【ConcurrentHashMap1.8源码】十分钟逐行深入ConcurrentHashMap并发之美
ConcurrentHashMap1.8源码
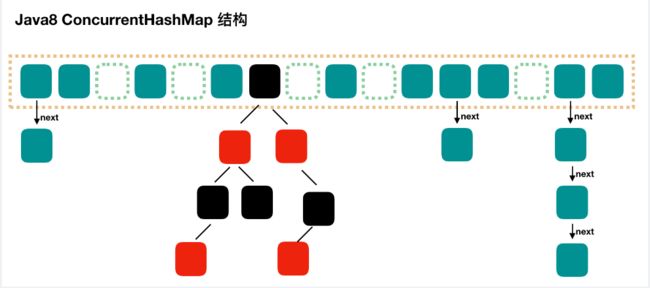
数据结构
区别与1.7,节点由Node和Treebin构成
四个核心要点
- 初始化
- PUT
- 扩容
- GET
五个构造方法
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-czroyzgE-1691249658658)(C:\Users\admin\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20230805121837937.png)]
/**
* Creates a new, empty map with the default initial table size (16).
*/
public ConcurrentHashMap() {
}
/**
* Creates a new, empty map with an initial table size
* accommodating the specified number of elements without the need
* to dynamically resize.
*
* @param initialCapacity The implementation performs internal
* sizing to accommodate this many elements.
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity of
* elements is negative
*/
public ConcurrentHashMap(int initialCapacity) {
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
int cap = ((initialCapacity >= (MAXIMUM_CAPACITY >>> 1)) ?
MAXIMUM_CAPACITY :
tableSizeFor(initialCapacity + (initialCapacity >>> 1) + 1));
this.sizeCtl = cap;
}
/**
* Creates a new map with the same mappings as the given map.
*
* @param m the map
*/
public ConcurrentHashMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) {
this.sizeCtl = DEFAULT_CAPACITY;
putAll(m);
}
/**
* Creates a new, empty map with an initial table size based on
* the given number of elements ({@code initialCapacity}) and
* initial table density ({@code loadFactor}).
*
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity. The implementation
* performs internal sizing to accommodate this many elements,
* given the specified load factor.
* @param loadFactor the load factor (table density) for
* establishing the initial table size
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity of
* elements is negative or the load factor is nonpositive
*
* @since 1.6
*/
public ConcurrentHashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
this(initialCapacity, loadFactor, 1);
}
/**
* Creates a new, empty map with an initial table size based on
* the given number of elements ({@code initialCapacity}), table
* density ({@code loadFactor}), and number of concurrently
* updating threads ({@code concurrencyLevel}).
*
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity. The implementation
* performs internal sizing to accommodate this many elements,
* given the specified load factor.
* @param loadFactor the load factor (table density) for
* establishing the initial table size
* @param concurrencyLevel the estimated number of concurrently
* updating threads. The implementation may use this value as
* a sizing hint.
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the initial capacity is
* negative or the load factor or concurrencyLevel are
* nonpositive
*/
public ConcurrentHashMap(int initialCapacity,
float loadFactor, int concurrencyLevel) {
if (!(loadFactor > 0.0f) || initialCapacity < 0 || concurrencyLevel <= 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
if (initialCapacity < concurrencyLevel) // Use at least as many bins
initialCapacity = concurrencyLevel; // as estimated threads
long size = (long)(1.0 + (long)initialCapacity / loadFactor);
int cap = (size >= (long)MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ?
MAXIMUM_CAPACITY : tableSizeFor((int)size);
this.sizeCtl = cap;
}
PUT方法
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(key, value, false);
}
final V putVal(K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) {
if (key == null || value == null) throw new NullPointerException();
// 计算key的hash值
int hash = spread(key.hashCode());
int binCount = 0;
for (Node<K,V>[] tab = table;;) {
Node<K,V> f; int n, i, fh;
// 如果tab为空,就去初始化node数组
if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
tab = initTable();
// 不为空计算hash值对应的tab的下标
else if ((f = tabAt(tab, i = (n - 1) & hash)) == null) {
// cas放入node节点
if (casTabAt(tab, i, null,
new Node<K,V>(hash, key, value, null)))
break; // no lock when adding to empty bin
}
// 对应下标节点被移除了,就会去helpTransfer,协助扩容转移
// 如果helpTransfer返回的老数组,可能继续helpTransfer
// 类似自旋
else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED)
tab = helpTransfer(tab, f);
// 下面else表示,hash值相等,key相等
else {
V oldVal = null;
// 锁的是node节点,相比1.7segement,锁粒度减小
synchronized (f) {
// check
if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) {
if (fh >= 0) {
binCount = 1;
// 同hashmap的原理修改node
for (Node<K,V> e = f;; ++binCount) {
K ek;
if (e.hash == hash &&
((ek = e.key) == key ||
(ek != null && key.equals(ek)))) {
oldVal = e.val;
if (!onlyIfAbsent)
e.val = value;
break;
}
Node<K,V> pred = e;
if ((e = e.next) == null) {
pred.next = new Node<K,V>(hash, key,
value, null);
break;
}
}
}
else if (f instanceof TreeBin) {
Node<K,V> p;
binCount = 2;
if ((p = ((TreeBin<K,V>)f).putTreeVal(hash, key,
value)) != null) {
oldVal = p.val;
if (!onlyIfAbsent)
p.val = value;
}
}
}
}
if (binCount != 0) {
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD)
treeifyBin(tab, i);
if (oldVal != null)
return oldVal;
break;
}
}
}
// 统计添加节点数
addCount(1L, binCount);
return null;
}
initTable
初始化数组方法,构造一个Node数组
/**
* Initializes table, using the size recorded in sizeCtl.
*/
private final Node<K,V>[] initTable() {
Node<K,V>[] tab; int sc;
while ((tab = table) == null || tab.length == 0) {
// private transient volatile int sizeCtl;
// sc = 0,sizeCtl = 0
if ((sc = sizeCtl) < 0)
// Thread.yield(),放弃当前CPU资源
Thread.yield(); // lost initialization race; just spin
// 只有一个线程能修改SIZECTL为-1
// private static final long SIZECTL;
else if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc, -1)) {
try {
if ((tab = table) == null || tab.length == 0) {
// private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 16;
// 默认容量是16
int n = (sc > 0) ? sc : DEFAULT_CAPACITY;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
// 默认构建大小为16的node数组
Node<K,V>[] nt = (Node<K,V>[])new Node<?,?>[n];
table = tab = nt;
// sc = 16 - (16/2/2) = 12
// sc也就是扩容阈值
sc = n - (n >>> 2);
}
} finally {
sizeCtl = sc;
}
break;
}
}
return tab;
}
当Put时,addCount(1L, binCount);
利用countcells+baseCount来统计节点数,总的来说就是多个线程去竞争baseCount,只能有一个线程能拿到资源,其他线程就会去countcells数组里竞争,在countcell里的value+1,最后size()方法就是统计countcells数组里所有的value值+basecount就是总的节点数
private final void addCount(long x, int check) {
CounterCell[] as; long b, s;
// 如果cells不为空,basecount也不会去竞争
if ((as = counterCells) != null ||
!U.compareAndSwapLong(this, BASECOUNT, b = baseCount, s = b + x)) {
CounterCell a; long v; int m;
