Lodash——使用与实例
1. 简介
- Lodash是一个一致性、模块化、高性能的JavaScript实用库。
- Lodash通过降低array、number、objects、string等等的使用难度从而让JavaScript变得简单。Lodash的模块方法,非常适用于:
- 遍历array、object 和 string
- 对值进行操作和检测
- 创建符合功能的函数
1.1 安装
- 浏览器环境:
- npm安装:
npm i --save lodash - Node.js环境中:
- // Load the full build.
var _ = require('lodash'); - // Load the core build.
var _ = require('lodash/core'); - // Load the FP build for immutable auto-curried iteratee-first data-last methods.
var fp = require('lodash/fp'); - // Load method categories.
var array = require('lodash/array');
var object = require('lodash/fp/object'); - // Cherry-pick methods for smaller browserify/rollup/webpack bundles.
var at = require('lodash/at');
var curryN = require('lodash/fp/curryN');
- // Load the full build.
2. API介绍之数组
2.1 _.drop(array, [n=1])
- 创建一个切片数组,去除array前面的n个元素。(n默认为1)。返回array剩余切片。
2.1.1 API讲解示例
_.drop([1, 2, 3]);
// => [2, 3]
_.drop([1, 2, 3], 2);
// => [3]
_.drop([1, 2, 3], 5);
// => []
_.drop([1, 2, 3], 0);
// => [1, 2, 3]
2.1.2 业务场景:
行情部分本身后端会返回全部规格信息数组,但只要求展示两个规格品类信息,若有三个及以上规格,默认展示除"通货"外的前两个需求。通货默认在第一个,所以我们可以通过 _.drop(arr, 1)来实现。
webapp-hq中:
this.specs = res.result.spec.slice(1);
---To---
this.specs = _.drop(res.result.spec, 1);
2.1.3 相似API
_.dropRight(array, [n=1])从末尾开始进行删除_.dropWhile(array, [predicate=_.identity])从头开始删除迭代器指定情形下的值,返回剩余值_.dropRightWhile(array, [predicate=_.identity])同上功能,只不过从后面开始删除
2.1.3 dropWhile对应业务场景 TODO:待补充
类似于filter,返回一堆数据,过滤出自己真正想要的数据,找个例子
2.2 _.head(array)
获取数组array的第一个元素。
2.2.1 API讲解示例
_.head([1, 2, 3]);
// => 1
_.head([]);
// => undefined
2.2.2 业务场景
if (!this.specId || this.specId === 0 || this.specId === "0") {
this.specId =
this.specs &&
this.specs.length &&
this.specs[0] &&
this.specs[0].id;
console.log(this.specId, "自己获取的");
// this.specId = _.head(this.specs) && _.head(this.specs).id;
// console.log(this.specId, "lodash获取的");
this.$emit("changeSpec", this.specId);
}
2.2.3 相似API
_.first别名
2.3 _.take(array, [n=1])
创建一个数组切片,从array数组的起始元素开始提取n个元素。
2.3.1 API 讲解示例
_.take([1, 2, 3]);
// => [1]
_.take([1, 2, 3], 2);
// => [1, 2]
_.take([1, 2, 3], 5);
// => [1, 2, 3]
_.take([1, 2, 3], 0);
// => []
2.3.2 业务场景
- 当规格较多时,我们只想保留前几条数据用于展示时,可以使用该API
- 我们可以先切掉头部内容,之后再进行take提取
this.specs = _.take(_.drop(res.result.spec, 1));
- 若最后规格表示最新出现的,可以通过takeRight进行提取
2.3.3 相似API
_.takeRight(array, [n=1])创建一个数组切片,从array数组的最后一个元素开始提取n个元素。_.takeRightWhile(array, [predicate=_.identity])从array数组的最后一个元素开始提取元素,直到 predicate 返回假值。predicate 会传入三个参数: (value, index, array)。_.takeWhile(array, [predicate=_.identity])从array数组的起始元素开始提取元素,,直到 predicate 返回假值。predicate 会传入三个参数: (value, index, array)。
3. API介绍之集合
3.1 _.filter(collection, [predicate=_.identity])
遍历 collection(集合)元素,返回 predicate(断言函数)返回真值 的所有元素的数组。 predicate(断言函数)调用三个参数:(value, index|key, collection)。
3.1.1 API讲解示例
var users = [
{ 'user': 'barney', 'age': 36, 'active': true },
{ 'user': 'fred', 'age': 40, 'active': false }
];
_.filter(users, function(o) { return !o.active; });
// => objects for ['fred']
// The `_.matches` iteratee shorthand.
