在不会影响其它数据的返回
_bulk操作
在Elasticsearch中,支持批量的插入、修改、删除操作,都是通过_bulk的api完成的。
请求格式如下:(请求格式不同寻常)
{ action: { metadata }}
{ request body }
{ action: { metadata }}
{ request body }
...
批量插入数据:
{"create":{"_index":"haoke","_type":"user","_id":2001}}
{"id":2001,"name":"name1","age": 20,"sex": "男"}
{"create":{"_index":"haoke","_type":"user","_id":2002}}
{"id":2002,"name":"name2","age": 20,"sex": "男"}
{"create":{"_index":"haoke","_type":"user","_id":2003}}
{"id":2003,"name":"name3","age": 20,"sex": "男"}
注意最后一行的回车。
批量删除:
{"delete":{"_index":"haoke","_type":"user","_id":2001}}
{"delete":{"_index":"haoke","_type":"user","_id":2002}}
{"delete":{"_index":"haoke","_type":"user","_id":2003}}
由于delete没有请求体,所以,action的下一行直接就是下一个action。
其他操作就类似了。一次请求多少性能最高?
-
整个批量请求需要被加载到接受我们请求节点的内存里,所以请求越大,给其它请求可用的内存就越小。有一 个最佳的bulk请求大小。超过这个大小,性能不再提升而且可能降低。
-
最佳大小,当然并不是一个固定的数字。它完全取决于你的硬件、你文档的大小和复杂度以及索引和搜索的负 载。
-
幸运的是,这个最佳点(sweetspot)还是容易找到的:试着批量索引标准的文档,随着大小的增长,当性能开始 降低,说明你每个批次的大小太大了。开始的数量可以在1000~5000个文档之间,如果你的文档非常大,可以使用较小的批次。
-
通常着眼于你请求批次的物理大小是非常有用的。一千个1kB的文档和一千个1MB的文档大不相同。一个好的 批次最好保持在5-15MB大小间。
分页
和SQL使用LIMIT 关键字返回只有一页的结果一样,Elasticsearch接受from 和size 参数:
-
size: 结果数,默认10
-
from: 跳过开始的结果数,默认0
如果你想每页显示5个结果,页码从1到3,那请求如下:
GET /_search?size=5 GET /_search?size=5&from=5 GET /_search?size=5&from=10
应该当心分页太深或者一次请求太多的结果。结果在返回前会被排序。但是记住一个搜索请求常常涉及多个分 片。每个分片生成自己排好序的结果,它们接着需要集中起来排序以确保整体排序正确。
GET /haoke/user/_1 search?size=1&from=2
-
string类型在ElasticSearch 旧版本中使用较多,从ElasticSearch 5.x开始不再支持string,由text和 keyword类型替代。
-
text 类型,当一个字段是要被全文搜索的,比如Email内容、产品描述,应该使用text类型。设置text类型 以后,字段内容会被分析,在生成倒排索引以前,字符串会被分析器分成一个一个词项。text类型的字段 不用于排序,很少用于聚合。
-
keyword类型适用于索引结构化的字段,比如email地址、主机名、状态码和标签。如果字段需要进行过 滤(比如查找已发布博客中status属性为published的文章)、排序、聚合。keyword类型的字段只能通过精 确值搜索到。
创建明确类型的索引:
如果你要像之前旧版版本一样兼容自定义 type ,需要将 *i*nclude_type_name=true 携带
put http://202.193.56.222:9200/itcast?include_type_name=true
{
"settings":{
"index":{
"number_of_shards":"2",
"number_of_replicas":"0"
}
},
"mappings":{
"person":{
"properties":{
"name":{
"type":"text"
},
"age":{
"type":"integer"
},
"mail":{
"type":"keyword"
},
"hobby":{
"type":"text"
}
}
}
}
}
查看映射
GET /itcast/_mapping
插入数据
POST /itcast/_bulk
{"index":{"_index":"itcast","_type":"person"}}
{"name":"张三","age": 20,"mail": "[email protected]","hobby":"羽毛球、乒乓球、足球"}
{"index":{"_index":"itcast","_type":"person"}}
{"name":"李四","age": 21,"mail": "[email protected]","hobby":"羽毛球、乒乓球、足球、篮球"}
{"index":{"_index":"itcast","_type":"person"}}
{"name":"王五","age": 22,"mail": "[email protected]","hobby":"羽毛球、篮球、游泳、听音乐"}
{"index":{"_index":"itcast","_type":"person"}}
{"name":"赵六","age": 23,"mail": "[email protected]","hobby":"跑步、游泳"}
{"index":{"_index":"itcast","_type":"person"}}
{"name":"孙七","age": 24,"mail": "[email protected]","hobby":"听音乐、看电影"}