boolean uncontended = true;
if (as == null || (m = as.length - 1) < 0 ||
// 每个线程生成一个随机数,随机数 & length-1
// 当前cell不为空,会去cell+1,成功不会走判断
(a = as[ThreadLocalRandom.getProbe() & m]) == null ||
!(uncontended =
U.compareAndSwapLong(a, CELLVALUE, v = a.value, v + x))) {
// cell竞争失败,就会执行fullAddCount
// cells初始化,cell创建,value+1
fullAddCount(x, uncontended);
return;
}
if (check <= 1)
return;
s = sumCount();
}
// 扩容,在第一次扩容后也会判断新数组需不需要扩容
if (check >= 0) {
Node<K,V>[] tab, nt; int n, sc;
// 总节点数超过阈值,sc默认是12
while (s >= (long)(sc = sizeCtl) && (tab = table) != null &&
(n = tab.length) < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
// resizeStamp(n)=resizeStamp(16)
int rs = resizeStamp(n);
if (sc < 0) {
// 另一个线程进来,nextTable开始是null
if ((sc >>> RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT) != rs || sc == rs + 1 ||
sc == rs + MAX_RESIZERS || (nt = nextTable) == null ||
transferIndex <= 0)
break;
// 所以执行下面逻辑
if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc, sc + 1))
// 核心是转移
transfer(tab, nt);
}
// 先走这个分支,rs << RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT=-2145714176
// 只有一个线程把sc改成负数
else if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc,
(rs << RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT) + 2))
// 只有一个线程去扩容
transfer(tab, null);
s = sumCount();
}
}
}
transfer
转移
/**
* Minimum number of rebinnings per transfer step. Ranges are
* subdivided to allow multiple resizer threads. This value
* serves as a lower bound to avoid resizers encountering
* excessive memory contention. The value should be at least
* DEFAULT_CAPACITY.
*/
private static final int MIN_TRANSFER_STRIDE = 16;
/**
* Moves and/or copies the nodes in each bin to new table. See
* above for explanation.
*/
private final void transfer(Node<K,V>[] tab, Node<K,V>[] nextTab) {
int n = tab.length, stride;
// 根据核心cup数,算步长,MIN_TRANSFER_STRIDE=16
if ((stride = (NCPU > 1) ? (n >>> 3) / NCPU : n) < MIN_TRANSFER_STRIDE)
stride = MIN_TRANSFER_STRIDE; // subdivide range
// 新数组为空
if (nextTab == null) { // initiating
try {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
// 2倍扩容
Node<K,V>[] nt = (Node<K,V>[])new Node<?,?>[n << 1];
// 新数组赋值
nextTab = nt;
} catch (Throwable ex) { // try to cope with OOME
sizeCtl = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return;
}
nextTable = nextTab;
// n默认是扩容之前的大小,int n = tab.length
transferIndex = n;
}
// nextn新数组的长度
int nextn = nextTab.length;
// fwd就是一个标记转移过的节点,如果线程查找到fwd,表示这个数组正在扩容
ForwardingNode<K,V> fwd = new ForwardingNode<K,V>(nextTab);
// 前面是否需要转移
boolean advance = true;
// 当前线程是不是所有都转移完了
boolean finishing = false; // to ensure sweep before committing nextTab
// bound和i,之间的步长范围就是转移范围
for (int i = 0, bound = 0;;) {
Node<K,V> f; int fh;
while (advance) {
int nextIndex, nextBound;
// 开始不符合
if (--i >= bound || finishing)
advance = false;
// 开始不符合
else if ((nextIndex = transferIndex) <= 0) {
i = -1;
advance = false;
}
// nextIndex = transferIndex
// nextBound = (nextIndex > stride ? nextIndex - stride : 0)
// 这里把bound从数组右边开始转移,算出开始的转移范围
// 对于其他线程,nextIndex就被修改了,所以不会有范围重复
else if (U.compareAndSwapInt
(this, TRANSFERINDEX, nextIndex,
nextBound = (nextIndex > stride ?
nextIndex - stride : 0))) {
bound = nextBound;
i = nextIndex - 1;
advance = false;
}
}
if (i < 0 || i >= n || i + n >= nextn) {
int sc;
if (finishing) {
nextTable = null;
table = nextTab;
sizeCtl = (n << 1) - (n >>> 1);
return;
}
// (sc - 2) != resizeStamp(n) << RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT = resizeStamp(n) << RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT
// 本质就是判断当前数组是不是老数组有没有扩容完成,扩容前sc+1,扩容后完成后sc-1
if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc = sizeCtl, sc - 1)) {
if ((sc - 2) != resizeStamp(n) << RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT)
return;
finishing = advance = true;
i = n; // recheck before commit
}
}
else if ((f = tabAt(tab, i)) == null)
advance = casTabAt(tab, i, null, fwd);
else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED)
advance = true; // already processed
else {
// 保证转移的节点不能put新节点
synchronized (f) {
if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) {
Node<K,V> ln, hn;
if (fh >= 0) {
int runBit = fh & n;
Node<K,V> lastRun = f;
for (Node<K,V> p = f.next; p != null; p = p.next) {
int b = p.hash & n;
if (b != runBit) {
runBit = b;
lastRun = p;
}
}
if (runBit == 0) {
ln = lastRun;
hn = null;
}
else {
hn = lastRun;
ln = null;
}
for (Node<K,V> p = f; p != lastRun; p = p.next) {
int ph = p.hash; K pk = p.key; V pv = p.val;
if ((ph & n) == 0)
ln = new Node<K,V>(ph, pk, pv, ln);
else
hn = new Node<K,V>(ph, pk, pv, hn);
}
setTabAt(nextTab, i, ln);
setTabAt(nextTab, i + n, hn);
setTabAt(tab, i, fwd);
advance = true;
}
else if (f instanceof TreeBin) {
TreeBin<K,V> t = (TreeBin<K,V>)f;
TreeNode<K,V> lo = null, loTail = null;
TreeNode<K,V> hi = null, hiTail = null;
int lc = 0, hc = 0;
for (Node<K,V> e = t.first; e != null; e = e.next) {
int h = e.hash;
TreeNode<K,V> p = new TreeNode<K,V>
(h, e.key, e.val, null, null);
if ((h & n) == 0) {
if ((p.prev = loTail) == null)
lo = p;
else
loTail.next = p;
loTail = p;
++lc;
}
else {
if ((p.prev = hiTail) == null)
hi = p;
else
hiTail.next = p;
hiTail = p;
++hc;
}
}
ln = (lc <= UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD) ? untreeify(lo) :
(hc != 0) ? new TreeBin<K,V>(lo) : t;
hn = (hc <= UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD) ? untreeify(hi) :
(lc != 0) ? new TreeBin<K,V>(hi) : t;
setTabAt(nextTab, i, ln);
setTabAt(nextTab, i + n, hn);
setTabAt(tab, i, fwd);
advance = true;
}
}
}
}
}
}
helpTransfer
/**
* Helps transfer if a resize is in progress.
*/
final Node<K,V>[] helpTransfer(Node<K,V>[] tab, Node<K,V> f) {
Node<K,V>[] nextTab; int sc;
if (tab != null && (f instanceof ForwardingNode) &&
(nextTab = ((ForwardingNode<K,V>)f).nextTable) != null) {
int rs = resizeStamp(tab.length);
while (nextTab == nextTable && table == tab &&
(sc = sizeCtl) < 0) {
if ((sc >>> RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT) != rs || sc == rs + 1 ||
sc == rs + MAX_RESIZERS || transferIndex <= 0)
break;
if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc, sc + 1)) {
transfer(tab, nextTab);
// 当前线程转移完成
break;
}
}
return nextTab;
}
return table;
}
resizeStamp
默认就是返回一个负数,rs << RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT=-2145714176
/**
* The number of bits used for generation stamp in sizeCtl.
* Must be at least 6 for 32bit arrays.
*/
private static int RESIZE_STAMP_BITS = 16;
/**
* Returns the stamp bits for resizing a table of size n.
* Must be negative when shifted left by RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT.
*/
static final int resizeStamp(int n) {
return Integer.numberOfLeadingZeros(n) | (1 << (RESIZE_STAMP_BITS - 1));
}
ForwardingNode
标记node节点为MOVED状态
/**
* A node inserted at head of bins during transfer operations.