_.filter(users, { 'age': 36, 'active': true });
// => objects for ['barney']
// The `_.matchesProperty` iteratee shorthand.
_.filter(users, ['active', false]);
// => objects for ['fred']
// The `_.property` iteratee shorthand.
_.filter(users, 'active');
// => objects for ['barney']
3.1.2 业务场景
当返回一个规格列表/任意对象列表,需要按照要求来过滤其中自己需要的数据,这时候需要用到_.filter进行过滤比较方便。
const testArr = [
{
id: 1,
name: '二两',
isShow: true
},
{
id: 2,
name: '四两',
isShow: false
},
{
id: 3,
name: '六两',
isShow: true
},
{
id: 4,
name: '八两',
isShow: true
},
{
id: 5,
name: '十两',
isShow: false
},
]
const filterArr = testArr.filter((item) => item.isShow)
const filterArr = _.filter(testArr, ['isShow', true])
const filterArr = _.filter(testArr, 'isShow')
3.2 _.find(collection, [predicate=_.identity], [fromIndex=0])
遍历 collection(集合)元素,返回 predicate(断言函数)第一个返回真值的第一个元素。predicate(断言函数)调用3个参数: (value, index|key, collection)。
3.2.1 API讲解示例
var users = [
{ 'user': 'barney', 'age': 36, 'active': true },
{ 'user': 'fred', 'age': 40, 'active': false },
{ 'user': 'pebbles', 'age': 1, 'active': true }
];
_.find(users, function(o) { return o.age < 40; });
// => object for 'barney'
// The `_.matches` iteratee shorthand.
_.find(users, { 'age': 1, 'active': true });
// => object for 'pebbles'
// The `_.matchesProperty` iteratee shorthand.
_.find(users, ['active', false]);
// => object for 'fred'
// The `_.property` iteratee shorthand.
_.find(users, 'active');
// => object for 'barney'
3.2.2 业务场景
大讲堂中,detail接口中返回了多个模块的数据,以code为标识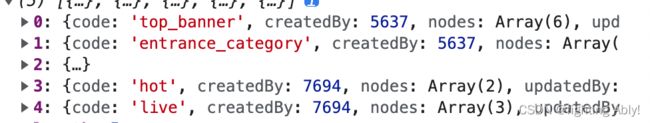
此时,我们将数据分别提取出来进行使用。
历史用法:
this.headerList =
res.data.find((item) => {
return item.code === "top_banner";
}).nodes || [];
lodash用法:
this.headerList = _.find(res.data, ['code', 'top_banner']).nodes || []
3.2.3 相似API
_.findLast(collection, [predicate=_.identity], [fromIndex=collection.length-1])类似于find,查到一个就停止,不同之处在于find是从左向右查找,findLast是从右向左查找。
3.3 _.sample(collection)
从collection(集合)中获得一个随机元素。
3.3.1 API讲解示例
_.sample([1, 2, 3, 4]);
// => 2
const arr = [
{
name: 'lihua',
age: 12,
},
{
name: 'xiaoming',
age: 32,
},
{
name: 'wang',
age: 28,
},
];
_.sample(arr)
// => {name: 'lihua', age: 12}
3.3.2 业务场景
平台专享处的轮播,会随机选取姓氏进行处理,通过Math.random()方式,我们可以通过_.sample来进行改写。
surnameArr 常见姓氏列表(取样集合)
const randomIdx = Math.floor(Math.random() * 43);
return surnameArr[randomIdx];
return _.sample(surnameArr);
3.3.3 相似API
_.sampleSize(collection, [n=1])从collection集合中随机获取n个元素