测试搜索
POST /itcast/person/_search
{
"query":{
"match":{
"hobby":"音乐"
}
}
}
结构化查询
term查询
term 主要用于精确匹配哪些值,比如数字,日期,布尔值或 not_analyzed 的字符串(未经分析的文本数据类型):
{ "term": { "age": 26 }}
{ "term": { "date": "2014-09-01" }}
{ "term": { "public": true }}
{ "term": { "tag": "full_text" }}
示例
POST /itcast/person/_search
{
"query":{
"term":{
"age":20
}
}
}
terms查询
terms 跟 term 有点类似,但 terms 允许指定多个匹配条件。 如果某个字段指定了多个值,那么文档需要一起去 做匹配:
{
"terms":{
"tag":[
"search",
"full_text",
"nosql"
]
}
}
示例:
POST /itcast/person/_search
{
"query":{
"terms":{
"age":[
20,
21
]
}
}
}
range查询
range 过滤允许我们按照指定范围查找一批数据:
{
"range":{
"age":{
"gte":20,
"lt":30
}
}
}
范围操作符包含:
-
gt : 大于
-
gte:: 大于等于
-
lt : 小于
-
lte: 小于等于
示例:
POST /itcast/person/_search
{
"query":{
"range":{
"age":{
"gte":20,
"lte":22
}
}
}
}
exists 查询
exists 查询可以用于查找文档中是否包含指定字段或没有某个字段,类似于SQL语句中的IS_NULL 条件
{
"exists": {
"field": "title"
}
}
这两个查询只是针对已经查出一批数据来,但是想区分出某个字段是否存在的时候使用。示例:
POST /haoke/user/_search
{
"query": {
"exists": { #必须包含
"field": "card"
}
}
}
match查询
match 查询是一个标准查询,不管你需要全文本查询还是精确查询基本上都要用到它。
如果你使用 match 查询一个全文本字段,它会在真正查询之前用分析器先分析match 一下查询字符:
{
"match": {
"tweet": "About Search"
}
}
如果用match 下指定了一个确切值,在遇到数字,日期,布尔值或者not_analyzed 的字符串时,它将为你搜索你 给定的值:
{ "match": { "age": 26 }}
{ "match": { "date": "2014-09-01" }}
{ "match": { "public": true }}
{ "match": { "tag": "full_text" }}
bool查询
-
bool 查询可以用来合并多个条件查询结果的布尔逻辑,它包含一下操作符:
-
must :: 多个查询条件的完全匹配,相当于 and 。
-
must_not :: 多个查询条件的相反匹配,相当于 not 。
-
should :: 至少有一个查询条件匹配, 相当于 or 。
这些参数可以分别继承一个查询条件或者一个查询条件的数组:
{
"bool":{
"must":{
"term":{
"folder":"inbox"
}
},
"must_not":{
"term":{
"tag":"spam"
}
},
"should":[
{
"term":{
"starred":true
}
},
{
"term":{
"unread":true
}
}
]
}
}
过滤查询
前面讲过结构化查询,Elasticsearch也支持过滤查询,如term、range、match等。
示例:查询年龄为20岁的用户。
POST /itcast/person/_search
{
"query":{
"bool":{
"filter":{
"term":{
"age":20
}
}
}
}
}
查询和过滤的对比
-
一条过滤语句会询问每个文档的字段值是否包含着特定值。
-
查询语句会询问每个文档的字段值与特定值的匹配程度如何。
-
一条查询语句会计算每个文档与查询语句的相关性,会给出一个相关性评分 _score,并且 按照相关性对匹 配到的文档进行排序。 这种评分方式非常适用于一个没有完全配置结果的全文本搜索。
-
一个简单的文档列表,快速匹配运算并存入内存是十分方便的, 每个文档仅需要1个字节。这些缓存的过滤结果集与后续请求的结合使用是非常高效的。
-
查询语句不仅要查找相匹配的文档,还需要计算每个文档的相关性,所以一般来说查询语句要比 过滤语句更耗时,并且查询结果也不可缓存。
建议:
做精确匹配搜索时,最好用过滤语句,因为过滤语句可以缓存数据。
中文分词
什么是分词
分词就是指将一个文本转化成一系列单词的过程,也叫文本分析,在Elasticsearch中称之为Analysis。
举例:我是中国人 --> 我/是/中国人
分词api
指定分词器进行分词
POST /_analyze
{
"analyzer":"standard",
"text":"hello world"
}
结果如下
在结果中不仅可以看出分词的结果,还返回了该词在文本中的位置。
指定索引分词
POST /itcast/_analyze
{
"analyzer": "standard",
"field": "hobby",
"text": "听音乐"
}
中文分词难点
中文分词的难点在于,在汉语中没有明显的词汇分界点,如在英语中,空格可以作为分隔符,如果分隔不正确就会造成歧义。如:
-
我/爱/炒肉丝
-
我/爱/炒/肉丝
常用中文分词器,IK、jieba、THULAC等,推荐使用IK分词器。
IK Analyzer是一个开源的,基于java语言开发的轻量级的中文分词工具包。从2006年12月推出1.0版开始,IKAnalyzer已经推出了3个大版本。最初,它是以开源项目Luence为应用主体的,结合词典分词和文法分析算法的中文分词组件。新版本的IK Analyzer 3.0则发展为面向Java的公用分词组件,独立于Lucene项目,同时提供了对Lucene的默认优化实现。
采用了特有的“正向迭代最细粒度切分算法“,具有80万字/秒的高速处理能力 采用了多子处理器分析模式,支持:英文字母(IP地址、Email、URL)、数字(日期,常用中文数量词,罗马数字,科学计数法),中文词汇(姓名、地名处理)等分词处理。 优化的词典存储,更小的内存占用。
IK分词器 Elasticsearch插件地址:GitHub - medcl/elasticsearch-analysis-ik: The IK Analysis plugin integrates Lucene IK analyzer into elasticsearch, support customized dictionary.
安装分词器
首先下载到最新的ik分词器:下载地址
下载完成后,使用xftp工具,拷贝到服务器上
#安装方法:将下载到的 es/plugins/ik 目录下 mkdir es/plugins/ik #解压 unzip elasticsearch-analysis-ik-7.9.1.zip #重启 ./bin/elasticsearch
我们通过日志,发现它已经成功加载了ik分词器插件
测试
POST /_analyze
{
"analyzer": "ik_max_word",
"text": "我是中国人"
}
我们发现ik分词器已经成功分词完成
全文搜索
全文搜索两个最重要的方面是:
-
相关性(Relevance) 它是评价查询与其结果间的相关程度,并根据这种相关程度对结果排名的一种能力,这 种计算方式可以是 TF/IDF 方法、地理位置邻近、模糊相似,或其他的某些算法。
-
分词(Analysis) 它是将文本块转换为有区别的、规范化的 token 的一个过程,目的是为了创建倒排索引以及查询倒排索引。
构造数据
ES 7.4 默认不在支持指定索引类型,默认索引类型是_doc
http://202.193.56.222:9200/itcast?include_type_name=true
{
"settings":{
"index":{
"number_of_shards":"1",
"number_of_replicas":"0"
}
},
"mappings":{
"person":{
"properties":{
"name":{
"type":"text"
},
"age":{
"type":"integer"
},
"mail":{
"type":"keyword"
},
"hobby":{
"type":"text",
"analyzer":"ik_max_word"
}
}
}
}
}
然后插入数据
POST http://202.193.56.222:9200/itcast/_bulk
{"index":{"_index":"itcast","_type":"person"}}
{"name":"张三","age": 20,"mail": "[email protected]","hobby":"羽毛球、乒乓球、足球"}
{"index":{"_index":"itcast","_type":"person"}}
{"name":"李四","age": 21,"mail": "[email protected]","hobby":"羽毛球、乒乓球、足球、篮球"}
{"index":{"_index":"itcast","_type":"person"}}
{"name":"王五","age": 22,"mail": "[email protected]","hobby":"羽毛球、篮球、游泳、听音乐"}
{"index":{"_index":"itcast","_type":"person"}}
{"name":"赵六","age": 23,"mail": "[email protected]","hobby":"跑步、游泳、篮球"}
{"index":{"_index":"itcast","_type":"person"}}
{"name":"孙七","age": 24,"mail": "[email protected]","hobby":"听音乐、看电影、羽毛球"}
单词搜索
POST /itcast/person/_search
{
"query":{
"match":{
"hobby":"音乐"
}
},
"highlight":{
"fields":{
"hobby":{
}
}
}
}
查询出来的结果如下,并且还带有高亮
过程说明:
-
检查字段类型
-
爱好 hobby 字段是一个 text 类型( 指定了IK分词器),这意味着查询字符串本身也应该被分词。
-
-
分析查询字符串 。
-
将查询的字符串 “音乐” 传入IK分词器中,输出的结果是单个项 音乐。因为只有一个单词项,所以 match 查询执行的是单个底层 term 查询。
-
-
查找匹配文档 。
-
用 term 查询在倒排索引中查找 “音乐” 然后获取一组包含该项的文档,本例的结果是文档:3 、5 。
-
-
为每个文档评分 。
-
用 term 查询计算每个文档相关度评分 _score ,这是种将 词频(term frequency,即词 “音乐” 在相关文档的hobby 字段中出现的频率)和 反向文档频率(inverse document frequency,即词 “音乐” 在所有文档的hobby 字段中出现的频率),以及字段的长度(即字段越短相关度越高)相结合的计算方式。
-
多词搜索
POST /itcast/person/_search
{
"query":{
"match":{
"hobby":"音乐 篮球"
}
},
"highlight":{
"fields":{
"hobby":{
}
}
}
}
可以看到,包含了“音乐”、“篮球”的数据都已经被搜索到了。可是,搜索的结果并不符合我们的预期,因为我们想搜索的是既包含“音乐”又包含“篮球”的用户,显然结果返回的“或”的关系。在Elasticsearch中,可以指定词之间的逻辑关系,如下:
POST /itcast/person/_search
