基于vscode+qemu的risc-v学习环境搭建
1. 环境说明
实验采用ubuntu22.04运行qemu模拟risc-v运行环境,使用vscode进行调试。
2. 交叉编译工具链的构建
risc-v工具分为两种:
- 适用于于linux环境的交叉编译工具链。
- 适用于裸机环境的交叉编译工具链。
2.1 使用ubuntu包管理工具直接安装
ubuntu22.04软件源包含risc-v安装包, 使用如下命令进行安装:
- 适用于linux运行环境的交叉编译工具链安装
sudo apt install gcc-riscv64-linux-gnu # 安装适用于linux环境的gcc sudo apt install binutils-riscv64-linux-gnu # 安装适用于linux环境的二进制工具集 - 适用于裸机运行环境的交叉编译工具链的安装
sudo apt install gcc-riscv64-unknown-elf # 安装适用于裸机环境的gcc sudo apt install binutils-riscv64-unknown-elf # 安装适用于裸机环境的二进制工具集 - 查看工具链是否安装成功
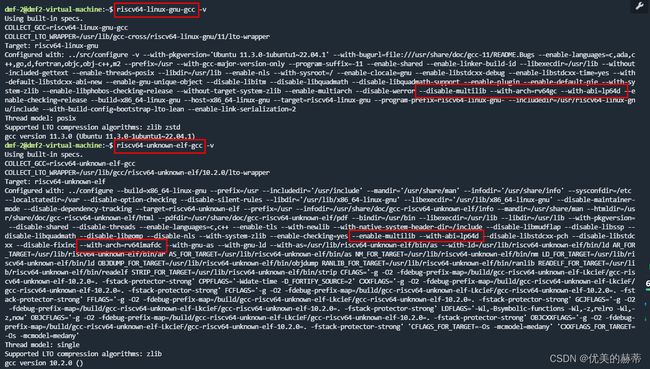
输出信息包含编译器版本及构造当前编译器时的编译选项,在此进行简单说明:# 执行下面命令可查看编译器工具链版本和编译时选项 riscv64-linux-gnu-gcc -v riscv64-unknown-elf-gcc -v- 在编译配置阶段使用 –enable-multilib 表示此编译器的 架构 和 ABI (Application Binary interface) 是可以通过 -march -mabi 指定的。–with-arch 和 –with-abi 则指定了默认的 架构 和 abi, 既支持 rv32 ,又支持 rv64。
- 在编译配置阶段使用 –disable-multilib 表示此编译器的 架构 和 ABI (Application Binary interface) 是不可以通过 -march -mabi 指定其他的 架构 和 abi 。只能编译 –with-arch 和 –with-abi 指定的 架构 和 abi
- 通过下图输出信息,我们可以知道
-
riscv64-linux-gnu-gcc 仅支持 -march=rv64gc -mabi=lp64d, 若要编译32位版本或者64位版本的其他架构此编译器便不再适用 ,此时便需要自己通过源码编译构造编译器,编译器的编译构造方法在下一节介绍;
-
riscv64-unknown-elf-gcc 则可通过 -march -mabi 指定多种 架构 和 abi ,此编译器可以满足所有 架构 和 abi 的需求,但此编译器在编译时并没有构造 gdb,若要使用gdb , 便需要通过源码重新构造和编译 (选择是否构造 gdb 的方法在后面介绍),编译器的使用示例如下:
riscv64-unknown-elf-gcc -march=rv32i -mabi=ilp32 -o main.elf main.c
-
2.2 自己编译工具链
2.2.1 前置知识 Autotools
我们在linux上通过源码编译和安装一个软件时,一般会经过以下几步,经过这几步进行编译安装的项目便是由 Autotools 发布的项目。
./configure # 确保能找到configure文件,执行完此步便会生成Makefile
make # 依据Makefile编译构建Makefile中的第一个目标
make install # 不是必须的, make xxx , xxx是指Makefile中的目标, 不指定目标便构建Makefile中的第一个目标
简单来讲 Autotools 是一个简化 Makefile 编写的工具,可自动生成 Makefile,类似 cmake gmake scons … ;GNU项目一般还是使用 Autotools 进行发布;Autotools 的介绍可以参考这篇文章这篇文章, 有兴趣的可以自行去学习。
2.2.2 构建risc-v工具链
2.2.2.1 安装依赖工具
编译需要 gcc autotools 等工具,ubuntu22.04使用如下命令安装依赖项:
sudo apt install git autoconf automake autotools-dev curl python3 libmpc-dev libmpfr-dev libgmp-dev gawk build-essential bison flex texinfo gperf patchutils bc libexpat1-dev libglib2.0-dev ninja-build zlib1g-dev pkg-config libboost-all-dev libtool libssl-dev libpixman-1-dev libpython2-dev virtualenv libmount-dev libsdl2-dev
