Springboot 封装整活 Mybatis 动态查询条件SQL自动组装拼接
前言
ps:最近在参与3100保卫战,战况很激烈,刚刚打完仗,来更新一下之前写了一半的博客。
该篇针对日常写查询的时候,那些动态条件sql 做个简单的封装,自动生成(抛砖引玉,搞个小玩具,不喜勿喷)。
正文
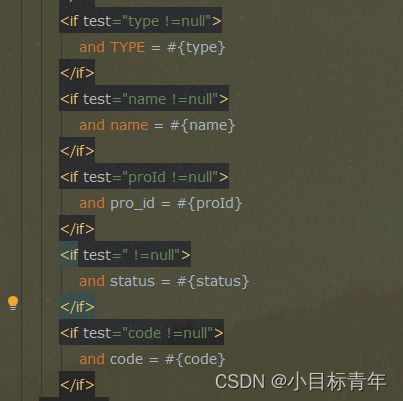
来看看我们平时写那些查询,基本上都要写的一些动态sql:
一个字段写一个if ,有没有人觉得烦的。
每张表的查询,很多都有这种需求,根据什么查询,根据什么查询,不为空就触发条件。
天天写天天写,copy 改,copy改, 有没有人觉得烦的。
可能有看官看到这就会说, 用插件自动生成就好了。
也有看官会说,用mybatis-plus就好了。
确实有道理,但是我就是想整个小玩具。你管我。
开整
本篇实现的封装小玩具思路:
①制定的规则(比如标记自定义注解 @JcSqlQuery 或是 函数命名带上JcDynamics)。
② 触发的查询符合规则的, 都自动去根据传参对象,不为空就自动组装 sql查询条件。
③ 利用mybatis @Select 注解,把默认表查询sql写好,顺便进到自定义的mybatis拦截器里面。
④组装完sql,就执行,完事。
先写mapper函数 :
/**
* @Author JCccc
* @Description
* @Date 2023/12/14 16:56
*/
@Mapper
public interface DistrictMapper {
@Select("select code,name,parent_code,full_name FROM s_district_info")
List queryListJcDynamics(District district);
@Select("select code,name,parent_code,full_name FROM s_district_info")
District queryOneJcDynamics(District district);
}
然后是ParamClassInfo.java 这个用于收集需要参与动态sql组装的类:
import lombok.Data;
/**
* @Author JCccc
* @Description
* @Date 2021/12/14 16:56
*/
@Data
public class ParamClassInfo {
private String classType;
private Object keyValue;
private String keyName;
}然后是一个自定义的mybatis拦截器(这里面写了一些小函数实现自主组装,下面有图解) :
MybatisInterceptor.java
import com.example.dotest.entity.ParamClassInfo;
import org.apache.ibatis.executor.Executor;
import org.apache.ibatis.mapping.*;
import org.apache.ibatis.plugin.*;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.ResultHandler;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.RowBounds;
import org.springframework.beans.BeanUtils;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.util.CollectionUtils;
import org.springframework.util.ReflectionUtils;
import java.beans.PropertyDescriptor;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.regex.Matcher;
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
import static java.util.regex.Pattern.*;
/**
* @Author JCccc
* @Description
* @Date 2021/12/14 16:56
*/
@Component
@Intercepts({
@Signature(type = Executor.class, method = "update", args = {MappedStatement.class, Object.class}),
@Signature(type = Executor.class, method = "query", args = {MappedStatement.class, Object.class, RowBounds.class, ResultHandler.class})
})
public class MybatisInterceptor implements Interceptor {
private final static String JC_DYNAMICS = "JcDynamics";
@Override
public Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {
//获取执行参数
Object[] objects = invocation.getArgs();
MappedStatement ms = (MappedStatement) objects[0];
Object objectParam = objects[1];
List paramClassInfos = convertParamList(objectParam);
String queryConditionSqlScene = getQueryConditionSqlScene(paramClassInfos);
//解析执行sql的map方法,开始自定义规则匹配逻辑
String mapperMethodAllName = ms.getId();
