原始套接字编程(AF_PACKET+SOCK_RAW)模拟一个PING
1. 背景
最近看一个客户的代码片段,发现他在用原始套接字编程,一般学习套接字都是流式套接字和数据报套接字,本来也不是搞网络的,原始套接字了解得很少,借着这次机会,自己来学习一下原始套接字编程。
2. 原始套接字是什么
我去翻看
但是这个描述并不完全,于是我参考: 信息安全课程9:raw socket编程 - 知乎
另外还了解到原始套接字在socket的创建上有不同的组合,例如: AF_INET+SOCK_RAW最多只能允许用户层与IP层直接通信,而AF_PACKET+SOCK_RAW就可以允许用户层与数据链路层直接通信了(这一点也是Linux_Unix系统编程手册说得不准确的地方)
另外,关于AF_PACKET+SOCK_RAW可以参考man packet:
3. 封装与PING包格式
同样参考
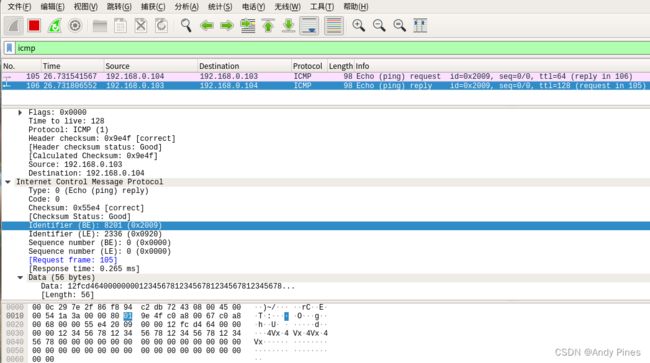
我自己用wireshark抓了一个ping包的格式如下:
上图是执行ping 192.168.0.103 -c 1抓的包,可以看到一个ping操作实际分为两个包,一个是由本机发出的包(echo ping request),另一个是收到对端发来的ack包(echo ping reply),不论怎样,这两个包组成都是相同的:
98byte = EthernetII(以太网头部14byte)+Internet Protocol Version4(IP包20byte)+ICMP(64byte)
4. 实验代码
实验代码实际上是受到下面博客的启发:Linux 网络编程——原始套接字实例:MAC 地址扫描器_siocgifhwaddr_Mike江的博客-CSDN博客
在这篇博客中,作者用AF_PACKET+SOCK_RAW的原始套接字在数据链路层模拟了一个地址解析协议的操作(Address Resolution Protocol),其中作者没有使用繁杂的包数据结构去构造发送数据,转而使用了直接赋值的方式,非常直观与暴力,可以对着wireshark的数据来构造自己的数据包,非常便于理解与学习,所以我自己模仿了一个PING操作,代码如下:
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include //struct ifreq
#include //ioctl、SIOCGIFADDR
#include
#include //ETH_P_ALL
#include //struct sockaddr_ll
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#define BUFFSIZE (1024)
#define IPPACKETLEN (20)
#define ICMPHEADERLEN (16)
#define ICMPDATALEN (48)
#define PINGPACKETLEN (98)
//#define DEBUG
static void test(void)
{
unsigned short a = 0x3623; /* in memory should be 0x23 0x36 */
unsigned short b = htons(a);
printf("network order b = %#x\n", b); /* in memory should be 0x36 0x23 */
printf("local order b' = %#x\n", ntohs(b));
return;
}
/* 2 bytes was a group
* totally lens group
*/
static unsigned short calc_checksum(unsigned short *addr, int len)
{
int i;
unsigned int sum = 0;
unsigned short tmp = 0;
/* in this algorithm,
* we use ntohs to convert the already constructed big endian data
*/
for (i = 0; i < len; i++) {
tmp = ntohs(*addr);
sum += tmp;
addr++;
}
sum = (sum >> 16) + (sum & 0xffff);
sum += (sum >>16);
tmp = ~sum;
return tmp;
}
int main(int argc,char *argv[])
{
int i = 1;
#ifdef DEBUG
test();
return 0;
#endif
unsigned char send_msg[BUFFSIZE] = {
//--------------Ethernet II------------------------14--------------------------
0xf8, 0x94, 0xc2, 0xdb, 0x72, 0x43, //dst_mac: F8-94-C2-DB-72-43
0x00, 0x0c, 0x29, 0x7e, 0x2f, 0x86, //src_mac: 00-0C-29-7E-2F-86
0x08, 0x00, //type: 0x0800 IPV4
//--------------Internet Protocol Version 4--------20--------------------------
0x45, //0100-version4, 0101-5*4byte=20byte
0x00, //DSCP:0, ECN-Not-ECT
0x00, 0x54, //total length: 0x54==84==20(IP)+64(ICMP)
0x36, 0x23, //identification: 0x36 0x23
0x40, 0x00, //flags: 0x4000, do not fragment
0x40, //time to live(TTL): 64
0x01, //protocol: ICMP(1)
0x00, 0x00, //checksum(need to calc later)
192, 168, 0, 104, //src ip addr