_.sampleSize([1, 2, 3], 2);
// => [3, 1]
_.sampleSize([1, 2, 3], 4);
// => [2, 3, 1]
4. API介绍之Seq
5. API介绍之语言
5.1 _.eq(value, other)
执行SameValueZero 比较两者的值,来确定它们是否相等。
5.1.1 API讲解示例
var object = { 'a': 1 };
var other = { 'a': 1 };
_.eq(object, object);
// => true
_.eq(object, other);
// => false
_.eq('a', 'a');
// => true
_.eq('a', Object('a'));
// => false
_.eq(NaN, NaN);
// => true
5.1.2 业务场景
当有需求需要判断两个值是否相等时,如:判断当前是否是vip
!_.eq(this.customer_vip, 0);
this.customer_vip !== 0;
5.1.3 相似API
_.gt(value, other)检查value是否大于other_.gte(value, other)检查value是够大于等于other_.isEqual(value, other)执行深比较来确定两者的值是否相等。支持比较 arrays, array buffers, booleans, date objects, error objects, maps, numbers, Object objects, regexes, sets, strings, symbols, 以及 typed arrays. Object 对象值比较自身的属性,不包括继承的和可枚举的属性。 不支持函数和DOM节点比较。_.isEqualWith(value, other, [customizer])这个方法类似_.isEqual。 除了它接受一个 customizer 用来定制比较值。_.lt(value, other)检查 value 是否小于 other。_.lte(value, other)检查 value 是否小于等于 other。
5.2 _.isEmpty(value)
检查 value 是否为一个空对象,集合,映射或者set。 判断的依据是除非是有枚举属性的对象,length 大于 0 的 arguments object, array, string 或类jquery选择器。
5.2.1 API讲解示例
_.isEmpty(null);
// => true
_.isEmpty(true);
// => true
_.isEmpty(1);
// => true
_.isEmpty([1, 2, 3]);
// => false
_.isEmpty({ 'a': 1 });
// => false
5.1.2 业务场景
我们经常为了兼容,获取数组中第一个元素进行压中或发送下一个网络请求的操作,之前是要判断这个数组是否存在,并且数组的length属性。&&下来就会使整个判断条件变得十分的长和复杂,此时,可以通过isEmpty来进行判断。
this.trend_id =
this.trendChartOptions &&
this.trendChartOptions.length &&
this.trendChartOptions[0] &&
this.trendChartOptions[0].id;
this.trendChartActive = this.trendChartOptions[0];
-----
this.trend_id =
!_.isEmpty(this.trendChartOptions) &&
this.trendChartOptions[0].id;
6. API介绍之对象
6.1 _.get(object, path, [defaultValue])
根据 object对象的path路径获取值。 如果解析 value 是 undefined 会以 defaultValue 取代。返回解析后的值。
6.1.1 API讲解示例
var object = { 'a': [{ 'b': { 'c': 3 } }] };
_.get(object, 'a[0].b.c');
// => 3
_.get(object, ['a', '0', 'b', 'c']);
// => 3
_.get(object, 'a.b.c', 'default');
// => 'default'
6.1.2 业务场景
在进行图表数据存储时对象进行存储,key作为几天的id,value则是这一天对应的数据。
const daysMap = {
0: ['七', '天', '图', '表', '数', '据'],
3: ['三', '十', '天', '图', '表', '数', '据'],
6: ['六', '十', '天', '图', '表', '数', '据'],
}
console.log(_.get(daysMap, 0, ['默', '认', '图', '表', '数', '据']));
这样,我们在点击对应的activeOptions(七天、30天、60天)时,即可获取当天对应的id,然后通过id就可以获取到当天对应的数据。
6.1.3 相似API
-
