C++ string类详解
⭐️ string
string 是表示字符串的字符串类,该类的接口与常规容器的接口基本一致,还有一些额外的操作 string 的常规操作,在使用 string 类时,需要使用 #include 以及 using namespace std;。
✨ 帮助文档:https://cplusplus.com/reference/string/string/string/
std::string::string 构造函数(constructor)
| 序号 | 构造函数 | 功能 |
|---|---|---|
| 1️⃣ | string() |
默认拷贝:构造空的string类对象,即空字符串,默认第一个字符位置是'\0',为了兼容c |
| 2️⃣ | string(const string& str) |
拷贝构造 |
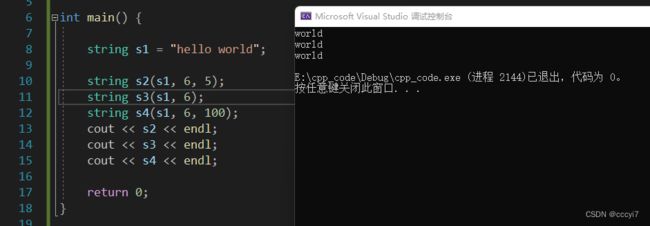
| 3️⃣ | string(const string& str , size_t pos , size_t len = npos) |
拷贝构造的重载,从字符串 pos 位置开始拷贝,拷贝 len 个字符 |
| 4️⃣ | string(const char * s) |
使用 c_string 来初始化 string 类对象 |
| 5️⃣ | string(const char * s , size_t n) |
从 s 指向的字符串中复制前 n 个字符 |
| 6️⃣ | string(size_t n , char c) |
使用 n 个 c 字符来填充字符串 |
| 7️⃣ | template |
复制一个迭代器序列的字符串 [first , last) |
#include output:
ps: npos 原型:static const size_t npos = -1;。npos 的访问:string::npos。无符号的 -1 相当于是整型的最大值,若当不传这个参数时, 或者 len 大于后面剩余字符的长度,那么使用默认参数 npos都是相当于 直到字符串的结束。[ 返回 ]
std::string::operator= 赋值重载
| 序号 | 函数名称 | 功能 |
|---|---|---|
| 1️⃣ | string& operator= (const string& str) |
用一个新的 string 对象替换当前 string 对象的内容 |
| 2️⃣ | string& operator= (const char * s) |
用一个c的字符串替换当前 string 对象内容 |
| 3️⃣ | string& operator= (char c) |
使用一个字符替换当前 string 对象的内容 |
#include output:
元素的访问
| 序号 | 函数名称 | 功能 |
|---|---|---|
| 1️⃣ | char& operator[] (size_t pos) |
返回当前 string 对象中 pos 位置字符的引用 |
| 2️⃣ | const char& operator[](size_t pos) const |
返回当前 const string 对象中 pos 位置字符的引用 |
| 3️⃣ | char& at (size_t pos) |
返回当前 string 对象中 pos 位置字符的引用 |
| 4️⃣ | const char& at (size_t pos) const |
返回当前 const string 对象中 pos 位置字符的引用 |
| 5️⃣ | char& back() |
返回当前 string 对象最后一个字符的引用 |
| 6️⃣ | const char& back() const |
返回当前 const string 对象最后一个字符的引用 |
| 7️⃣ | char& front() |
返回当前 string 对象第一个字符的引用 |
| 8️⃣ | const char& front() const |
返回当前 const string 对象第一个字符的引用 |
ps: at 和 [] 的行为是一样的,函数都会检查 pos 是否是合法位置,若不是,[] 是断言错误,而 at 是抛异常。
ps: back == [xx.size() - 1]、front == [0]。
#include output:
元素的长度
| 序号 | 函数名称 | 功能 |
|---|---|---|
| 1️⃣ | size_t size() const |
返回 string 对象实际字符的长度 |
| 2️⃣ | size_t length() const |
返回 string 对象实际字符的长度 |
#include string 迭代器
| 序号 | 函数名称 | 功能 |
|---|---|---|
| 1️⃣ | iterator begin() |
返回一个迭代器,该迭代器指向 string 对象的第一个字符 |
| 2️⃣ | const_iterator begin() const |
返回一个迭代器,该迭代器指向 const string 对象的第一个字符 |
| 3️⃣ | iterator end() |
返回一个迭代器,该迭代器指向 string 对象最后一个实际字符的下一个位置 |
| 4️⃣ | const_iterator end() const |
返回一个迭代器,该迭代器指向 const string 对象最后一个实际字符的下一个位置 |
| 5️⃣ | reverse_iterator rbegin() |
返回一个反向迭代器,该迭代器指向 string 对象最后一个实际字符的位置 |
| 6️⃣ | const_reverse_iterator rbegin() const |
返回一个反向迭代器,该迭代器指向 const string 对象最后一个实际字符的位置 |
| 7️⃣ | reverse_iterator() rend() |
返回一个反向迭代器,该迭代器指向 string 对象第一个字符的前一个位置 |
| 8️⃣ | const_reverse_iterator() rend() const |
返回一个反向迭代器,该迭代器指向 const string 对象第一个字符的前一个位置 |
ps: [ begin() , end() )、( rend() , rbegin() ]
#include output:
string 对象修改
| 序号 | 函数名称 | 功能 |
|---|---|---|
| 1️⃣ | void push_back (char c) |
在当前 string 对象的末尾追加一个 c 字符 |
| 2️⃣ | string& append (const string& str) |
在当前 string 对象的末尾追加一个 const string str 对象 |
| 3️⃣ | string& append (const string& str , size_t subpos , size_t sublen) |
在当前 string 对象的末尾追加一个 const string str 对象的子串,从 subpos 位置开始,拷贝 sublen 个字符过去 类似上面构造函数的 npos 用法 |
| 4️⃣ | string& append (const char* s); |
在当前 string 对象的末尾追加一个 c_string 字符串 |
| 5️⃣ | template |
追加一个迭代器序列的字符串 [first , last) |
#include output:
std::string::operator+= 运算符重载
| 序号 | 函数名称 | 功能 |
|---|---|---|
| 6️⃣ | string& operator+= (const string& str); |
在当前 string 对象的末尾追加一个 const string str 对象 |
| 7️⃣ | string& operator+= (const char* s); |
在当前 string 对象的末尾追加一个 c_string 字符串 |
| 8️⃣ | string& operator+= (char c); |
在当前 string 对象的末尾追加一个 c 字符 |
#include 元素的容量
| 序号 | 函数名称 | 功能 |
|---|---|---|
| 1️⃣ | size_t capacity() const |
返回当前 string 对象的容量大小 |
| 2️⃣ | void reserve (size_t n = 0) |
改变当前 string 对象的容量为 n |
| 3️⃣ | void resize (size_t n) |
将当前 string 对象的 size() 调整为 n 并初始化为 '\0' |
| 4️⃣ | void resize (size_t n , char c) |
将当前 string 对象的 size() 调整为 n 并初始化为 c |
| 5️⃣ | void clear(); |
删除当前 string 对象的所有内容,size() = 0 |
| 6️⃣ | bool empty() const |
若当前 string 对象为空返回 true,否则返回 false |
ps: reserve 是改变容量,而 resize 是改变 size() + 初始化,当 resize 的 n 传的比 string 的大小还小,则就是删除。
#include output:
std::string::insert 插入
ps: 需要的查文档即可,效率不高很少用。
std::string::erase 删除
std::string::c_str 返回c的字符串
| 序号 | 函数名称 | 功能 |
|---|---|---|
| 1️⃣ | const char* c_str() const |
返回c的字符串使用 '\0' 结尾 |
查找
| 序号 | 函数名称 | 功能 |
|---|---|---|
| 1️⃣ | size_t find (char c , size_t pos = 0) const |
从当前 string 对象的 pos 位置开始查找 c 字符,返回这个字符第一次出现的位置,否则返回 string::npos |
| 2️⃣ | string substr (size_t pos = 0 , size_t len = npos) const |
返回当前对象 pos 位置开始的 len 个字符的子串 |
#include | 序号 | 函数名称 | 功能 |
|---|---|---|
| 3️⃣ | size_t rfind (char c , size_t pos = npos) const |
从当前 string 对象的 pos 位置从后向前开始查找 c 字符,返回这个字符最后一次出现的位置,否则返回 string::npos |
其他
| 序号 | 函数名称 | 功能 |
|---|---|---|
| 1️⃣ | istream& getline (istream& is , string& str , char delim) |
输入一行字符遇到 delim 终止 |
| 2️⃣ | istream& getline (istream& is , string& str) |
输入一行字符遇到 \n 终止 |
| 3️⃣ | string to_string (int val) |
返回一个 val 的 string 对象 |
| 4️⃣ | int stoi (const string& str, size_t* idx = 0, int base = 10) |
字符串转整数。 idx 通常都为 nullptr,base 代表进制 |
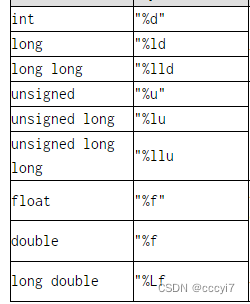
ps: to_string 支持的转换类型
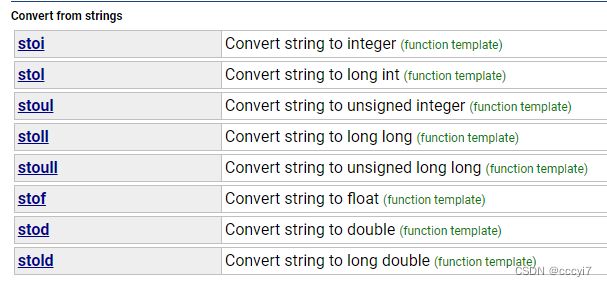
ps: string 可以转换为的类型
#include