2.2.2.2 使用默认配置进行编译
- 下载总仓库:
git clone https://github.com/riscv/riscv-gnu-toolchain # github上的代码仓库,下载比较慢。 git clone https://gitee.com/mirrors/riscv-gnu-toolchain # 码云上的代码仓库 - 下载成功后,使用 autotools 流程化编译方法即可完成编译安装:
cd riscv-gnu-toolchain # 进入源码目录 mkdir build # 创建一个名为build的目录,编译过程会生成一系列中间文件,编译构建过程在build目录中进行,避免污染源码。 cd build ../configure # 配置源码,生成Makefile,不带任何参数表示都使用默认配置。 make -j8 # 执行make 启动8个线程并行编译, - 使用此方法编译存在如下问题:
我们通过 git clone https://gitee.com/mirrors/riscv-gnu-toolchain 下载的源码其实是个基本的框架,大家可以看一仓库文件夹的内容都是空的,依据 make 目标在上游仓库下载对应源码,默认源都在外国的服务器上,下载速度很慢,我试了基本成功不了。
- 针对此问题我们可以从国内站点下载先把需要的子模块源码下载下来,配置阶段指定源码路径,需要的的子模块如下:
riscv-qemu(虚拟机)
riscv-newlib (用嵌入式的轻量级C库)
riscv-binutils(二进制工具集,如objcopy等)
riscv-gdb
riscv-dejagnu(测试框架)
riscv-glibc(编译linux版本时用)
riscv_musl(编译linux版本时用,可用于替代glibc)
riscv-gcc
如下示例是在配置阶段指定子模块源码路径的方法:cd riscv-gnu-toolchain # 进入源码目录,将子模块都克隆到此目录 git clone https://gitee.com/mirrors/riscv-gcc # 克隆riscv-gcc源码 git clone https://gitee.com/mirrors/riscv-dejagnu # 克隆riscv-dejagnu源码 git clone https://gitee.com/mirrors/riscv-glibc # 克隆riscv-glibc源码 git clone https://gitee.com/mirrors/riscv-newlib # 克隆riscv-newlib源码 git clone -b riscv-binutils-2.35 https://gitee.com/mirrors/riscv-binutils-gdb riscv-binutils # 克隆riscv-binutils源码 git clone -b fsf-gdb-10.1-with-sim https://gitee.com/mirrors/riscv-binutils-gdb riscv-gdb # 克隆riscv-gdb源码 git clone https://gitee.com/personal-summary/riscv_musl.git # 克隆riscv_musl源码 git clone https://mirrors.bfsu.edu.cn/git/qemu.git # 克隆qemu源码../configure \ --with-gcc-src=/home/dmf/riscv-gnu-toolchain/riscv-gcc \ --with-binutils-src=/home/dmf/riscv-gnu-toolchain/riscv-binutils \ --with-newlib-src=/home/dmf/riscv-gnu-toolchain/riscv-newlib \ --with-glibc-src=/home/dmf/riscv-gnu-toolchain/riscv-glibc \ --with-gdb-src=/home/dmf/riscv-gnu-toolchain/riscv-gdb
2.2.2.3 定制编译器
- 支持的配置选项
通过 ./configure 命令行参数配置编译器, 通过 ./configure --help 查看 configure 的用法和参数以及默认配置,建议将此打印信息读一遍,基本也就有感觉了。
`configure' configures riscv-toolchain 1.0 to adapt to many kinds of systems.
Usage: ../configure [OPTION]... [VAR=VALUE]...