192, 168, 0, 103, //dst ip addr
//--------------ICMP-Header------------------------16--------------------------
0x08, //type: 8(echo ping request)
0x00, //code:0
0x00, 0x00, //checksum(need to calc later)
0x20, 0x09, //identifier: 0x20 0x09
0x00, 0x00, //sequence number
0x12, 0xfc, 0xd4, 0x64,
0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, //timestamp from icmp data
//--------------ICMP-Data--------------------------48--------------------------
0x12, 0x34, 0x56, 0x78,
0x12, 0x34, 0x56, 0x78,
0x12, 0x34, 0x56, 0x78,
0x12, 0x34, 0x56, 0x78,
};
unsigned short checksum = 0;
unsigned short checksum_be = 0;
/* handle checksum of IP packet */
checksum = calc_checksum((unsigned short *)(&send_msg[14]), IPPACKETLEN/2);
printf("IP packet checksum = %#x\n", checksum);
checksum_be = htons(checksum);
memcpy(&send_msg[24], &checksum_be, sizeof(checksum_be));
/* handle checksum of ICMP packet */
checksum = calc_checksum((unsigned short *)(&send_msg[34]), (ICMPHEADERLEN + ICMPDATALEN)/2);
printf("ICMP packet checksum = %#x\n", checksum);
checksum_be = htons(checksum);
memcpy(&send_msg[36], &checksum_be, sizeof(checksum_be));
/* socket create failed, why: Operation not permitted
* should have root permission to create the socket raw
*/
int sock_raw_fd = socket(AF_PACKET, SOCK_RAW, htons(ETH_P_ALL));
if (sock_raw_fd < 0) {
printf("socket create failed, why: %s\n", strerror(errno));
return -1;
}
printf("socket create success.\n");
struct sockaddr_ll sll;
struct ifreq req;
strncpy(req.ifr_name, "ens33", IFNAMSIZ);
ioctl(sock_raw_fd, SIOCGIFINDEX, &req);
bzero(&sll, sizeof(sll));
sll.sll_ifindex = req.ifr_ifindex;
int len = sendto(sock_raw_fd, send_msg, PINGPACKETLEN, 0 , (struct sockaddr *)&sll, sizeof(sll));
if (len == -1) {
printf("sendto failed, why: %s\n", strerror(errno));
close(sock_raw_fd);
return -1;
}
printf("\n%d bytes sended.\n", len);
unsigned char recv_msg[BUFFSIZE] = {0};
len = recvfrom(sock_raw_fd, recv_msg, sizeof(recv_msg), 0, NULL, NULL);
if (len < 0) {
printf("recvfrom failed, why: %s\n", strerror(errno));
close(sock_raw_fd);
return -1;
}
printf("\n%d bytes received, check the wireshark.\n", len);
close(sock_raw_fd);
return 0;
} 需要注意的是send_msg的数据全部是依据wireshark包来构造的,自己机器的ip和mac,对端机器的ip和mac需要自行适配,另外,IP包和ICMP包是有 checksum需要计算的,一个偷懒的办法是先胡乱写一个checksum进去,发包的时候wireshark会识别到错误并告诉你正确的checksum是什么,再回填进去即可,通常,IP包的checksum wireshark不检查(显示validation disabled),但是如果构造不对的话是收不到echo ping reply包的,可以按照下图的方法打开wireshark IP包的checksum检查结果:
不过话说回来,我们应该搞清楚checksum的计算原理,参考:
IP数据报首部checksum的计算_ipchecksum计算_Allen_Kao的博客-CSDN博客
另外注意的是由于我们暴力构造数据已经是网络字节序了,所以计算的时候有必要用htons和ntohs转换一下,参考代码中的calc_checksum()函数。
5. 实验结果
本机X86 ubuntu的ip是192.168.0.104,mac是00:0c:29:7e:2f:86
PC的ip是192.168.0.103,mac是f8:94:c2:db:72:43
因为原始套接字权限要求,必须给与权限运行:
wireshark抓包: