SpringBoot
创建SpringBoot项目
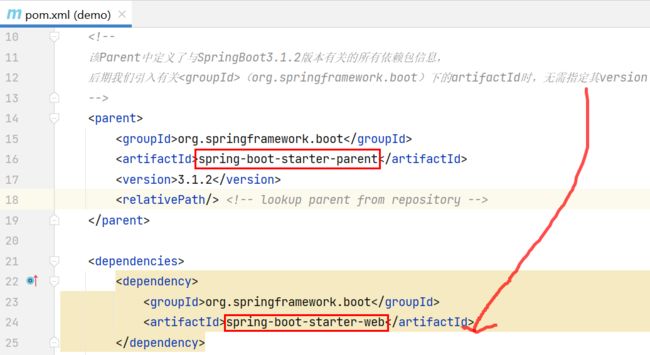
pom.xml 文件
启动程序类【DemoApplication】
package com.example.demo;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class DemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// @param args JAR运行时传入的自定义参数
SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args);
}
}
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class<?>[] primarySources, String[] args) {
return new SpringApplication(primarySources).run(args);
}
SpringBootApplication复合注解
【自动扫描Bean】@ComponentScan,自动扫描DemoApplication启动类同级目录中符合条件的组件的Bean纳入IOC容器
【自动配置Bean】@EnableAutoConfiguration,将DemoApplication启动类同级目录中符合自动配置条件(被@Configuration修饰的类)的Bean纳入IOC容器
【基于JavaConfig创建Bean】@SpringBootConfiguration继承@Configuration,将当前类标记为配置类并纳入IOC容器
启动SpringBoot项目
创建 SpringApplication 对象
public SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class<?>... primarySources) {
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;
Assert.notNull(primarySources, "PrimarySources must not be null");
this.primarySources = new LinkedHashSet<>(Arrays.asList(primarySources));
// 推断当前应用的类型:SERVLET、REACTIVE、NONE,默认SERVLET类型
this.webApplicationType = WebApplicationType.deduceFromClasspath();
/**
* 从 /META-INF/spring.factories 文件中加载指定接口的实现类,并初始化到SpringApplication对象的指定变量上
*/
this.bootstrapRegistryInitializers = new ArrayList<>(
getSpringFactoriesInstances(BootstrapRegistryInitializer.class)
);
// ApplicationContextInitializer上下文初始化
setInitializers((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationContextInitializer.class));
// ApplicationListener上下文监听器
setListeners((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class));
this.mainApplicationClass = deduceMainApplicationClass();
}
调用 SpringApplication 对象run方法
/**
* Run the Spring application, creating and refreshing a new {@link ApplicationContext}.
* @param args the application arguments (usually passed from a Java main method)
* @return a running {@link ApplicationContext}
*/
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
long startTime = System.nanoTime();
DefaultBootstrapContext bootstrapContext = createBootstrapContext();
configureHeadlessProperty();
// 该接口规定了SpringBoot的生命周期,在各个生命周期广播相应事件,调用实际的ApplicationListener类
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
// 启动 SpringApplicationRunListeners 监听器,开始监听SpringBoot的启动流程
listeners.starting(bootstrapContext, this.mainApplicationClass);
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
try {
// 自定义的命令参数对象
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);
// 从配置文件中解析出来的数据,封装成PropertySource对象,存放在ConfigurableEnvironment中
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, bootstrapContext, applicationArguments);
Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);
// 创建Spring容器
context = createApplicationContext();
context.setApplicationStartup(this.applicationStartup);
// Spring容器前置处理
prepareContext(bootstrapContext, context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner);
// 刷新Spring容器
refreshContext(context);
// Spring容器后置处理
afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
Duration timeTakenToStartup = Duration.ofNanos(System.nanoTime() - startTime);
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass).logStarted(getApplicationLog(), timeTakenToStartup);
}
// 监听器 SpringBoot 启动流程完毕
listeners.started(context, timeTakenToStartup);
// 处理一些执行后的定制化需求
callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
} catch (Throwable ex) {
if (ex instanceof AbandonedRunException) {
throw ex;
}
handleRunFailure(context, ex, listeners);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
try {
if (context.isRunning()) {
Duration timeTakenToReady = Duration.ofNanos(System.nanoTime() - startTime);
listeners.ready(context, timeTakenToReady);
}
} catch (Throwable ex) {
if (ex instanceof AbandonedRunException) {
throw ex;
}
handleRunFailure(context, ex, null);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
return context;
}
prepareContext
refreshContext
afterRefresh
callRunners
ApplicationRunner接口和CommandLineRunner接口分别用于在Spring Boot应用程序启动后执行一些定制化操作
@Component
public class MyApplicationRunner implements ApplicationRunner {
@Override
public void run(ApplicationArguments args) throws Exception {
System.out.println(JSONObject.toJSONString(args));
}
}
@Component
public class MyCommandLineRunner implements CommandLineRunner {
@Override
public void run(String... args) throws Exception {
System.out.println(JSONObject.toJSONString(args));
}
}
其它
启动参数配置
java -jar demo.jar --spring.profiles.active=test
在默认 application.properties 或 application.yml 基础上追加项目中的 application-test.properties 或 application-test.yaml
java -jar demo.jar --spring.config.additional-location=./application-test.yml
在默认 application.properties 或 application.yml 基础上追加本地硬盘上的 application-test.yml
JavaBean Properties Binding
my:
service:
remote-address: 192.168.1.1
security:
username: "admin"
password: "password"
roles:
- "USER"
- "ADMIN"
@ConfigurationProperties("my.service")
public class MyProperties {
private boolean enabled;
private InetAddress remoteAddress;
private final Security security = new Security();
// getters / setters...