To assign environment variables (e.g., CC, CFLAGS...), specify them as
VAR=VALUE. See below for descriptions of some of the useful variables.
Defaults for the options are specified in brackets.
Configuration:
-h, --help display this help and exit
--help=short display options specific to this package
--help=recursive display the short help of all the included packages
-V, --version display version information and exit
-q, --quiet, --silent do not print `checking ...' messages
--cache-file=FILE cache test results in FILE [disabled]
-C, --config-cache alias for `--cache-file=config.cache'
-n, --no-create do not create output files
--srcdir=DIR find the sources in DIR [configure dir or `..']
Installation directories:
--prefix=PREFIX install architecture-independent files in PREFIX
[/usr/local]
--exec-prefix=EPREFIX install architecture-dependent files in EPREFIX
[PREFIX]
By default, `make install' will install all the files in
`/usr/local/bin', `/usr/local/lib' etc. You can specify
an installation prefix other than `/usr/local' using `--prefix',
for instance `--prefix=$HOME'.
For better control, use the options below.
Fine tuning of the installation directories:
--bindir=DIR user executables [EPREFIX/bin]
--sbindir=DIR system admin executables [EPREFIX/sbin]
--libexecdir=DIR program executables [EPREFIX/libexec]
--sysconfdir=DIR read-only single-machine data [PREFIX/etc]
--sharedstatedir=DIR modifiable architecture-independent data [PREFIX/com]
--localstatedir=DIR modifiable single-machine data [PREFIX/var]
--runstatedir=DIR modifiable per-process data [LOCALSTATEDIR/run]
--libdir=DIR object code libraries [EPREFIX/lib]
--includedir=DIR C header files [PREFIX/include]
--oldincludedir=DIR C header files for non-gcc [/usr/include]
--datarootdir=DIR read-only arch.-independent data root [PREFIX/share]
--datadir=DIR read-only architecture-independent data [DATAROOTDIR]
--infodir=DIR info documentation [DATAROOTDIR/info]
--localedir=DIR locale-dependent data [DATAROOTDIR/locale]
--mandir=DIR man documentation [DATAROOTDIR/man]
--docdir=DIR documentation root [DATAROOTDIR/doc/riscv-toolchain]
--htmldir=DIR html documentation [DOCDIR]
--dvidir=DIR dvi documentation [DOCDIR]
--pdfdir=DIR pdf documentation [DOCDIR]
--psdir=DIR ps documentation [DOCDIR]
Optional Features:
--disable-option-checking ignore unrecognized --enable/--with options
--disable-FEATURE do not include FEATURE (same as --enable-FEATURE=no)
--enable-FEATURE[=ARG] include FEATURE [ARG=yes]
--enable-linux set linux as the default make target
[--disable-linux]
--enable-debug-info build glibc/musl/newlibc/libgcc with debug
information
--enable-multilib build both RV32 and RV64 runtime libraries (only
RV64 for musl libc) [--disable-multilib]
--enable-gcc-checking Enable gcc internal checking, it will make gcc very
slow, only enable it when developing gcc
[--disable-gcc-checking]
--disable-gdb Don't build GDB, as it's not upstream
--enable-libsanitizer Build libsanitizer, which only supports rv64
--enable-qemu-system Build qemu with system-mode emulation
Optional Packages:
--with-PACKAGE[=ARG] use PACKAGE [ARG=yes]
--without-PACKAGE do not use PACKAGE (same as --with-PACKAGE=no)
--with-arch=rv64imafdc Sets the base RISC-V ISA, defaults to rv64imafdc
--with-abi=lp64d Sets the base RISC-V ABI, defaults to lp64d
--with-tune=rocket Set the base RISC-V CPU, defaults to rocket
--with-isa-spec=20191213
Set the default ISA spec version, default to
20191213, available options: 2.2, 20190608, 20191213
--with-sim=qemu Sets the base RISC-V Simulator, defaults to qemu
--with-multilib-generator
Multi-libs configuration string, only supported for
bare-metal/elf toolchain, this option implied
--enable-multilib
--with-cmodel Select the code model to use when building libc and
libgcc [--with-cmodel=medlow]
--with-target-cflags Add extra target flags for C for library code
--with-target-cxxflags Add extra target flags for C++ for library code
--with-host=x86_64-w64-mingw32
Sets the host for the tools, you probably want
nothing
--without-system-zlib use the builtin copy of zlib from GCC
--with-guile Set which guile to use, if any
--with-gcc-src Set gcc source path, use builtin source by default
--with-binutils-src Set binutils source path, use builtin source by
default
--with-newlib-src Set newlib source path, use builtin source by
default
--with-glibc-src Set glibc source path, use builtin source by default
--with-musl-src Set musl source path, use builtin source by default
--with-gdb-src Set gdb source path, use builtin source by default
--with-qemu-src Set qemu source path, use builtin source by default
--with-spike-src Set spike source path, use builtin source by default
--with-pk-src Set pk source path, use builtin source by default
--with-dejagnu-src Set dejagnu source path, use builtin source by
default
--with-linux-headers-src
Set linux-headers source path, use builtin source by
default
Some influential environment variables:
CC C compiler command
CFLAGS C compiler flags
LDFLAGS linker flags, e.g. -L<lib dir> if you have libraries in a
nonstandard directory <lib dir>
LIBS libraries to pass to the linker, e.g. -l<library>
CPPFLAGS (Objective) C/C++ preprocessor flags, e.g. -I<include dir> if
you have headers in a nonstandard directory <include dir>
Use these variables to override the choices made by `configure' or to help
it to find libraries and programs with nonstandard names/locations.
Report bugs to the package provider.
- 一些配置示例,详细配置 请参考 …/configure --help 的输出文件
- 指定安装路径
../configure --prefix=/opt/riscv- 指定编译器架构,此种方法编译出的编译器仅支持指定的 架构 和 abi
../configure --prefix=/opt/riscv --with-arch=rv32gc --with-abi=ilp32d- 支持所有 架构 和 abi 即支持32位又支持64位
./configure --prefix=/opt/riscv --enable-multilib- 支持指定的 架构 和 abi
./configure --with-multilib-generator="rv32i-ilp32--;rv32imafd-ilp32--" - 指定编译目标
默认配置下是使用 newlib 作为默认目标,当然也可以在配置阶段使用 –enable-linux 将 linux 作为目标。执行 make 命令时会使用默认目标进行构建。- 构建riscv64-unknown-elf-xxx
# 在默认配置下下面两条命令是等效的,都是使用目标 newlib 为目标进行构建 make make newllib- 构建riscv64-linux-gnu-xxx
make linux # 使用glibc make musl # 使用musl libc - 关键点说明
xxx
3. qemu的安装
qemu可选择源码安装或者直接通过包管理工具apt进行安装。
3.1 源码安装
qemu源码也是使用 Autotools 进行发布,编译方法类似,可使用如下配置选项:
../configure \
--prefix=/opt/riscv/qemu \
--enable-sdl \
--enable-tools \
--enable-debug \
--target-list=riscv32-softmmu,riscv64-softmmu,riscv32-linux-user,riscv64-linux-user
–enable-sdl 表示使用sdl图形库
–enable-tools 表示生成 QEMU 工具集
–enable-debug 启用debug功能
–target-list 选项说明
| 选项 | 支持的平台 |
|---|---|
| riscv32-softmmu | riscv32系统模式平台 |
| riscv64-softmmu | riscv64系统模式平台 |
| riscv32-linux-user | riscv32用户模式平台 |
| riscv32-linux-user | riscv64用户模式平台 |
3.2 apt安装
sudo apt install qemu-system qemu-user # 支持所有平台
4. 使用vscode调试
4.1 vscode的安装
上述 编译工具链 和 qemu 均在 ubuntu22.04 虚拟机上安装,vscode 可直接安装在 ubuntu 上也可安装在其他主机上通过远程连接 ubuntu 进行调试,安装过程在此不过多赘述,有了 vscode 还不能编译和调试代码,要给 vscode 安装 C/C++ 扩展,如下图所示:

4.2 vscode远程调试说明
4.2.1 远程插件说明
远程调试需要安装远程调试插件,vscode 提供 Remote Development 插件,它是一个远程开发插件包,包含了已下3类远程开发插件。
- Remote - SSH插件 : 通过SSH服务打开远程机器上的文件夹。
- Remote - Containers插件:基于容器技术,把 Docker作为开发环境。
- Romote - WSL:打开WLS的文件夹。
4.2.2 Remote-SSH插件安装与使用
4.2.3 vscode 的C/C++调试
vscode的调试功能由 C/C++插件 提供,所以必须首先安装 C/C++插件,要调试一个程序,主要依赖两个文件 task.json 和 launch.json。
4.2.3.1 task.json 文件说明
task.json 的目的是 把重复的工作自动化,vscode 在创建 task.json 时提供了一些模板,可以根据模板进行修改,在此我仅仅说明一下 task.json 文件的创建和调用过程,并提供一个针对一个简单的 Makefile 项目的 task.json 文件,大家看下注释就能理解了,这个task.json 文件中描述了三个任务:
- 通过 make 命令编译工程生成可执行文件。(编译必须加 -g 选项,在可执行文件中生成调试信息段 )。
- 在后台运行 qemu, 打开gdb服务端口,等待gdb连接调试。
- 打包前面两个任务,运行第三个任务等于先后调用前两个任务。
{
// See https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=733558
// for the documentation about the tasks.json format
"version": "2.0.0",
"tasks": [
{
// 仅仅相当于在命令行中执行了一个make命令
"label": "Build", // 任务名
"type": "shell", // 在shell中运行
"command": "make", // 在shell中运行make命令
"isBackground": false, // 不需要后台运行,编译完进程结束
},
{
"label": "Run RISCV-QEMU", // 任务名
"type": "shell", // 在shell中运行
"command": "echo Starting RISCV-QEMU&qemu-riscv32 -g 1234 ./*.elf", // 在shell中要运行的命令
"isBackground": true, // qemu-riscv32 -g 1234 ./*.elf 执行完此命令后,启动了GDB服务,端口是1234,需要等待客户端连接,所以不能杀死这个进程,故这里要选择ture,让其后台运行
"problemMatcher": {
"pattern": {
"regexp": "^(Starting RISCV-QEMU)",
"line": 1
},
"background": {
"activeOnStart": true,
"beginsPattern": "^(Starting RISCV-QEMU)",
"endsPattern": "^(Starting RISCV-QEMU)"
}
}
},
{
"label": "Build and run", // 任务名
"dependsOrder": "sequence", // 描述依赖其他任务的任务
"dependsOn": [
"Build", // 先运行Build任务
"Run RISCV-QEMU" // 再 Run RISCV-QEMU 任务
]
}
]
}
创建一个task.json 文件的方法如下图,大家按照图示点一下就知道了

4.2.3.2 launch.json 文件说明
同样,这里也仅提供一个与上面 task.json 配套使用的示例,通过注释应该能看懂,在此不过多赘述。
{
// 使用 IntelliSense 了解相关属性。
// 悬停以查看现有属性的描述。
// 欲了解更多信息,请访问: https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid=830387
"version": "0.2.0",
"configurations": [
{
"name": "(gdb) 启动", // 这个配置的名字
"type": "cppdbg", // 调试器的类型,这里选的是c/c++的调试器, 例如json的调试器类型就是 "node"
"request": "launch", // 调试的模式 launch:启动 "program"中的程序并调试;
// attach: 将"program"中的程序附加到一个正在运行的进程中调试
"miDebuggerServerAddress": "127.0.0.1:1234",//GDB连接的地址和端口,task.json中启动的服务
"program": "${workspaceFolder}/main.elf", //GDB调试的可执行程序名称,里面必须有代码和符号等信息, 编译时要加 -g 选项
"args": [], // 要传给"program"的参数
"stopAtEntry": true, //调试时是否停止在程序的入口点处
"cwd": "${fileDirname}", // 调试器的工作目录
"externalConsole": false, //调试时是否使用vscode集成的终端
"miDebuggerPath": "/opt/riscv/gcc/bin/riscv64-unknown-elf-gdb", //gdb调试器的路径
"MIMode": "gdb",
"preLaunchTask": "Build and run" //运行GDB之前,先执行tasks.json文件中的"Build and run"任务,即先编译程序,在启动qemu,在通过gdb连接qemu
}
]
}