00|Java中常见错误或不清楚
00. 多变量声明并初始化
- 同时声明同类型的多变量
String a = "Hello", c = "hello";
int x = 5, y = 5;
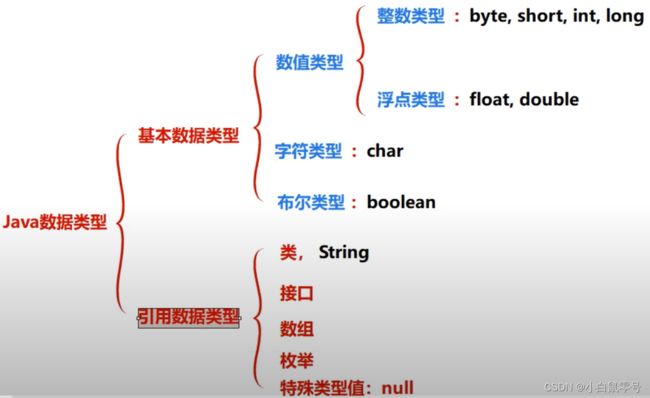
01. 变量类型
01.0 浮点类型
- 默认是double类型,如果需要指定float类型,可以
float f = 1.0F;
01.1 类型装换
- 如果将大的类型转为小的类型,可以用强制转换,但是会丢失精度。
01.2 引用类型
- 注意:类,String,接口,数组这些都属于引用类型。
02. 运算符
02.0 除法运算注意点
1/2 = 0分析:除法按照最大的类型显示。这里两个数都是Int类型,所以会舍弃掉小数- 除法是没有四舍五入的。
1.0/2 = 0.5或者1/2.0 = 0.5
02.1 赋值运算符注意点
- 使用赋值运算符,数据类型不会发生变化
- eg:
byte b1=10; b1 = b1+10;这个就会犯大类型转小类型的错误 - eg:
b1 += 10;
02.2 短路运算符注意点
- 会根据第一个条件表达式的结果来判断,是否执行第二个条件表达式
- 验证程序:(如果j变为了21,则代表后面判断被执行了)
int i=10,j=20;
boolean result = (i>10) && (++j>30);
System.out.println(result);
System.out.println(j);
03 抽象方法&&抽象类
- 抽象方法:只声明,没有实现的方法
abstract 返回值类型 方法名(参数)
- 抽象类:不完整的类
abstract class 类名- 抽象类是无法直接构造对象的,即
Person p = new Person()这种对于抽象类来说是不行的。需要先继承,在构造:
class Chinese extends Person{……}
Chinese p = new Person();
- 类中只要含抽象方法,这个类就是抽象类(要加abstract)
abstract class Person{……} - 类是抽象类,单它的方法不一定是抽象方法。
- final修饰的方法是不能被重写的,所以abstract和final不同时修饰
03.0 例子
abstract class Person{
public abstract void eat();
}
class Chinese extends Person{
public void eat(){
Sysout.out.println("使用筷子吃饭")
}
}
Chinese p = new Chinese();
p.eat();
04. 接口(interface)
- 语法:
interface 接口名称{规则属性,规则的行为} - 接口是抽象的
- 属性是静态的,行为是抽象的
- 接口和类是两个层面的东西
- 接口可继承其他接口
- 类的对象需要遵循接口,在java中,则称之为实现(implement)。即:类需要实现(多个)接口。
04.0 案例
interface USBInterface{
}
// 下面的规则符合USBInterface,行为就是powerXXX();
// 接口中的行为powerXXX是抽象的
interface USBSupply extends USBInterface{
public void powerSupply();
}
interface USBReceive extends USBInterface{
public void powerReceive();
}
// 电脑类中有两个USB接口,接口的功能是提供电源
class Computer implements USBSupply{
public USBReceive usb1;
public USBReceive usb2;
public void powerSupply(){
System.out.println("电脑提供能源");
usb1.powerReceive();
usb2.powerReceive();
}
}
// 灯
class Light implements USBReceive{
public void powerReceive(){
System.out.println("电灯接受能源");
}
}
// main中实现
Computer c = new Computer();
Light light = new Light();
c.usb1 = light;
c.powerSupply();
05. Bean规范
- 类要求必须含有无参,公共的构造方法
- 属性必须私有化,有提供getXXX(),setXXX()方法
06. 对象数组
- 声明方式:类型[] 变量 即:
String[] names - 数组创建:new 类型[容量] 即:
new String[3]
String[] names = new String[3];
// 或者声明时,直接赋值
String[] nums = {"1","3","5"};
07. 字符串类
- 源于
java.lang.String,系统自动加载的
String name = "这是字符串";
07.0 比较
- 完全相等(包括大小写)
a.equals(b) - 相等(不考虑大小写)
a.equalsIgnoreCase(b) - 比较大小:
a.compareTo(b)
07.1 截取(substring)
String s = "01234 6789";
s.substring(0,3); //截取0-2,不包含3
s.substring(6);//只传一个参数,表示截取到末尾。6-9
07.2 分割(split)
String s = "01234 6789";
String[] s1 = s.split(" ");//按空格来分割字符串
System.out.println(s1.length);
for(String s2:s1){
System.out.println(s2);
}
07.3 去掉空格(trim)
- 这是去掉字符串首尾空格
String s = " H e l l o ,mygoodfriend ";
System.out.println(s.trim());
System.out.println("!"+s.trim()+"!");
07.4 替换(replace、replaceAll)
- 替换所有:replace
String s = "Hello World, World Li";
System.out.println(s.replace("World","Java");
- 按照自己的规则替换:replaceAll
如果我想将World,Li这两个都替换成Java,就按下面操作:
String s = "Hello World, World Li";
System.out.println(s.replaceAll("World|Li","Java");
07.5 大小写转换(toLowerCase、toUpperCase)
String s = "Hello mygoodfriend";
System.out.println(s.toLowerCase());
System.out.println(s.toUpperCase());
如果只想将username的第一个u变成大写,怎么操作:
String name = "username";
String s1 = name.substring(0,1);
String s2 = name.substring(1);
System.out.println(s1.toUpperCase() + s2);
07.6 查找(charAt、indexOf)
- charAt:通过索引找到指定位置的字符
String s = "Hello, my friends";
System.out.println(s.charAt(0));
- indexOf:查找字符串第一次出现的下标
String s = "Hello, my friends";
System.out.println(s.indexOf("my"));
- lastIndexOf:获取字符串最后一次出现的下标
String s = "Hello, my friends";
System.out.println(s.lastIndexOf("friends"));
07.7 判断包含(contains())
- contains:判断是否包含指定的字符串,返回布尔类型
String s = "Hello, my friends";
System.out.println(s.contains("mygood"));
System.out.println(s.contains("friends"));
07.8 判断空(isEmpty())
String s = "Hello";
System.out.println(s.isEmpty());
String str = "";
System.out.println(str.isEmpty());
08. 字符串StringBuilder
- 这个StringBuilder是为了优化拼接操作时应持续创建新的空间造成的利用率不高。
- StringBuilder 构建字符串,是个类,提供了大量的字符串操作。
StringBuilder s = new StringBuilder();
for(int i=0;i<100;++i){
s.append(i);
}
System.out.println(s.toString());
- 上面代码的效率就是比下面的效率高
String s = "";
for(int i=0;i<100;++i){
s = s+i;
}
System.out.println(s);
08.0 添加(append())
StringBuilder s = new StringBuilder();
s.append("abc");
08.1 转成字符串(toString())
StringBuilder s = new StringBuilder();
s.append("abc");
System.out.println(s.toString());
08.1 长度(length())
StringBuilder s = new StringBuilder();
s.append("abc");
System.out.println(s.length());
08.2 翻转(reverse())
StringBuilder s = new StringBuilder();
s.append("abc");
System.out.println(s.reverse());
08.3 插入(insert())
StringBuilder s = new StringBuilder();
s.append("012");
System.out.println(s.insert(1,"dr")); // 在下标为1的地方插入字符串dr