public static class Security {
private String username;
private String password;
private List<String> roles = new ArrayList<>(Collections.singleton("USER"));
// getters / setters...
}
}
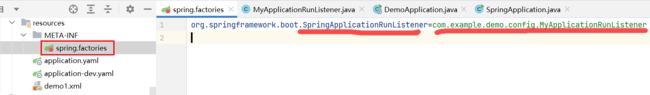
SpringApplicationRunListener接口
/**
* SpringApplicationRunListener属于应用程序启动层面的监听器,在springboot启动时调用run方法进行反射加载初始化【此时上下文还未加载,如果通过@Compnant是不起作用的】
*/
public class MyApplicationRunListener implements SpringApplicationRunListener {
private final SpringApplication application;
private final String[] args;
public MyApplicationRunListener(SpringApplication sa, String[] args) {
this.application = sa;
this.args = args;
}
/**
* Called immediately when the run method has first started. Can be used for very early initialization
*/
@Override
public void starting(ConfigurableBootstrapContext bootstrapContext) {
//SpringApplicationRunListener.super.starting(bootstrapContext);
System.out.println("【第一步】SpringApplicationRunListener.starting:SpringApplicationRunListeners监听器启动后立即执行");
}
/**
* Called once the environment has been prepared, but before the {@link ApplicationContext} has been created
*/
@Override
public void environmentPrepared(ConfigurableBootstrapContext bootstrapContext, ConfigurableEnvironment environment) {
//SpringApplicationRunListener.super.environmentPrepared(bootstrapContext, environment);
System.out.println("【第二步】SpringApplicationRunListener.environmentPrepared:ConfigurableEnvironment创建成功后立即执行");
}
/**
* Called once the {@link ApplicationContext} has been created and prepared, but before sources have been loaded.
*/
@Override
public void contextPrepared(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
//SpringApplicationRunListener.super.contextPrepared(context);
System.out.println("【第三步】SpringApplicationRunListener.contextPrepared:ApplicationContext构建完成后立即执行");
}
/**
* Called once the application context has been loaded but before it has been refreshed.
*/
@Override
public void contextLoaded(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
//SpringApplicationRunListener.super.contextLoaded(context);
System.out.println("【第四步】SpringApplicationRunListener.contextLoaded:ApplicationContext构建完成后,但没有被刷新前");
}
/**
* The context has been refreshed and the application has started
* but {@link CommandLineRunner CommandLineRunners} and {@link ApplicationRunner ApplicationRunners} have not been called.
*/
@Override
public void started(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, Duration timeTaken) {
//SpringApplicationRunListener.super.started(context, timeTaken);
System.out.println("【第五步】SpringApplicationRunListener.started:ApplicationContext被刷新后,但CommandLineRunners和ApplicationRunner未被调用前");
}
/**
* Called immediately before the run method finishes, when the application context has been refreshed
* and all {@link CommandLineRunner CommandLineRunners} and {@link ApplicationRunner ApplicationRunners} have been called.