{
"query":{
"match":{
"hobby":"音乐 篮球"
"operator":"and"
}
},
"highlight":{
"fields":{
"hobby":{
}
}
}
}
通过这样的话,就会让两个关键字之间存在and关系了
可以看到结果符合预期。
前面我们测试了“OR” 和 “AND”搜索,这是两个极端,其实在实际场景中,并不会选取这2个极端,更有可能是选取这种,或者说,只需要符合一定的相似度就可以查询到数据,在Elasticsearch中也支持这样的查询,通过 minimum_should_match来指定匹配度,如:70%;
示例:
{
"query":{
"match":{
"hobby":{
"query":"游泳 羽毛球",
"minimum_should_match":"80%"
}
}
},
"highlight": {
"fields": {
"hobby": {}
}
}
}
#结果:省略显示
"hits": {
"total": 4, #相似度为80%的情况下,查询到4条数据
"max_score": 1.621458,
"hits": [
}
#设置40%进行测试:
{
"query":{
"match":{
"hobby":{
"query":"游泳 羽毛球",
"minimum_should_match":"40%"
}
}
},
"highlight": {
"fields": {
"hobby": {}
}
}
}
#结果:
"hits": {
"total": 5, #相似度为40%的情况下,查询到5条数据
"max_score": 1.621458,
"hits": [
}
相似度应该多少合适,需要在实际的需求中进行反复测试,才可得到合理的值。
组合搜索
在搜索时,也可以使用过滤器中讲过的bool组合查询,示例:
POST /itcast/person/_search
{
"query":{
"bool":{
"must":{
"match":{
"hobby":"篮球"
}
},
"must_not":{
"match":{
"hobby":"音乐"
}
},
"should":[
{
"match":{
"hobby":"游泳"
}
}
]
}
},
"highlight":{
"fields":{
"hobby":{
}
}
}
}
上面搜索的意思是: 搜索结果中必须包含篮球,不能包含音乐,如果包含了游泳,那么它的相似度更高。
结果:
评分的计算规则
bool 查询会为每个文档计算相关度评分 _score , 再将所有匹配的 must 和 should 语句的分数 _score 求和,最后除以 must 和 should 语句的总数。
must_not 语句不会影响评分; 它的作用只是将不相关的文档排除。
默认情况下,should中的内容不是必须匹配的,如果查询语句中没有must,那么就会至少匹配其中一个。当然了,也可以通过minimum_should_match参数进行控制,该值可以是数字也可以的百分比。
示例:
POST /itcast/person/_search
{
"query":{
"bool":{
"should":[
{
"match":{
"hobby":"游泳"
}
},
{
"match":{
"hobby":"篮球"
}
},
{
"match":{
"hobby":"音乐"
}
}
],
"minimum_should_match":2
}
},
"highlight":{
"fields":{
"hobby":{
}
}
}
}
minimum_should_match为2,意思是should中的三个词,至少要满足2个。
权重
有些时候,我们可能需要对某些词增加权重来影响该条数据的得分。如下:
搜索关键字为“游泳篮球”,如果结果中包含了“音乐”权重为10,包含了“跑步”权重为2。
POST /itcast/person/_search
{
"query":{
"bool":{
"must":{
"match":{
"hobby":{
"query":"游泳篮球",
"operator":"and"
}
}
},
"should":[
{
"match":{
"hobby":{
"query":"音乐",
"boost":10
}
}
},
{
"match":{
"hobby":{
"query":"跑步",
"boost":2
}
}
}
]
}
},
"highlight":{
"fields":{
"hobby":{
}
}
}
}
ElasticSearch集群
集群节点
ELasticsearch的集群是由多个节点组成的,通过cluster.name设置集群名称,并且用于区分其它的集群,每个节点通过node.name指定节点的名称。
在Elasticsearch中,节点的类型主要有4种:
-
master节点
-
配置文件中node.master属性为true(默认为true),就有资格被选为master节点。master节点用于控制整个集群的操作。比如创建或删除索引,管理其它非master节点等。
-
-
data节点
-
配置文件中node.data属性为true(默认为true),就有资格被设置成data节点。data节点主要用于执行数据相关的操作。比如文档的CRUD。
-
-
客户端节点
-
配置文件中node.master属性和node.data属性均为false。
-
该节点不能作为master节点,也不能作为data节点。
-
可以作为客户端节点,用于响应用户的请求,把请求转发到其他节点
-
-
部落节点
-
当一个节点配置tribe.*的时候,它是一个特殊的客户端,它可以连接多个集群,在所有连接的集群上执行 搜索和其他操作。
-
搭建集群
#启动3个虚拟机,分别在3台虚拟机上部署安装Elasticsearch mkdir /itcast/es-cluster #分发到其它机器 scp -r es-cluster [email protected]:/itcast #node01的配置: cluster.name: es-itcast-cluster node.name: node01 node.master: true node.data: true network.host: 0.0.0.0 http.port: 9200 discovery.zen.ping.unicast.hosts: ["192.168.40.133","192.168.40.134","192.168.40.135"] # 最小节点数 discovery.zen.minimum_master_nodes: 2 # 跨域专用 http.cors.enabled: true http.cors.allow-origin: "*" #node02的配置: cluster.name: es-itcast-cluster node.name: node02 node.master: true node.data: true network.host: 0.0.0.0 http.port: 9200 discovery.zen.ping.unicast.hosts: ["192.168.40.133","192.168.40.134","192.168.40.135"] discovery.zen.minimum_master_nodes: 2 http.cors.enabled: true http.cors.allow-origin: "*" #node03的配置: cluster.name: es-itcast-cluster node.name: node02 node.master: true node.data: true network.host: 0.0.0.0 http.port: 9200 discovery.zen.ping.unicast.hosts: ["192.168.40.133","192.168.40.134","192.168.40.135"] discovery.zen.minimum_master_nodes: 2 http.cors.enabled: true http.cors.allow-origin: "*" #分别启动3个节点 ./elasticsearch
查看集群
分发阶段由以下步骤构成:
-
协调节点辨别出哪个document需要取回,并且向相关分片发出GET 请求。
-
每个分片加载document并且根据需要丰富(enrich)它们,然后再将document返回协调节点。
-
一旦所有的document都被取回,协调节点会将结果返回给客户端。
Java客户端
在Elasticsearch中,为java提供了2种客户端,一种是REST风格的客户端,另一种是Java API的客户端
REST客户端
Elasticsearch提供了2种REST客户端,一种是低级客户端,一种是高级客户端。
-
Java Low Level REST Client:官方提供的低级客户端。该客户端通过http来连接Elasticsearch集群。用户在使 用该客户端时需要将请求数据手动拼接成Elasticsearch所需JSON格式进行发送,收到响应时同样也需要将返回的JSON数据手动封装成对象。虽然麻烦,不过该客户端兼容所有的Elasticsearch版本。
-
Java High Level REST Client:官方提供的高级客户端。该客户端基于低级客户端实现,它提供了很多便捷的 API来解决低级客户端需要手动转换数据格式的问题。
构造数据
POST /haoke/house/_bulk
{"index":{"_index":"haoke","_type":"house"}}
{"id":"1001","title":"整租 · 南丹大楼 1居室 7500","price":"7500"}
{"index":{"_index":"haoke","_type":"house"}}
{"id":"1002","title":"陆家嘴板块,精装设计一室一厅,可拎包入住诚意租。","price":"8500"}
{"index":{"_index":"haoke","_type":"house"}}
{"id":"1003","title":"整租 · 健安坊 1居室 4050","price":"7500"}
{"index":{"_index":"haoke","_type":"house"}}
{"id":"1004","title":"整租 · 中凯城市之光+视野开阔+景色秀丽+拎包入住","price":"6500"}
{"index":{"_index":"haoke","_type":"house"}}
{"id":"1005","title":"整租 · 南京西路品质小区 21213三轨交汇 配套齐* 拎包入住","price":"6000"}
{"index":{"_index":"haoke","_type":"house"}}
{"id":"1006","title":"祥康里 简约风格 *南户型 拎包入住 看房随时","price":"7000"}
REST低级客户端
创建项目,加入依赖
4.0.0 org.example Study_ElasticSearch_Code 1.0-SNAPSHOT org.apache.maven.plugins maven-compiler-plugin 7 7 org.elasticsearch.client elasticsearch-rest-client 6.8.5 junit junit 4.12 test com.fasterxml.jackson.core jackson-databind 2.11.1
编写测试类
import com.fasterxml.jackson.core.JsonProcessingException;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import org.apache.http.HttpHost;
import org.apache.http.util.EntityUtils;
import org.elasticsearch.client.Request;
import org.elasticsearch.client.Response;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RestClient;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RestClientBuilder;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* 使用低级客户端 访问
