第三讲:ApplicationContext的实现
这里写目录标题
- 一、前文回顾
- 二、基础代码准备
- 三、基于XML的ClassPathXmlApplicationContext
-
- 1. 创建spring-config.xml配置文件
- 2. 指定配置文件的路径
- 四、基于注解的AnnotationConfigApplicationContext
-
- 1. 新增一个配置类
- 2.指定配置类信息
- 五、基于注解和ServletWebServer应用容器支持的ApplicationContext
-
- 1. 内嵌一个基于Servlet技术的Web容器
- 2. Web的核心(DispatcherServlet)
- 3. 关联Web容器和DispatcherServlet
- 4. 注册一个Controller
一、前文回顾
在上一篇文章中,我们使用的一直是DefaultListableBeanFactory,他只是一个Bean工厂,不会自动运行,所有的功能都需要我们手动去调用,比如:注册BeanDefinition、调用AnnotationConfigUtils.registerAnnotationConfigProcessors(beanFactory)去注册处理器、往beanFactory里添加Bean后置处理器等操作。
但实际上,ApplicationContext的实现类会帮我们去做这些事情(refresh())。因此,我们一般使用到的都是ApplicationContext的实现类。
接下来,我们来看几个ApplicationContext的实现类。
二、基础代码准备
/**
* 测试ApplicationContext实现类
*
* @Author linqibin
* @Date 2023/8/20 18:51
* @Email [email protected]
*/
public class AcImplApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO coding here
}
static class Bean01{
public Bean01() {
System.out.println("Bean01构造函数~~~~");
}
}
static class Bean02{
private Bean01 bean01;
public Bean02() {
System.out.println("Bean02构造函数");
}
public Bean01 getBean01() {
return bean01;
}
}
}
三、基于XML的ClassPathXmlApplicationContext
该方式运行Spring是非常经典的,SSM时代用的就是ClassPathXmlApplicationContext。
1. 创建spring-config.xml配置文件
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="bean01" class="com.linqibin.spring.impl.AcImplApplication.Bean01"/>
<bean id="bean02" class="com.linqibin.spring.impl.AcImplApplication.Bean02">
<property name="bean01" ref="bean01"/>
bean>
beans>
2. 指定配置文件的路径
/**
* 基于配置文件的ApplicationContext实现类
*/
public static void testClassPathXmlApplicationContext() {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-config.xml");
Arrays.stream(context.getBeanDefinitionNames()).forEach(System.out::println);
// 获取注入的bean
Bean02 bean02 = (Bean02) context.getBean("bean02");
System.out.println(bean02.getBean01());
}
然后在main()调用testClassPathXmlApplicationContext()。
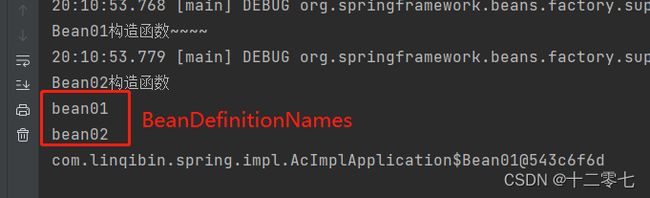
可以观察到,只要创建ClassPathXmlApplicationContext对象,就几乎把前文的功能实现了。
但BeanDefinitionNames的输出却只有两个,相比之下少了几个处理器的BeanDefinition。
这是因为基于XML方式默认不支持使用注解,只需在xml文件中加入如下配置,就能引入这些后置处理器的BeanDefinition。
四、基于注解的AnnotationConfigApplicationContext
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext是比较新的注解,非web应用的Springboot使用的就是该实现。需要指定一个配置类作为入口。
1. 新增一个配置类
@Configuration
static class Config {
@Bean
public Bean01 bean01() {
return new Bean01();
}
@Bean
public Bean02 bean02(Bean01 bean01) {
Bean02 bean02 = new Bean02();
bean02.setBean01(bean01);
return bean02;
}
}
2.指定配置类信息
/**
* 基于注解文件的ApplicationContext实现类
*/
public static void testAnnotationConfigApplicationContext() {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(Config.class);
Arrays.stream(context.getBeanDefinitionNames()).forEach(System.out::println);
// 获取注入的bean
Bean02 bean02 = (Bean02) context.getBean("bean02");
System.out.println(bean02.getBean01());
}
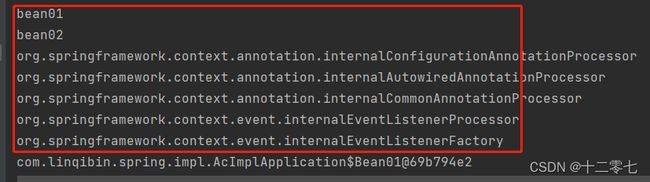
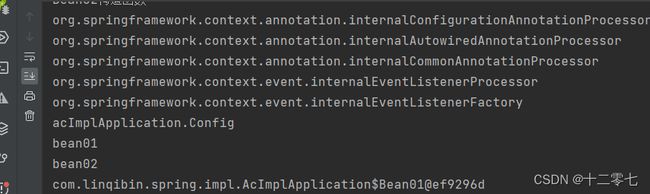
运行结果如下图,在BeanDefinitionNames中还额外多了一个BeanDefinition,因为配置类本身也会被管理。
五、基于注解和ServletWebServer应用容器支持的ApplicationContext
AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext是web应用使用的ApplicationContext。需要配置一些Web组件,并将配置文件作为参数启动。
1. 内嵌一个基于Servlet技术的Web容器
/**
* 启动内嵌的Tomcat
* @return
*/
@Bean
public TomcatServletWebServerFactory tomcatServletWeb() {
return new TomcatServletWebServerFactory();
}
2. Web的核心(DispatcherServlet)
/**
* 需要有前端调度器
* @return
*/
@Bean
public DispatcherServlet dispatcherServlet() {
return new DispatcherServlet();
}
3. 关联Web容器和DispatcherServlet
/**
* 将前面两者关联起来
* @param dispatcherServlet
* @return
*/
@Bean
public RegistrationBean dispatcherRegistrationBean(DispatcherServlet dispatcherServlet) {
return new DispatcherServletRegistrationBean(dispatcherServlet, "/");
}
4. 注册一个Controller
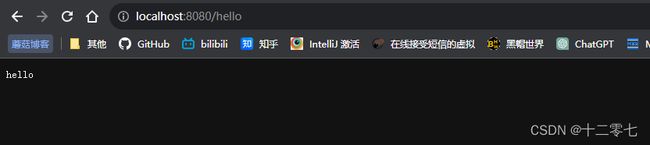
如果Bean的名称是/开头,并且返回值是Controller,那么他就是一个控制器方法。
@Bean("/hello")
public Controller helloController() {
return (request, response) -> {
response.getWriter().write("hello");
return null;
};
}
创建容器
new AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext(WebConfig.class);
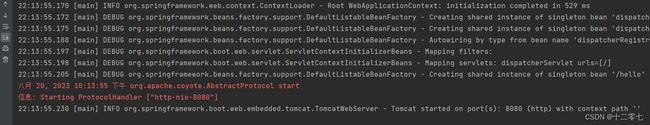
内嵌的Tomcat成功运行并监听了8080端口,打开浏览器访问指定路径: