csapp 深入理解计算机系統 笔记
csapp 深入理解计算机系統 笔记
- 参考
-
- lab
- 第1章:计算机系统漫游
- 第 2 章:信息的表示和处理
-
- Data Lab
- 第03章:程序的机器级表示
-
- Bomb Lab
参考
- 计算机速成课 | Crash Course 字幕组 (全40集 2018-5-1 精校完成)
- csapp重点解读
- 深入理解计算机系統 csapp
lab
- Lab Assignments
- Lab 直接下载
- 参考
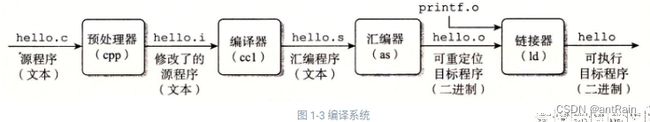
第1章:计算机系统漫游
Amdahl定律: 当我们对系统的某个部分加速时,其对系统整体性能的影响取决于该部分的重要性和加速程度, 某一个部分占的时间百分比为 α \alpha α ,然后,把这一部分的性能提升 k 倍,系统性能提速的倍数为:
S = 1 ( 1 − α ) + α / k S=\frac{1}{(1-\alpha)+\alpha/k} S=(1−α)+α/k1
第 2 章:信息的表示和处理
#include 输出:
gcc -g -O0 -o main main.c
./main
"小端表示:"
0x7fff82d76b84 0x67
0x7fff82d76b85 0x45
0x7fff82d76b86 0x23
0x7fff82d76b87 0x01
Data Lab
Data Lab: Manipulating Bits
wget http://csapp.cs.cmu.edu/3e/datalab-handout.tar
tar -xf datalab-handout.tar
# 直接安装gcc-multilib 可能会报
/usr/bin/ld: skipping incompatible /usr/lib/gcc/x86_64-linux-gnu/9/libgcc.a when searching for -lgcc
/usr/bin/ld: cannot find -lgcc: No such file or directory
# 安装对应版本的
sudo apt install -y gcc-9-multilib
# 编译与测试
make
./btest -f bitXor
参考
/* 德摩根定律
(1) x^y = (~x&y)|(~y&x) = ~(~((~x&y)) & (~((~y&x)))
(2)x ^ y = (x | y) & ~(x & y)
* bitXor - x^y using only ~ and &
*/
int bitXor(int x, int y) {
// return (~(x & y)) & (~(~x & ~y));
int a = ~(~x & y); //
int b = ~((~y)&x);
return ~(a&b);
}
// https://stackoverflow.com/questions/7300650/how-to-find-tmax-without-using-shifts
int isTmax(int x) {
int a = ~((x + 1) ^ x); // 当是最大值是为0
int b = !(x + 1);
return !(a + b);
}
/*
* allOddBits - return 1 if all odd-numbered bits in word set to 1
*/
int allOddBits(int x) {
int a1 = 0xAA;
int a2 = (a1<<8) | a1;
int a3 = (a2<<16) | a2;
return !(a3^(x&a3));
}
/*
* negate - return -x
* Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >>
*/
int negate(int x) {
return (~x)+1;
}
//3
/*
* isAsciiDigit - return 1 if 0x30 <= x <= 0x39 (ASCII codes for characters '0' to '9')
* Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >>
*/
int isAsciiDigit(int x) {
int a = !((x >> 3) ^ 0x06); // 判断 x>>3 是否为 110
return a | (!(x ^ 0x38)) | (!(x ^ 0x39)); // 0x38 0x39 单独判断
}
/*
* conditional - same as x ? y : z
* Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >> */
int conditional(int x, int y, int z) {
int mask = ((!!x) << 31) >> 31; // x 为真是 0xffffffff
return ((mask & y) | (~mask & z)) ;
}
/*
* isLessOrEqual - if x <= y then return 1, else return 0
* Legal ops: ! ~ & ^ | + << >>
*/
int isLessOrEqual(int x, int y) {
int sx = (x >> 31) & 0x1; // 获取最高符号位
int sy = (y >> 31) & 0x1;
int c1 = (~sy & sx); //y正x负,直接可以判定y>x
int c2 = (~sx & sy); //y负x正,直接可以判定y
int y_x = y + (~x + 1); // y-x
int sign = y_x >> 31; // 判断 y-x是否溢出
return c1 | (!c2 & !sign);
}
/*
* logicalNeg - implement the ! operator
* Legal ops: ~ & ^ | + << >>
*/
int logicalNeg(int x) {
// 特殊情况 0x80000000 相反数是一样的
int s1 = (x >> 31) & 1;
int s2 = ((~x+1) >> 31) & 1;
return (~(s1|s2))+2; // 所以不能使用 ^
}
第03章:程序的机器级表示
Bomb Lab
- CSAPP | Lab2-Bomb Lab 深入解析
- CSAPP实验之Bomb Lab详解
- x86-64 下函数调用及栈帧原理
- 【arm】常见函数调用约定(x86、x64、arm、arm64)
X64只有一种 fastcall 函数调用约定。
参数1、参数2、参数3、参数4分别保存在 RCX、RDX、R8D、R9D ,剩下的参数从右往左一次入栈,被调用者实现栈平衡,返回值存放在 RAX 中。
objdump -d ./bomb > bomb.asm
main 部分:
400e32: e8 67 06 00 00 call 40149e <read_line>
400e37: 48 89 c7 mov %rax,%rdi
400e3a: e8 a1 00 00 00 call 400ee0 <phase_1>
400e3f: e8 80 07 00 00 call 4015c4 <phase_defused>
0000000000401338 <strings_not_equal>:
401338: 41 54 push %r12
40133a: 55 push %rbp
40133b: 53 push %rbx
40133c: 48 89 fb mov %rdi,%rbx
40133f: 48 89 f5 mov %rsi,%rbp
401342: e8 d4 ff ff ff call 40131b <string_length>
401347: 41 89 c4 mov %eax,%r12d
40134a: 48 89 ef mov %rbp,%rdi
40134d: e8 c9 ff ff ff call 40131b <string_length>
调试
gdb ./bomb
(gdb) disassemble phase_1
Dump of assembler code for function phase_1:
0x0000000000400ee0 <+0>: sub $0x8,%rsp
0x0000000000400ee4 <+4>: mov $0x402400,%esi
0x0000000000400ee9 <+9>: call 0x401338 <strings_not_equal>
0x0000000000400eee <+14>: test %eax,%eax
0x0000000000400ef0 <+16>: je 0x400ef7 <phase_1+23>
0x0000000000400ef2 <+18>: call 0x40143a <explode_bomb>
0x0000000000400ef7 <+23>: add $0x8,%rsp
0x0000000000400efb <+27>: ret
End of assembler dump.
是将读入的%rdi 和 %rsi 进行对比
x [Address expression]
x /[Format] [Address expression]
x /[Length][Format] [Address expression]
x
(gdb) x/s 0x402400
0x402400: "Border relations with Canada have never been better."