java学习笔记12——IO流解析
IO流在java中也是很重要的一章,在文件读取,信息的发送等方面都会用到。
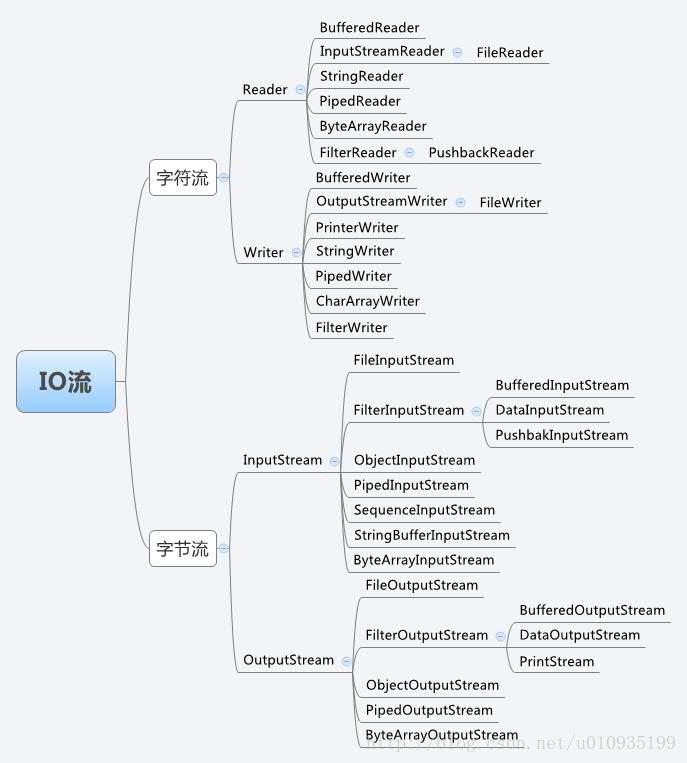
一、IO流的分类
流是一组有顺序的,有起点和终点的字节集合,是对数据传输的总称或抽象。即数据在两设备间的传输称为流,流的本质是数据传输,根据数据传输特性将流抽象为各种类,方便更直观的进行数据操作。 :
java中的流,根据不同的使用可以进行分类:
- 按照数据流的方法不同可以分为:输入流和输出流
- 按照处理数据单位不同可以分为:字节流和字符流
- 按照实现功能不同可以分为:节点流和处理流
在这里,输入流和输出流是在程序的角度进行说明:程序–>文件,输出流/程序<—文件,输入流。
- 字节流:每一次的读取或者输出都是8位二进制;
- 字符流:每一次的读取或者输出都是16位二进制。
这里的原理是一样的,唯一的区别就是处理单位不同。由于数据编码的不同,所以,对于不同的处理对象,字节流能处理所有的类型数据(如图片和视频),而字符流只能处理字符类型的数据。所以在这里给出的建议:只要处理纯文本数据,就优先考虑字符流,除此之外的处理都用字节流。
在java中,字符流是Reader和Writer。字节流是InputStream和OutputStream。
二、File
File主要是对文件进行操作的一个类,看下面例子
public class FileIODemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File file = new File("D:/file.txt");
if (!file.exists()) {// 文件是否存在
// 不存在,创建文件
file.createNewFile();
}
System.out.println("获取文件名:" + file.getName());
System.out.println("获取文件路径:" + file.getPath());
}
}结果:
获取文件名:file.txt
获取文件路径:D:\file.txtFile中有很多的方法,可以对文件进行操作,这里简单介绍以上几种。
三、InputStream
这里首先介绍一下FileInputStream,FileInputStream主要是对文件的输入输出操作
文件中输入:

代码:
public class FileIODemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File file = new File("D:/file.txt");
InputStream in = new FileInputStream(file);
byte[] b = new byte[1024];
int temp = 0;
int count = 0;
while ((temp = in.read()) != -1) {
b[count++] = (byte) temp;
}
in.close();
System.out.println(new String(b));
}
}结果:
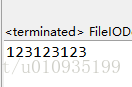
以上方法可以在不知道文件大小的情况下,用(temp = in.read()) != -1判断条件进行判断,直到文件读取完毕。
这里需要注意一点:在读取中文的时候,需要注意中文的编码问题,否则会出现乱码问题!
四、OutputStream
OutputStream为输出流,是程序向文件写入的流,请看下面代码:
public class FileIODemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File file = new File("D:/file.txt");
OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(file);
String data = "好好学习,天天向上!";
byte[] b = data.getBytes();
for (int i = 0; i < b.length; i++) {
out.write(b[i]);
}
out.close();
}
}五、Reader
Reader是字符流的输入流,这里请看下面代码:
文件:
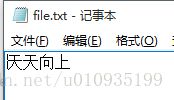
代码:
public class FileIODemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File file = new File("D:/file.txt");
Reader reader = new FileReader(file);
int i = 0;
while ((i = reader.read()) != -1) {
System.out.println((char) i);
}
reader.close();
}
}结果:
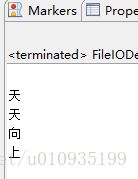
该读取是以字节的形式读取的,所以如果没有char的强制类型转换,输出的是ascii 码。
六、Writer
writer是字符流的输出流,看下面的代码:
public class FileIODemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File file = new File("D:/file.txt");
Writer writer = new FileWriter(file);
writer.write("好好学习,天天向上!");
writer.close();
}
}七、缓存流
java里面有一个缓存流,本身并没有IO的功能,只是对其的包装,为流提高了效率。可以提高文件输入输出的效率。
冲流分为字节和字符缓冲流
字节缓冲流为:
- BufferedInputStream—字节输入缓冲流
- BufferedOutputStream—字节输出缓冲流
字符缓冲流为:
- BufferedReader—字符输入缓冲流
- BufferedWriter—字符输出缓冲流
下面就举一个例子,其实用法和输入输出流是一样的:
代码:
public class FileIODemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(new File("D:/file.txt"));
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(out);
bos.write("好好学习java知识".getBytes());
bos.flush();
bos.close();
out.close();
}
}八、总结一下
字符流和字节流以及缓冲流在编程中的用处很大,需要熟练掌握这方面的知识。
那么在使用过程中也有这些需要注意的:
1. 字节流还是字符流的选择需要注意,一般建议建议:当我们在处理媒体介质时,请选择字节流;当我们在处理字符介质时,请选择字符流;当我们不明确操作的介质的类型时,请选择字节流。
2. 在流的操作完成以后,一定要close();进行资源的释放。同时但是用缓存流的时候,需要注意使用flush();进行刷新,把流中的信息进行写入。
3. 在对中文进行流操作的时候需要注意中文的编码格式。否则会出现乱码的情况。