*/
@Override
public void ready(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, Duration timeTaken) {
//SpringApplicationRunListener.super.ready(context, timeTaken);
System.out.println("【第六步】SpringApplicationRunListener.ready:CommandLineRunners和ApplicationRunner都被调用后");
}
/**
* Called when a failure occurs when running the application
*/
@Override
public void failed(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, Throwable exception) {
//SpringApplicationRunListener.super.failed(context, exception);
System.out.println("【容器启动失败】SpringApplicationRunListener.failed");
}
}
自定义Bean
package com.example.demo.demo2;
import jakarta.annotation.PostConstruct;
import jakarta.annotation.PreDestroy;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
/**
* Demo2初始化过程:
* Demo2 static
* Demo2 Initializing by name
* 【BeanPostProcessor】spring中bean实例:demo3 初始化之前处理......
* 【@PostConstruct】Demo2 postConstruct
* 【init】Demo2 init
* 【BeanPostProcessor】spring中bean实例:demo3 初始化之后处理......
*/
@Data
@Slf4j
public class Demo2 {
private String name;
static {
log.info("Demo2 static");
}
public Demo2(){
log.info("Demo2 Initializing");
}
public Demo2(String name){
this.name = name;
log.info("Demo2 Initializing by name");
}
@PostConstruct
public void postConstruct(){
log.info("Demo2 postConstruct");
}
public void init(){
log.info("Demo2 init");
}
public void destroy(){
log.info("Demo2 destroy");
}
@PreDestroy
public void preDestroy(){
log.info("Demo2 preDestroy");
}
}
package com.example.demo.demo2;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Lazy;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Scope;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.Order;
/**
* 声明一个类为配置类,通过JavaConfig的方式注册bean对象
*/
@Configuration
public class MyConfiguration {
@Bean(value = "demo2", initMethod = "init", destroyMethod = "destroy") // 注册bean对象
@Scope("singleton") // 声明bean作用域:singleton、prototype、request、session、global session
@Lazy(false) // 标记bean是否开启懒加载
@Order(value = 1) // 指定的数值越小,表示加载的优先级越高
public Demo2 getDemo2(){
// 省略....
return new Demo2("我是Demo2");
}
}
FactoryBean和@Configuration的功能类似,个人比较推荐@Configuration来实现自定义Bean并纳入容器管理
/**
* @Component
* @Slf4j
* public class Demo2FactoryBean implements FactoryBean {
* @Override
* public Demo2 getObject() throws Exception {
* Demo2 demo2 = new Demo2();
* demo2.setName("在这里可以自定义创建的过程");
* return demo2;
* }
*
* @Override
* public Class getObjectType() {
* return Demo2.class;
* }
*
* @Override
* public boolean isSingleton() {
* return FactoryBean.super.isSingleton();
* }
* }
*/
基于观察者模式的事件传播机制
场景案例:订单入库成功后,需要发送短信通知用户。一般情况都会把短信通知加在订单入库的后边,这样做违反了单一职责(订单保存功能里变不应该杂糅消息通知功能),如果后期需要添加微信消息通知功能,则需要在原有的基础上进行额外添加,这样做又违反了开闭原则(对拓展开放,对修改关闭)。优化方案:通过观察者模式使创建订单和消息通知功能进行分离
- 创建订单保存成功的事件(OrderSaveEvent)
public class OrderSaveEvent extends ApplicationEvent {
private String orderNum;
public String getOrderNum() { return orderNum; }
public void setOrderNum(String orderNum) { this.orderNum = orderNum; }
private String desc;
public String getDesc() { return desc; }
public void setDesc(String desc) { this.desc = desc; }
public OrderSaveEvent(Object source, String orderNum, String desc) {
super(source);
this.desc = desc;
this.orderNum = orderNum;
}
}
- 创建基于发送短信的订单入库成功监听器(OrderSmsListener)
@Component
@Async("asyncTaskExecutor")
public class OrderSmsListener implements ApplicationListener<OrderSaveEvent> {
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(OrderSaveEvent event) {
LoggerUtil.info(MessageFormat.format("短信提示:订单【{0}】{1}",event.getOrderNum(),event.getDesc()));
}
}
- 发布订单保存成功消息
@Resource
private ApplicationContext applicationContext;
public Object pushOrderSaveEvent() throws Exception {
// TODO 创建事件
OrderSaveEvent orderSaveEvent = new OrderSaveEvent(this,"000000","创建成功");
// TODO 发布事件
applicationContext.publishEvent(orderSaveEvent);
return ResponseUtil.success();
}