*
* @author: 陌溪
* @create: 2020-09-23-16:33
*/
public class ESApi {
private RestClient restClient;
private static final ObjectMapper MAPPER = new ObjectMapper();
/**
* 初始化
*/
public void init() {
RestClientBuilder restClientBuilder = RestClient.builder(new HttpHost("202.193.56.222", 9200, "http"));
this.restClient = restClientBuilder.build();
}
/**
* 查询集群状态
*/
public void testGetInfo() throws IOException {
Request request = new Request("GET", "/_cluster/state");
request.addParameter("pretty", "true");
Response response = this.restClient.performRequest(request);
System.out.println(response.getStatusLine());
System.out.println(EntityUtils.toString(response.getEntity()));
}
/**
* 根据ID查询数据
* @throws IOException
*/
public void testGetHouseInfo() throws IOException {
Request request = new Request("GET", "/haoke/house/Z3CduXQBYpWein3CRFug");
request.addParameter("pretty", "true");
Response response = this.restClient.performRequest(request);
System.out.println(response.getStatusLine());
System.out.println(EntityUtils.toString(response.getEntity()));
}
public void testCreateData() throws IOException {
Request request = new Request("POST", "/haoke/house");
Map data = new HashMap<>();
data.put("id", "2001");
data.put("title", "张江高科");
data.put("price", "3500");
// 写成JSON
request.setJsonEntity(MAPPER.writeValueAsString(data));
Response response = this.restClient.performRequest(request);
System.out.println(response.getStatusLine());
System.out.println(EntityUtils.toString(response.getEntity()));
}
// 搜索数据
public void testSearchData() throws IOException {
Request request = new Request("POST", "/haoke/house/_search");
String searchJson = "{\"query\": {\"match\": {\"title\": \"拎包入住\"}}}";
request.setJsonEntity(searchJson);
request.addParameter("pretty","true");
Response response = this.restClient.performRequest(request);
System.out.println(response.getStatusLine());
System.out.println(EntityUtils.toString(response.getEntity()));
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ESApi esApi = new ESApi();
esApi.init();
// esApi.testGetInfo();
// esApi.testGetHouseInfo();
esApi.testCreateData();
}
}
REST高级客户端
创建项目,引入依赖
org.elasticsearch.client elasticsearch-rest-high-level-client 6.8.5
编写测试用例
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import org.apache.http.HttpHost;
import org.apache.http.util.EntityUtils;
import org.elasticsearch.action.ActionListener;
import org.elasticsearch.action.delete.DeleteRequest;
import org.elasticsearch.action.delete.DeleteResponse;
import org.elasticsearch.action.get.GetRequest;
import org.elasticsearch.action.get.GetResponse;