int lastIndex = mapperMethodAllName.lastIndexOf(".");
String mapperClassStr = mapperMethodAllName.substring(0, lastIndex);
String mapperClassMethodStr = mapperMethodAllName.substring((lastIndex + 1));
Class mapperClass = Class.forName(mapperClassStr);
Method[] methods = mapperClass.getMethods();
for (Method method : methods) {
if (method.getName().equals(mapperClassMethodStr) && mapperClassMethodStr.contains(JC_DYNAMICS)) {
BoundSql boundSql = ms.getSqlSource().getBoundSql(objects[1]);
String originalSql = boundSql.getSql().toLowerCase(Locale.CHINA).replace("[\\t\\n\\r]", " ");
//进行自动的 条件拼接
String newSql = originalSql + queryConditionSqlScene;
BoundSql newBoundSql = new BoundSql(ms.getConfiguration(), newSql,
boundSql.getParameterMappings(), boundSql.getParameterObject());
MappedStatement newMs = newMappedStatement(ms, new MyBoundSqlSqlSource(newBoundSql));
for (ParameterMapping mapping : boundSql.getParameterMappings()) {
String prop = mapping.getProperty();
if (boundSql.hasAdditionalParameter(prop)) {
newBoundSql.setAdditionalParameter(prop, boundSql.getAdditionalParameter(prop));
}
}
Object[] queryArgs = invocation.getArgs();
queryArgs[0] = newMs;
System.out.println("打印新SQL语句" + newSql);
}
}
//继续执行逻辑
return invocation.proceed();
}
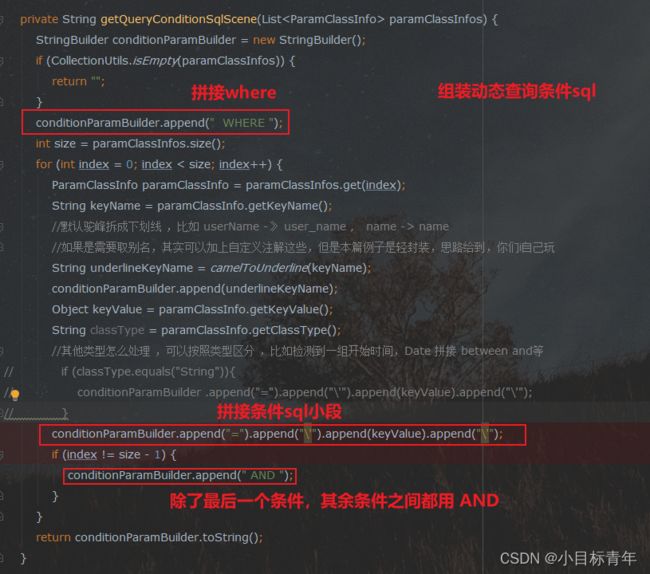
private String getQueryConditionSqlScene(List paramClassInfos) {
StringBuilder conditionParamBuilder = new StringBuilder();
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(paramClassInfos)) {
return "";
}
conditionParamBuilder.append(" WHERE ");
int size = paramClassInfos.size();
for (int index = 0; index < size; index++) {
ParamClassInfo paramClassInfo = paramClassInfos.get(index);
String keyName = paramClassInfo.getKeyName();
//默认驼峰拆成下划线 ,比如 userName -》 user_name , name -> name
//如果是需要取别名,其实可以加上自定义注解这些,但是本篇例子是轻封装,思路给到,你们i自己玩
String underlineKeyName = camelToUnderline(keyName);
conditionParamBuilder.append(underlineKeyName);
Object keyValue = paramClassInfo.getKeyValue();
String classType = paramClassInfo.getClassType();
//其他类型怎么处理 ,可以按照类型区分 ,比如检测到一组开始时间,Date 拼接 between and等
// if (classType.equals("String")){
// conditionParamBuilder .append("=").append("\'").append(keyValue).append("\'");
// }
conditionParamBuilder.append("=").append("\'").append(keyValue).append("\'");
if (index != size - 1) {
conditionParamBuilder.append(" AND ");
}
}
return conditionParamBuilder.toString();
}
private static List convertParamList(Object obj) {
List paramClassList = new ArrayList<>();
for (PropertyDescriptor pd : BeanUtils.getPropertyDescriptors(obj.getClass())) {
if (!"class".equals(pd.getName())) {
if (ReflectionUtils.invokeMethod(pd.getReadMethod(), obj) != null) {
ParamClassInfo paramClassInfo = new ParamClassInfo();
paramClassInfo.setKeyName(pd.getName());
paramClassInfo.setKeyValue(ReflectionUtils.invokeMethod(pd.getReadMethod(), obj));
paramClassInfo.setClassType(pd.getPropertyType().getSimpleName());
paramClassList.add(paramClassInfo);
}
}
}
return paramClassList;
}
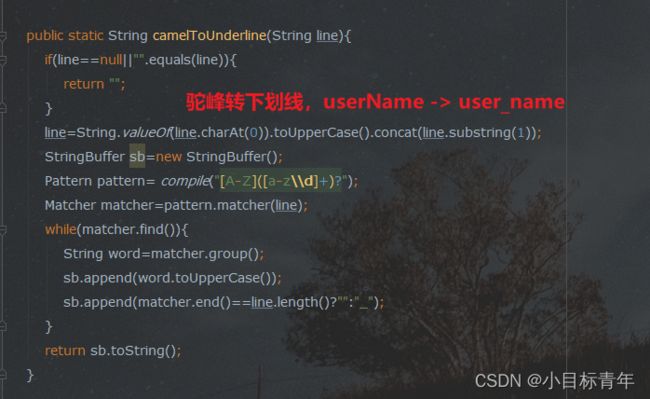
public static String camelToUnderline(String line){
if(line==null||"".equals(line)){
return "";
}
line=String.valueOf(line.charAt(0)).toUpperCase().concat(line.substring(1));
StringBuffer sb=new StringBuffer();
Pattern pattern= compile("[A-Z]([a-z\\d]+)?");
Matcher matcher=pattern.matcher(line);
while(matcher.find()){
String word=matcher.group();
sb.append(word.toUpperCase());
sb.append(matcher.end()==line.length()?"":"_");
}
return sb.toString();
}
@Override
public Object plugin(Object o) {
//获取代理权
if (o instanceof Executor) {
//如果是Executor(执行增删改查操作),则拦截下来
return Plugin.wrap(o, this);
} else {
return o;
}
}
/**
* 定义一个内部辅助类,作用是包装 SQL
*/
class MyBoundSqlSqlSource implements SqlSource {
private BoundSql boundSql;
public MyBoundSqlSqlSource(BoundSql boundSql) {
this.boundSql = boundSql;
}
@Override
public BoundSql getBoundSql(Object parameterObject) {
return boundSql;
}
}
private MappedStatement newMappedStatement(MappedStatement ms, SqlSource newSqlSource) {
MappedStatement.Builder builder = new
MappedStatement.Builder(ms.getConfiguration(), ms.getId(), newSqlSource, ms.getSqlCommandType());
builder.resource(ms.getResource());
builder.fetchSize(ms.getFetchSize());
builder.statementType(ms.getStatementType());
builder.keyGenerator(ms.getKeyGenerator());
if (ms.getKeyProperties() != null && ms.getKeyProperties().length > 0) {
builder.keyProperty(ms.getKeyProperties()[0]);
}
builder.timeout(ms.getTimeout());
builder.parameterMap(ms.getParameterMap());
builder.resultMaps(ms.getResultMaps());
builder.resultSetType(ms.getResultSetType());
builder.cache(ms.getCache());
builder.flushCacheRequired(ms.isFlushCacheRequired());
builder.useCache(ms.isUseCache());
return builder.build();
}
@Override
public void setProperties(Properties properties) {
//读取mybatis配置文件中属性
}
代码简析:
通过反射把 sql入参的对象 不为空的属性名和对应的值,拿出来:
组件动态查询的sql 语句 :
写个简单测试用例:
@Autowired
DistrictMapper districtMapper;
@Test
public void test() {
District query = new District();
query.setCode("110000");
query.setName("北京市");
District district = districtMapper.queryOneJcDynamics(query);
System.out.println(district.toString());
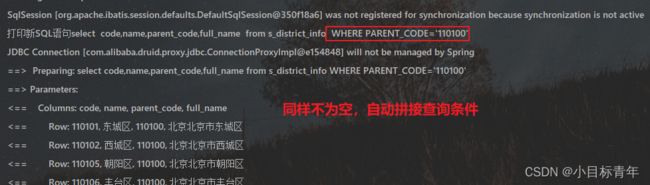
District listQuery = new District();
listQuery.setParentCode("110100");
List districts = districtMapper.queryListJcDynamics(listQuery);
System.out.println(districts.toString());
} 看下效果,可以看到都自动识别把不为空的字段属性和值拼接成查询条件了: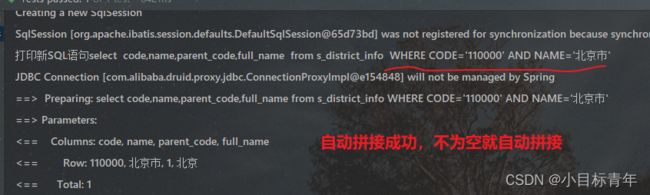
好了,该篇就到这。 抛砖引玉,领悟分步封装思路最重要,都去搞些小玩具娱乐娱乐吧。