类的创建、原型对象、原型链、继承
目录
一、类的创建
1、在ES5中创建
2、在ES6中创建
二、原型对象
1、构造函数(类)的原型对象
2、对象的原型对象
3、访问对象的构造方法
4、原型对象的原型对象
三、原型链的结构特点
1、构造函数和原型对象
2、实例对象和原型对象
3、Object对象的__proto__属性是null
四、this指针的指向
五、更改this指针的指向
1、apply()方法
2、call()方法
3、两个方法的区别
六、bind()方法
七、JavaScript代码的错误处理
1、try
2、throw抛出错误对象
3、常见的错误类型
八、继承
1、ES6的继承
2、ES5的继承
4、在继承过程中确定原型对象和实例对象之间关系的方法
5、原型链的问题
6、原型链问题的解决方法
(1)ES6中实现
(2)在ES5中实现
九、类的实例化
一、类的创建
1、在ES5中创建
构造函数名就是类名
2、在ES6中创建
(1)类的创建
(2)类表达式
二、原型对象
1、构造函数(类)的原型对象
通过prototype属性访问
class Student{
constructor(school,name,sex){
Student.school = school
this.name = name
this.sex = sex
}
display = function(){
let str = '学校:'+Student.school +'\n姓名:'+this.name+'\n性别:'+this.sex
console.log(str)
}
static sayHello(){ //静态成员方法使用static关键字进行定义
console.log('Hello'+Student.school)
}
}
console.log('构造方法的原型对象:',Student.prototype)
2、对象的原型对象
通过对象的__proto__属性访问(__两个下划线)
class Student{
constructor(school,name,sex){
Student.school = school
this.name = name
this.sex = sex
}
display = function(){
let str = '学校:'+Student.school +'\n姓名:'+this.name+'\n性别:'+this.sex
console.log(str)
}
static sayHello(){ //静态成员方法使用static关键字进行定义
console.log('Hello'+Student.school)
}
}
var s1 = new Student('西安交通大学','周瑜','男')
console.log('对象的原型对象:',s1.__proto__)![]()
3、访问对象的构造方法
访问对象的构造方法:在原型对象里面有一个constructor属性,指向对象的构造方法
(1)构造方法名 . prototype . constructor
(2)对象名 . constructor
function Person(){}
console.log(Person.prototype.constructor) //输出:[Function: Person]
var p1 = new Person()
console.log(p1.constructor) //输出:[Function: Person]
4、原型对象的原型对象
原型对象的原型对象:原型对象本身也是一个对象,所以它也有一个原型对象
(1)获取原型对象的原型对象: 构造方法名.prototype.__proto
(2)原型对象的原型对象构造方法: 构造方法名.prototype.__proto.constructor
function Student(){}
//输出原型对象的原型对象
console.log(Student.prototype.__proto__) //输出为:[Object: null prototype] {}
//输出原型对象的原型对象的构造方法
console.log(Student.prototype.__proto__.constructor) //输出为:[Function: Object]强调:A、JavaScript中的所有类都直接或间接的继承自Object;B、所有的对象都是通过构造方法生成的
三、原型链的结构特点
1、构造函数和原型对象
构造函数 ----(prototype)---->原型对象
原型对象 ----(constructor)---->构造函数
2、实例对象和原型对象
实例对象 ----(__proto__)---->原型对象
构造方法 ----( new )-----> 实例对象
3、Object对象的__proto__属性是null
四、this指针的指向
1、构造函数内部的this指向新创建的对象(当前对象)
function Person(){
this.name = 'AA'
}
var p1 = new Person() //this指向对象p1
var p2 = new Person() //this指向对象p2
console.log(p1)
console.log(p2)2、直接通过函数名调用函数时,this指向全局对象window
function sayHelli(){
return this //this指向全局对象window
}
var t = sayHello() //t的值是window
console.log(t)3、若将函数作为对象的方法调用,this指向该对象
function Student(n,s){
this.name = n;
this.sex = s;
this.display = function(){
console.log('姓名:'+this.name+'\n性别:'+this.sex)
}
}
var s1 = new Student('张飞','男')
s1.display() //通过对象名调用函数,此时this指向s1对象五、更改this指针的指向
1、apply()方法
/更改this指针的指向
function method(){
console.log(this.name)
}
var n1 = {name:'张三'}
var n2 = {name:'李四'}
method.apply(n1) //此时method方法的this指针指向n1
method.apply(n2) //此时method方法的this指针指向n2
2、call()方法
function method(){
console.log(this.name)
}
var n1 = {name:'张三'}
var n2 = {name:'李四'}
method.call(n1) //此时method方法的this指针指向n1
method.call(n2) //此时method方法的this指针指向n2
3、两个方法的区别
(1)在调用函数时,第一个参数默认是对象
(2)apply方法:除第一参数外,后面的参数打包成数组
(3)call方法:除第一参数外,后面的参数一个一个的传递
//apply()和call()的区别
function fun(a,b){
console.log(a)
console.log(b)
console.log(a+b)
}
fun.apply({},[1,2])
fun.call({},1,2)六、bind()方法
bind()方法:实现提前绑定,在绑定时提前传入调用函数时的参数
function method(a,b){
console.log(this.name+a+b)
}
var name = '张三'
var test = method.bind({name:'李四'},'3','4') //提前绑定参数
test()![]()
七、JavaScript代码的错误处理
1、try
一般情况下代码错误:
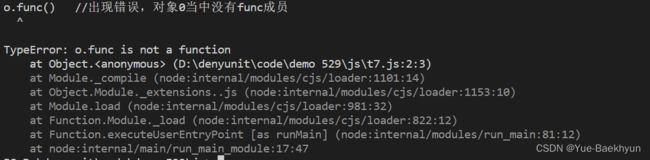
var o = {}
o.func() //出现错误,对象0当中没有func成员
console.log('test') //当上一条语句出现错误后,该语句不会被执行
利用try处理错误之后
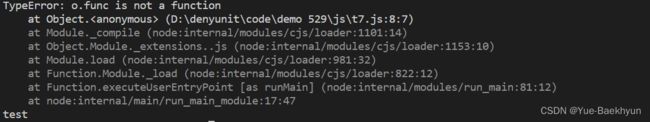
var o = {}
try{
o.func() //出现错误,对象0当中没有func成员
console.log('AAAAA')//不执行。因为上一条语句出现了错误TypeError(错误类型): o.func is not a function(错误的详细信息)
}catch(e){
console.log(e) //执行。打印错误的类型及其详细信息
}
console.log('test') //执行。前一条语句的错误已经被try-catch捕获并处理了,不影响该语句的执行
2、throw抛出错误对象
try {
let e1 = new Error('错误信息') //创建错误对象, Error是内置的错误类
throw e1 //抛出错误对象e1
} catch (error) { //catch捕获throw抛出的错误对象e1,将e1赋给参数error
console.log(error.message) //输出错误对象的信息
}![]()
3、常见的错误类型
(1)Error:普通错误。是其他错误对象的基类(其他错误对象都是继承Error)
(2)TypeError:变量或函数的参数出现类型错误
(3)SyntaxError:语法错误
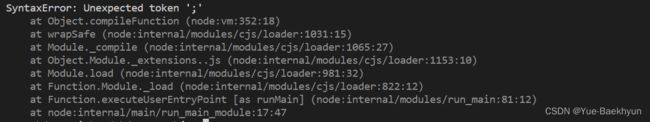
//语法错误
try {
var k = {;}
} catch (error) { //catch捕获throw抛出的错误对象e1,将e1赋给参数error
console.log(error.message) //输出错误对象的信息
}(4)RangeError:数值超出有效范围
//数值越界
try {
let arr = new Array(-1)// RangeErroe:Invalid array length
} catch (error) { //catch捕获throw抛出的错误对象e1,将e1赋给参数error
console.log(error) //输出错误对象的信息
}(5)URIError:解析URI编码出错
URI:统一资源标识符(Uniform Resource Identifier)
URL:全球资源定位器(Uniform Resource Locator)
八、继承
1、ES6的继承
ES6的继承:是单一继承(一个类的直接父类只能有一个)
2、ES5的继承
ES5的继承:通过原型对象实现(将父类的实例对象赋给子类的原型对象)
//1、定义父类
function SuperType(){
this.property = '中国农业银行'
}
//2、给SuperType的原型对象添加方法
SuperType.prototype.getSuperValue = function(){
return this.property
}
//3、定义子类构造方法
function SubType(){
this.subProperty = '中国工商银行'
}
//4、实现SubType对SuperType的继承
SubType.prototype = new SuperType() //通过原型对象实现子类对父类的继承。 把父类的实例对象赋给了子类的原型对象3、在原型链继承中实现方法的覆盖(Override)——子类的方法和父类的方法同名时,子类的方法就覆盖了父类的方法
实现方法:在子类的原型对象上添加和父类完全同名的方法
//1、定义父类
function SuperType(){
this.property = '中国农业银行'
}
//2、给SuperType的原型对象添加方法
SuperType.prototype.getSuperValue = function(){
return this.property
}
//3、定义子类构造方法
function SubType(){
this.subProperty = '中国工商银行'
}
//4、实现SubType对SuperType的继承
SubType.prototype = new SuperType() //通过原型对象实现子类对父类的继承。 把父类的实例对象赋给了子类的原型对象
//5、在子类的原型对象上增加了一个方法
SubType.prototype.getSubValue = function(){
return this.subProperty
}
//同名覆盖
SubType.prototype.getSuperValue = function(){
return '中国建设银行'
}
//6、创建一个子类的实例对象
let sub = new SubType()
let s1 = new SuperType()
console.log('调用父类的方法',sub.getSuperValue()) //子类的实例对象调用父类的方法
console.log('调用子类的方法',sub.getSubValue())
4、在继承过程中确定原型对象和实例对象之间关系的方法
(1)instanceof运算符:判断实例对象的类型
(2)isPrototypeOf()方法:判断原型对象的类型
//1、定义父类
function SuperType(){
this.property = '中国农业银行'
}
//2、给SuperType的原型对象添加方法
SuperType.prototype.getSuperValue = function(){
return this.property
}
//3、定义子类构造方法
function SubType(){
this.subProperty = '中国工商银行'
}
//4、实现SubType对SuperType的继承
SubType.prototype = new SuperType() //通过原型对象实现子类对父类的继承。 把父类的实例对象赋给了子类的原型对象
//5、在子类的原型对象上增加了一个方法
SubType.prototype.getSubValue = function(){
return this.subProperty
}
//6、创建一个子类的实例对象
let sub = new SubType()
let s1 = new SuperType()
console.log(sub instanceof Object) //true
console.log(sub instanceof SuperType) //true 子类对象的实例对象是父类
console.log(sub instanceof SubType) // true
console.log(s1 instanceof Object) //true
console.log(s1 instanceof SuperType) //true
console.log(s1 instanceof SubType) //false
console.log(Object.prototype.isPrototypeOf(sub)) //true
console.log(SuperType.prototype.isPrototypeOf(sub)) //true
console.log(SubType.prototype.isPrototypeOf(sub)) //true5、原型链的问题
(1)若原型中包含引用值,则该引用值会在所有的实例对象中共享。这是属性放在构造方法中定义而不放在原型对象中定义的原因
(2)子类的实例对象不能给父类的构造方法传参
6、原型链问题的解决方法
原型链问题的解决方法:盗用构造方法(又称为‘对象伪造’或‘经典继承’),基本思路就是在子类的构造方法中调用父类的构造方法
(1)ES6中实现
class Father{ //父类
constructor(name){ //形参name
this.name = name //this.name的name是属性
}
show(){
console.log('姓名:',this.name)
}
}
class Son extends Father{//子类
constructor(name){
super(name) //在子类方法中调用父类的构造方法 ----经典继承(对象伪造或盗用构造方法)
}
}(2)在ES5中实现
//ES5中
function Father(name){
this.name = name
this.colors = ['red','blue','green']
this.show = function(){
console.log('姓名:',this.name)
}
}
function Son(subname){
Father.call(this,subname) //继承父类;在子类的构造方法中通过call函数调用父类的构造方法
}
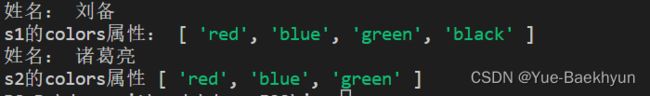
var s1 = new Son('刘备')
s1.colors.push('black')
s1.show()
console.log('s1的colors属性:',s1.colors)
let s2 = new Son('诸葛亮')
s2.show()
console.log('s2的colors属性',s2.colors)九、类的实例化
类的实例化:使用new运算符创建实例对象的过程。在使用new运算符调用类的构造方法时,会执行的操作有哪些?
1、在内存中创建一个新对象,给该对象分配一块存储区
2、在新对象的内部的[prototype]指针会指向构造函数的constructor属性
3、构造函数内部this指针指向新对象
4、执行构造函数的内部代码;即给新对象添加属性和方法
5、(如果构造函数返回非空对象,则返回该对象,否则)返回刚创建的新对象