【C++习题集】-- 堆
(用于复习)
目录
树概念及结构
名词概念
二叉树概念及结构
特殊的二叉树
满二叉树
完全二叉树
运算性质
二叉树存储结构
顺序存储
链式存储
堆 - 顺序存储
堆的性质
堆的实现
堆的应用
堆排序
直接建堆法
树概念及结构
概念:非线性的数据结构(形成的倒挂似树的结构 - 根朝上,叶朝下,子树之间不能有交集)。
名词概念
- 节点的度:一个节点含有的子树的个数称为该节点的度。
- 叶节点或终端节点:度为0的节点称为叶节点。
- 非终端节点或分支节点:度不为0的节点。
- 双亲节点或父节点:若一个节点含有子节点,则这个节点称为其子节点的父节点。
- 孩子节点或子节点:一个节点含有的子树的根节点称为该节点的子节点。
- 兄弟节点:具有相同父节点的节点互称为兄弟节点。
- 树的度:一棵树中,最大的节点的度称为树的度。
- 节点的层次:从根开始定义起,根为第1层,根的子节点为第2层,以此类推。
- 树的高度或深度:树中节点的最大层次。
- 堂兄弟节点:双亲在同一层的节点互为堂兄弟。
- 节点的祖先:从根到该节点所经分支上的所有节点。
- 子孙:以某节点为根的子树中任一节点都称为该节点的子孙。
- 森林:由m(m>0)棵互不相交的树的集合称为森林。
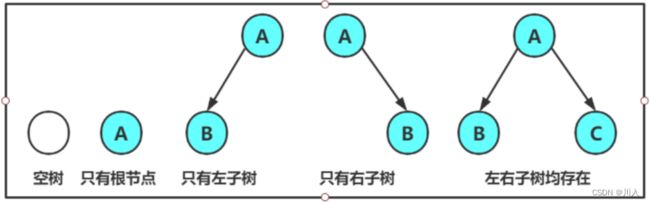
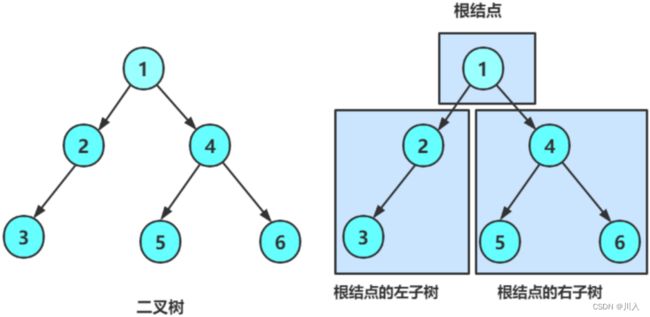
二叉树概念及结构
由一个根节点加上两棵别称为左子树和右子树的二叉树组成 - 子树可为空。
-
不存在度大于2的结点。
特殊的二叉树
满二叉树
每一个层的结点数都达到最大值,则结点总数:2^k - 1(K层数)。
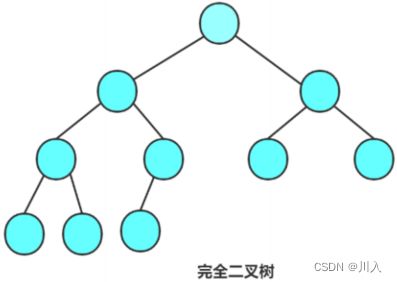
完全二叉树
特殊的完全二叉树 - 最后一层不满,但是是左到右是连续的。
(满二叉树是特殊的完全二叉树)
运算性质
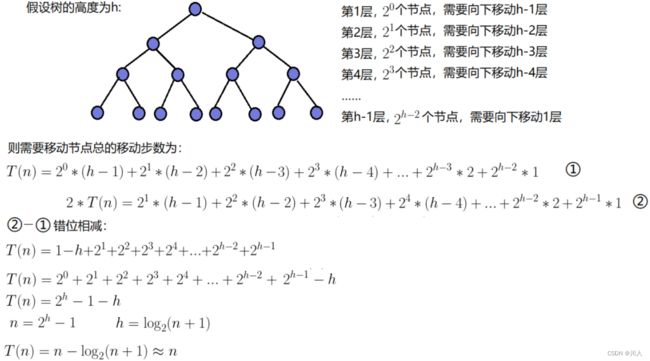
- 根节点的层数为1,则第i层上最多有2^(i - 1)个结点
-
根节点的层数为1,则深度h的最大结点数是2^h - 1
-
根节点的层数为1,n个结点的满二叉树的深度h = log2(n + 1)
-
如果度为0其叶结点个数为n,度为2的分支结点个数为m,则有:n = m + 1
-
n个结点的完全二叉树,以数组顺序对所有节点开始编号:
- 若i>0,i位置节点的双亲序号:(i - 1) / 2
- 若2i + 1 < n,左孩子序号:2i + 1,2i + 1 >= n否则无左孩子
- 若2i + 2 < n,右孩子序号:2i + 2,2i + 2 >= n否则无右孩子
一个具有767个节点的完全二叉树,其叶子节点个数为()
A、383B、384C、385D、386------------------------------------------正确答案:B------------------------------------------解析:不要只想最后一层,倒数第二层也是会有叶子节点的。首先以:
可以推算出是第1 ~ 9层为满二叉树,对应节点数:511。可以知道最后一层一定为叶子节点:256个。
然后根据完全二叉树是最后一层不满,但是是左到右是连续的,于是256 / 2 = 128,所以倒数第二层有128个是最后一层的父节点。
再根据:
可知倒数第二层有256个节点,于是叶子节点:256 + 256 - 128 = 384。
二叉树存储结构
顺序存储
用数组来存储,适合表示完全二叉树。
- 物理上:数组
- 逻辑上:二叉树
链式存储
用链表来表示一棵二叉树。
- 二叉链:数据域和左右指针域
- 三叉链:数据域和左右上指针域
堆 - 顺序存储
堆是一种特殊的完全二叉树,只不过父亲与儿子节点间有关系。顺序存储的完全二叉树典型的就是堆。(普通的二叉树是不适合用数组来存储的,因为可能会存在大量的空间浪费。而完全二叉树更适合使用顺序结构存储)
堆的性质
- 堆中某个节点的值总是不大于或不小于其父节点的值
- 小堆:父亲位,比孩子位,要小
- 大堆:父亲位,比孩子位,要大
- 堆总是一棵完全二叉树
堆的实现
#include
#include
namespace qcr_heap
{
typedef int HeapType;
struct Heap
{
int64_t _capacity; // 动态开辟可用大小
int64_t _size; // 实际数据占用大小
HeapType *_array; // 动态开辟一维数组
};
/*********
* 初始化堆
*********/
void HeapInit(Heap *heap)
{
assert(heap);
heap->_capacity = 0;
heap->_size = 0;
heap->_array = 0;
}
/*********
* 销毁堆
*********/
void HeapDestory(Heap *heap)
{
assert(heap);
heap->_capacity = 0;
heap->_size = 0;
free(heap->_array);
heap->_array = nullptr;
}
/*********
* 小根堆
*********/
bool less(HeapType element_1, HeapType element_2)
{
return element_1 < element_2;
}
/*********
* 大根堆
*********/
bool greater(HeapType element_1, HeapType element_2)
{
return element_1 > element_2;
}
/*********
* 交换数据
*********/
void swap(HeapType *element_1, HeapType *element_2)