*/
static final class ForwardingNode<K,V> extends Node<K,V> {
final Node<K,V>[] nextTable;
// 标记node节点为MOVED
ForwardingNode(Node<K,V>[] tab) {
super(MOVED, null, null, null);
this.nextTable = tab;
}
fullAddCount
2次失败,就会选择扩容
// See LongAdder version for explanation
private final void fullAddCount(long x, boolean wasUncontended) {
int h;
if ((h = ThreadLocalRandom.getProbe()) == 0) {
ThreadLocalRandom.localInit(); // force initialization
h = ThreadLocalRandom.getProbe();
wasUncontended = true;
}
boolean collide = false; // True if last slot nonempty
for (;;) {
CounterCell[] as; CounterCell a; int n; long v;
if ((as = counterCells) != null && (n = as.length) > 0) {
if ((a = as[(n - 1) & h]) == null) {
if (cellsBusy == 0) { // Try to attach new Cell
CounterCell r = new CounterCell(x); // Optimistic create
if (cellsBusy == 0 &&
U.compareAndSwapInt(this, CELLSBUSY, 0, 1)) {
boolean created = false;
try { // Recheck under lock
CounterCell[] rs; int m, j;
if ((rs = counterCells) != null &&
(m = rs.length) > 0 &&
rs[j = (m - 1) & h] == null) {
rs[j] = r;
created = true;
}
} finally {
cellsBusy = 0;
}
if (created)
break;
continue; // Slot is now non-empty
}
}
collide = false;
}
else if (!wasUncontended) // CAS already known to fail
wasUncontended = true; // Continue after rehash
else if (U.compareAndSwapLong(a, CELLVALUE, v = a.value, v + x))
break;
else if (counterCells != as || n >= NCPU)
collide = false; // At max size or stale
else if (!collide)
collide = true;
else if (cellsBusy == 0 &&
U.compareAndSwapInt(this, CELLSBUSY, 0, 1)) {
try {
if (counterCells == as) {// Expand table unless stale
CounterCell[] rs = new CounterCell[n << 1];
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
rs[i] = as[i];
counterCells = rs;
}
} finally {
cellsBusy = 0;
}
collide = false;
continue; // Retry with expanded table
}
h = ThreadLocalRandom.advanceProbe(h);
}
else if (cellsBusy == 0 && counterCells == as &&
U.compareAndSwapInt(this, CELLSBUSY, 0, 1)) {
boolean init = false;
try { // Initialize table
if (counterCells == as) {
// 初始化cells数组
CounterCell[] rs = new CounterCell[2];
rs[h & 1] = new CounterCell(x);
counterCells = rs;
init = true;
}
} finally {
cellsBusy = 0;
}
if (init)
break;
}
else if (U.compareAndSwapLong(this, BASECOUNT, v = baseCount, v + x))
break; // Fall back on using base
}
}
LongAdder
java.util.concurrent.atomic.LongAdder;
与LongAdder的逻辑一样,也是cells数组统计
public class LongAdder extends Striped64 implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 7249069246863182397L;
/**
* Creates a new adder with initial sum of zero.
*/
public LongAdder() {
}
/**
* Adds the given value.
*
* @param x the value to add
*/
public void add(long x) {
Cell[] as; long b, v; int m; Cell a;
if ((as = cells) != null || !casBase(b = base, b + x)) {
boolean uncontended = true;
if (as == null || (m = as.length - 1) < 0 ||
(a = as[getProbe() & m]) == null ||
!(uncontended = a.cas(v = a.value, v + x)))
longAccumulate(x, null, uncontended);
}
}
GET方法
同hashmap原理
public V get(Object key) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> e, p; int n, eh; K ek;
int h = spread(key.hashCode());
if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&
(e = tabAt(tab, (n - 1) & h)) != null) {
if ((eh = e.hash) == h) {
if ((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek)))
return e.val;
}
else if (eh < 0)
return (p = e.find(h, key)) != null ? p.val : null;
while ((e = e.next) != null) {
if (e.hash == h &&
((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek))))
return e.val;
}
}
return null;
}