_.result(object, path, [defaultValue])这个方法类似_.get, 除了如果解析到的值是一个函数的话,就绑定 this 到这个函数并返回执行后的结果。 -
_.set(object, path, value)设置 object对象中对应 path 属性路径上的值,如果path不存在,则创建。 缺少的索引属性会创建为数组,而缺少的属性会创建为对象。 使用_.setWith 定制path创建。 -
_.setWith(object, path, value, [customizer])这个方法类似_.set,除了它接受一个 customizer,调用生成对象的 path。 如果 customizer 返回 undefined 将会有它的处理方法代替。 customizer 调用3个参数: (nsValue, key, nsObject)。
6.2 _.invoke(object, path, [args])
调用object对象path上的方法。
6.2.1 API讲解示例
var object = { 'a': [{ 'b': { 'c': [1, 2, 3, 4] } }] };
_.invoke(object, 'a[0].b.c.slice', 1, 3);
// => [2, 3]
6.2.2 业务场景
之前有一次后端处理数据有误,7天和30天请求时都返回了30天的数据,因为后期开发需要时间,所以需要前端暂时将返回的30天数据截取7天来进行使用,此时,我们就可以通过invoke进行截取。
const daysDataMap = {
0: {
trend: {
price_list: [
{
tem: "1.01",
time: "04-26",
},
{
tem: "1.81",
time: "04-27",
},
{
tem: "2.01",
time: "04-28",
},
{
tem: "1.51",
time: "04-29",
},
{
tem: "0.91",
time: "04-30",
},
{
tem: "1.31",
time: "05-01",
},
{
tem: "1.11",
time: "05-02",
},
]
}
}
}
console.log(_.invoke(daysDataMap, '0.trend.price_list.slice', 0, 3))
6.3 _.omitBy(object, [predicate=_.identity])
这个方法一个对象,这个对象忽略 predicate(断言函数)判断不是真值的属性后,object自身和继承的可枚举属性组成。predicate调用与2个参数:(value, key)。
6.3.1 API讲解示例
var object = { 'a': 1, 'b': '2', 'c': 3 };
_.omitBy(object, _.isNumber);
// => { 'b': '2' }
6.3.2 业务场景
过滤接口参数,若不同场景有的参数存在,则不必传给后端。
let queryParams = {
stateCode: options.stateCode,
customerId: options.qrid,
};
之前过滤参数写法:
Object.entries(queryParams).forEach((f) => {
if (!(f && f.length && f[1])) {
delete queryParams[f[0]];
}
});
console.log(queryParams, "之前方式过滤后的参数值");
lodash 过滤参数写法:
const lodashRes = _.omitBy(queryParams, _.isEmpty);
console.log(lodashRes, "lodash处理后的值");
6.3.3 相似API
_.omit(object, [props])这个方法一个对象,这个对象由忽略属性之外的object自身和继承的可枚举属性组成。(注:可以理解为删除object对象的属性)。
var object = { 'a': 1, 'b': '2', 'c': 3 };
_.omit(object, ['a', 'c']);
// => { 'b': '2' }
_.pick(object, [props])创建一个从 object 中选中的属性的对象。
var object = { 'a': 1, 'b': '2', 'c': 3 };
_.pick(object, ['a', 'c']);
// => { 'a': 1, 'c': 3 }
_.pickBy(object, [predicate=_.identity])创建一个对象,这个对象组成为从 object 中经 predicate 判断为真值的属性。 predicate调用2个参数:(value, key)。
var object = { 'a': 1, 'b': '2', 'c': 3 };
_.pickBy(object, _.isNumber);
// => { 'a': 1, 'c': 3 }
Seq、函数
总结:
- 处理数组对象时的 js 方法例如 forEach、map、filter、reduce、find等,使用lodash封装好的会更加整洁、代码行数更少。
注意事项
注意事项一: lodash在不同平台上的使用情况
- 微信小程序可通过该方法引入lodash
如果有用,点个赞呗~
总结用法,希望可以帮助到你,
我是Ably,你无须超越谁,只要超越昨天的自己就好~