{
HeapType tmp = *element_1;
*element_1 = *element_2;
*element_2 = tmp;
}
/*****************************
* 向上调整
* heap: 输入型参数,堆地址
* child: 输入型参数,排序的插入节点
* Func: 输入型参数,大小堆
*****************************/
void AdjustUp(Heap *heap, int64_t child, bool (*Func)(HeapType, HeapType))
{
assert(heap);
int64_t parent = (child - 1) / 2;
while (child > 0)
{
if (Func(heap->_array[child], heap->_array[parent]))
{
swap(&(heap->_array[child]), &(heap->_array[parent]));
child = parent;
parent = (child - 1) / 2;
}
else
break;
}
}
/*****************************
* 向下调整
* heap: 输入型参数,堆地址
* root: 输入型参数,排序的根节点
* Func: 输入型参数,大小堆
*****************************/
void AdjustDown(Heap *heap, int64_t root, bool (*Func)(HeapType, HeapType))
{
assert(heap);
int64_t parent = root;
int64_t child = parent * 2 + 1;
while (child < heap->_size)
{
if (child + 1 < heap->_size && Func(heap->_array[child + 1], heap->_array[child]))
{
child++;
}
if (Func(heap->_array[child], heap->_array[parent]))
{
swap(&(heap->_array[child]), &(heap->_array[parent]));
parent = child;
child = parent * 2 + 1;
}
else
{
break; // 符合堆就成立了,就没必要进行交换了。
}
}
}
/*****************************
* 存入数据
* heap: 输入型参数,堆地址
* data: 输入型参数,插入的数据
* Func: 输入型参数,大小堆
*****************************/
void HeapPush(Heap *heap, HeapType data, bool (*Func)(HeapType, HeapType))
{
assert(heap);
if (heap->_capacity == heap->_size)
{
int64_t newcapacity = heap->_capacity == 0 ? 5 : heap->_capacity * 2;
HeapType * tmp = (HeapType *)realloc(heap->_array, heap->_capacity*sizeof(HeapType);
if (tmp == nullptr)
{
printf("Capacuty Get Error!\n");
exit(-1);
}
heap->_array = tmp;
heap->_capacity = newcapacity;
}
heap->_array[heap->_size] = data;
AdjustUp(heap, heap->_size, Func);
(heap->_size)++;
}
/*****************************
* 按顺序全部输出
* heap: 输入型参数,堆地址
*****************************/
void HeapPrint(Heap *heap)
{
assert(heap);
for (uint64_t i = 0; i < heap->_size; i++)
{
std::cout << heap->_array[i] << " ";
}
std::cout << '\n';
}
/*****************************
* 首元素
* heap: 输入型参数,堆地址
*****************************/
HeapType HeapTop(Heap *heap)
{
assert(heap);
assert(heap->_size > 0);
return heap->_array[0];
}
/*****************************
* 判空
* heap: 输入型参数,堆地址
*****************************/
bool HeapEmpty(Heap *heap)
{
assert(heap);
return heap->_size == 0;
}
/*****************************
* 有效数据个数
* heap: 输入型参数,堆地址
*****************************/
int HeapSize(Heap *heap)
{
assert(heap);
return heap->_size;
}
/*****************************
* 判空
* heap: 输入型参数,堆地址
* Func: 输入型参数,大小堆
*****************************/
void HeapPop(Heap *heap, bool (*Func)(HeapType, HeapType))
{
assert(heap);
assert(heap->_size > 0);
heap->_array[0] = heap->_array[heap->_size - 1];
(heap->_size)--;
AdjustDown(heap, 0, Func);
}
} 已知小根堆为8,15,10,21,34,16,12,删除关键字 8 之后需重建堆,在此过程中,关键字之间的比较次数是()A、1B、2C、3D、4------------------------------------------正确答案:B------------------------------------------解析:首先我们需要知道,删除对应的调整算法是向下调整,所以其实在比较中有一个很重要的一项就是左右节点的比较,于是此处本质上的比较是需要在加上一次左右节点的比较。
堆的应用
堆排序
利用堆删除思想来进行排序。
TOP-K问题
1. 用数据集合中前K个元素来建堆
- 前k个最大的元素,则建小堆
- 前k个最小的元素,则建大堆
面试题 17.14. 最小K个数 - 力扣(LeetCode)
class Solution
{
public:
// 向上建堆
void adjustUp(vector &nums, int child)
{
int parent = (child - 1) / 2;
while (child > 0)
{
if (nums[child] > nums[parent])
{
swap(nums[child], nums[parent]);
child = parent;
parent = (child - 1) / 2;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
// 向下建堆
void adjustDown(vector &nums, int parent)
{
int child = parent * 2 + 1;
while (child < nums.size())
{
if (child + 1 < nums.size() && nums[child + 1] > nums[child])
{
child++;
}
if (nums[child] > nums[parent])
{
swap(nums[child], nums[parent]);
parent = child;
child = parent * 2 + 1;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
// 堆排序的TOP-k问题
vector smallestK(vector &arr, int k)
{
vector nums;
nums.reserve(k);
// 前K个元素来建堆
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++)
{
nums.push_back(arr[i]);
adjustUp(nums, nums.size() - 1);
}
// 对比堆顶元素
if (k != 0)
{
for (int i = k; i < arr.size(); i++)
{
if (arr[i] < nums[0])
{
nums[0] = arr[i];
adjustDown(nums, 0);
}
}
}
return nums;
}
}; 并不是最优的,并且还实现了两个堆算法,编码效率过低。
直接建堆法
原本利用向上建堆的方式,是并不够完美的,建堆的时间复杂度为O(N)。
而直接建堆法时间复杂度O(logn),其根本是利用向下建堆实现。
for (int i = (size - 1 - 1) / 2; i >= 0; i--)
{
ADjustDown(nums, i);
}class Solution
{
public:
// 向下建堆
void adjustDown(vector &nums, int parent)
{
int child = parent * 2 + 1;
while (child < nums.size())
{
if (child + 1 < nums.size() && nums[child + 1] > nums[child])
{
child++;
}
if (nums[child] > nums[parent])
{
swap(nums[child], nums[parent]);
parent = child;
child = parent * 2 + 1;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
// 堆排序的TOP-k问题
vector smallestK(vector &arr, int k)
{
vector nums;
nums.reserve(k);
// 前K个元素来建堆
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++)
{
nums.push_back(arr[i]);
}
for(int i = (k - 1 - 1) / 2; i >= 0; i--)
{
adjustDown(nums, i);
}
// 对比堆顶元素
if (k != 0)
{
for (int i = k; i < arr.size(); i++)
{
if (arr[i] < nums[0])
{
nums[0] = arr[i];
adjustDown(nums, 0);
}
}
}
return nums;
}
};