import org.elasticsearch.action.index.IndexRequest;
import org.elasticsearch.action.index.IndexResponse;
import org.elasticsearch.action.search.SearchRequest;
import org.elasticsearch.action.search.SearchResponse;
import org.elasticsearch.action.update.UpdateRequest;
import org.elasticsearch.action.update.UpdateResponse;
import org.elasticsearch.client.*;
import org.elasticsearch.common.Strings;
import org.elasticsearch.common.unit.TimeValue;
import org.elasticsearch.index.query.QueryBuilders;
import org.elasticsearch.search.SearchHit;
import org.elasticsearch.search.SearchHits;
import org.elasticsearch.search.builder.SearchSourceBuilder;
import org.elasticsearch.search.fetch.subphase.FetchSourceContext;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
* ES高级客户端
*
* @author: 陌溪
* @create: 2020-09-23-16:56
*/
public class ESHightApi {
private RestHighLevelClient client;
public void init() {
RestClientBuilder restClientBuilder = RestClient.builder(
new HttpHost("202.193.56.222", 9200, "http"));
this.client = new RestHighLevelClient(restClientBuilder);
}
public void after() throws Exception {
this.client.close();
}
/**
* 新增文档,同步操作
*
* @throws Exception
*/
public void testCreate() throws Exception {
Map data = new HashMap<>();
data.put("id", "2002");
data.put("title", "南京西路 拎包入住 一室一厅");
data.put("price", "4500");
IndexRequest indexRequest = new IndexRequest("haoke", "house")
.source(data);
IndexResponse indexResponse = this.client.index(indexRequest,
RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
System.out.println("id->" + indexResponse.getId());
System.out.println("index->" + indexResponse.getIndex());
System.out.println("type->" + indexResponse.getType());
System.out.println("version->" + indexResponse.getVersion());
System.out.println("result->" + indexResponse.getResult());
System.out.println("shardInfo->" + indexResponse.getShardInfo());
}
/**
* 异步创建文档
* @throws Exception
*/
public void testCreateAsync() throws Exception {
Map data = new HashMap<>();
data.put("id", "2003");
data.put("title", "南京东路 最新房源 二室一厅");
data.put("price", "5500");
IndexRequest indexRequest = new IndexRequest("haoke", "house")
.source(data);
this.client.indexAsync(indexRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT, new
ActionListener() {
@Override
public void onResponse(IndexResponse indexResponse) {
System.out.println("id->" + indexResponse.getId());
System.out.println("index->" + indexResponse.getIndex());
System.out.println("type->" + indexResponse.getType());
System.out.println("version->" + indexResponse.getVersion());
System.out.println("result->" + indexResponse.getResult());
System.out.println("shardInfo->" + indexResponse.getShardInfo());
}
@Override
public void onFailure(Exception e) {
System.out.println(e);
}
});
System.out.println("ok");
Thread.sleep(20000);
}
/**
* 查询
* @throws Exception
*/
public void testQuery() throws Exception {
GetRequest getRequest = new GetRequest("haoke", "house",
"GkpdE2gBCKv8opxuOj12");
// 指定返回的字段
String[] includes = new String[]{"title", "id"};
String[] excludes = Strings.EMPTY_ARRAY;
FetchSourceContext fetchSourceContext =
new FetchSourceContext(true, includes, excludes);
getRequest.fetchSourceContext(fetchSourceContext);
GetResponse response = this.client.get(getRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
System.out.println("数据 -> " + response.getSource());
}
/**
* 判断是否存在
*
* @throws Exception
*/
public void testExists() throws Exception {
GetRequest getRequest = new GetRequest("haoke", "house",
"GkpdE2gBCKv8opxuOj12");
// 不返回的字段
getRequest.fetchSourceContext(new FetchSourceContext(false));
boolean exists = this.client.exists(getRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
System.out.println("exists -> " + exists);
}
/**
* 删除数据
*
* @throws Exception
*/
public void testDelete() throws Exception {
DeleteRequest deleteRequest = new DeleteRequest("haoke", "house",
"GkpdE2gBCKv8opxuOj12");
DeleteResponse response = this.client.delete(deleteRequest,
RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
System.out.println(response.status());// OK or NOT_FOUND
}
/**
* 更新数据
*
* @throws Exception
*/
public void testUpdate() throws Exception {
UpdateRequest updateRequest = new UpdateRequest("haoke", "house",
"G0pfE2gBCKv8opxuRz1y");
Map data = new HashMap<>();
data.put("title", "张江高科2");
data.put("price", "5000");
updateRequest.doc(data);
UpdateResponse response = this.client.update(updateRequest,
RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
System.out.println("version -> " + response.getVersion());
}
/**
* 测试搜索
*
* @throws Exception
*/
public void testSearch() throws Exception {
SearchRequest searchRequest = new SearchRequest("haoke");
searchRequest.types("house");
SearchSourceBuilder sourceBuilder = new SearchSourceBuilder();
sourceBuilder.query(QueryBuilders.matchQuery("title", "拎包入住"));
sourceBuilder.from(0);
sourceBuilder.size(5);
sourceBuilder.timeout(new TimeValue(60, TimeUnit.SECONDS));
searchRequest.source(sourceBuilder);
SearchResponse search = this.client.search(searchRequest,
RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
System.out.println("搜索到 " + search.getHits().totalHits + " 条数据.");
SearchHits hits = search.getHits();
for (SearchHit hit : hits) {
System.out.println(hit.getSourceAsString());
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ESHightApi esHightApi = new ESHightApi();
esHightApi.init();
esHightApi.testCreate();
}
}