【K8S源码之Pod漂移】整体概况分析 controller-manager 中的 nodelifecycle controller(Pod的驱逐)
参考
-
k8s 污点驱逐详解-源码分析 - 掘金
-
k8s驱逐篇(5)-kube-controller-manager驱逐 - 良凯尔 - 博客园
-
k8s驱逐篇(6)-kube-controller-manager驱逐-NodeLifecycleController源码分析 - 良凯尔 - 博客园
-
k8s驱逐篇(7)-kube-controller-manager驱逐-taintManager源码分析 - 良凯尔 - 博客园
整体概况分析
- 基于 k8s 1.19 版本分析
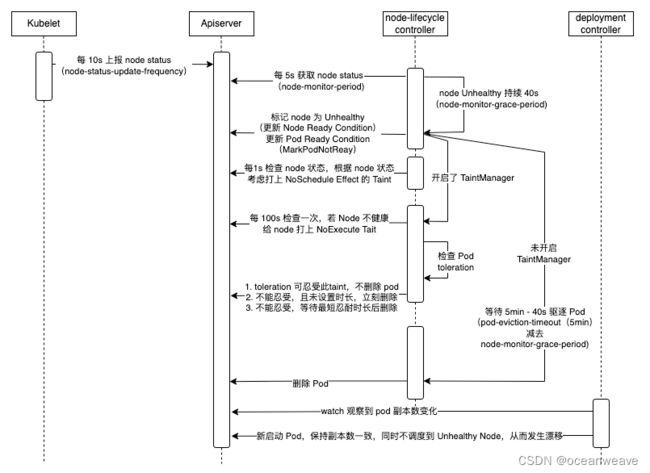
TaintManager 与 非TaintManager
- TaintManager 模式
- 发现 Node Unhealthy 后(也就是 Node Ready Condition = False 或 Unknown),会更新 Pod Ready Condition 为 False(表示 Pod 不健康),也会给 Node 打上 NoExecute Effect 的 Taint
- 之后 TaintManager 根据 Pod 的 Toleration 判断,是否有设置容忍 NoExecute Effect Taint 的 Toleration
- 没有 Toleration 的话,就立即驱逐
- 有 Toleration ,会根据 Toleration 设置的时长,定时删除该 Pod
- 默认情况下,会设置个 5min 的Toleration,也就是 5min 后会删除此 Pod
- 非 TaintManager 模式(默认模式)
- 发现 Node Unhealthy 后,会更新 Pod Ready Condition 为 False(表示 Pod 不健康)
- 之后会记录该 Node,等待 PodTimeout(5min) - nodegracePeriod(40s) 时间后,驱逐该 Node 上所有 Pod(Node级别驱逐),之后标记该 Node 为 evicted 状态(此处是代码中标记,资源上没有此状态)
- 之后便只考虑单 Pod 的驱逐(可能考虑部分 Pod 失败等)
- 若 Node 已经被标记为 evicted 状态,那么可以进行单 Pod 的驱逐
- 若 Node 没有被标记为 evicted 状态,那将 Node 标记为 tobeevicted 状态,等待上面 Node 级别的驱逐
代码中的几个存储结构
| nodeEvictionMap *nodeEvictionMap | // nodeEvictionMap stores evictionStatus *data for each node. *type nodeEvictionMap struct { lock sync.Mutex nodeEvictions map[string]evictionStatus } |
记录所有 node 的状态 1. 健康 unmarked 2. 等待驱逐 tobeevicted 3. 驱逐完成 evicted |
| zoneStates map[string]ZoneState | type ZoneState string | 记录 zone 的健康状态 1. 新zone Initial 2. 健康的zone Normal 3. 部分健康zone PartialDisruption 4. 完全不健康 FullDisruption 这个是用于设置该zone 的驱逐速率 |
| zonePodEvictor map[string]*scheduler.RateLimitedTimedQueue | 失联(不健康)的 Node 会放入此结构中,等待被驱逐,之后nodeEvictionMap 对应的状态记录会被设置为 evicted 1. 该结构,key 为zone,value 为限速队列处理(也就是上面驱逐效率起作用的地方) 2. 当一个 node 不健康,首先会计算出该 node 对应的zone 3. 然后放入该结构中 |
|
| nodeHealthMap *nodeHealthMap | type nodeHealthMap struct { lock sync.RWMutex nodeHealths map[string]*nodeHealthData } |
|
| type nodeHealthData struct { probeTimestamp metav1.Time readyTransitionTimestamp metav1.Time status *v1.NodeStatus lease *coordv1.Lease } |
记录每个node的健康状态,主要在 monitorHealth 函数中使用 1. 其中 probeTimestamp 最关键,该参数记录该 Node 最后一次健康的时间,也就是失联前最后一个 lease 的时间 2. 之后根据 probeTimestamp 和宽限时间 gracePeriod,判断该 node 是否真正失联,并设置为 unknown 状态 |
整体代码流程分析
// Run starts an asynchronous loop that monitors the status of cluster nodes.
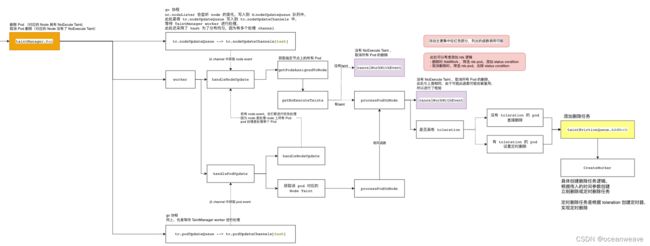
func (nc *Controller) Run(stopCh <-chan struct{}) {
defer utilruntime.HandleCrash()
klog.Infof("Starting node controller")
defer klog.Infof("Shutting down node controller")
// 1.等待leaseInformer、nodeInformer、podInformerSynced、daemonSetInformerSynced同步完成。
if !cache.WaitForNamedCacheSync("taint", stopCh, nc.leaseInformerSynced, nc.nodeInformerSynced, nc.podInformerSynced, nc.daemonSetInformerSynced) {
return
}
// 2.如果enable-taint-manager=true,开启nc.taintManager.Run
if nc.runTaintManager {
go nc.taintManager.Run(stopCh)
}
// Close node update queue to cleanup go routine.
defer nc.nodeUpdateQueue.ShutDown()
defer nc.podUpdateQueue.ShutDown()
// 3.执行doNodeProcessingPassWorker,这个是处理nodeUpdateQueue队列的node
// Start workers to reconcile labels and/or update NoSchedule taint for nodes.
for i := 0; i < scheduler.UpdateWorkerSize; i++ {
// Thanks to "workqueue", each worker just need to get item from queue, because
// the item is flagged when got from queue: if new event come, the new item will
// be re-queued until "Done", so no more than one worker handle the same item and
// no event missed.
go wait.Until(nc.doNodeProcessingPassWorker, time.Second, stopCh)
}
// 4.doPodProcessingWorker,这个是处理podUpdateQueue队列的pod
for i := 0; i < podUpdateWorkerSize; i++ {
go wait.Until(nc.doPodProcessingWorker, time.Second, stopCh)
}
// 5. 如果开启了feature-gates=TaintBasedEvictions=true,执行doNoExecuteTaintingPass函数。否则执行doEvictionPass函数
if nc.useTaintBasedEvictions {
// Handling taint based evictions. Because we don't want a dedicated logic in TaintManager for NC-originated
// taints and we normally don't rate limit evictions caused by taints, we need to rate limit adding taints.
go wait.Until(nc.doNoExecuteTaintingPass, scheduler.NodeEvictionPeriod, stopCh)
} else {
// Managing eviction of nodes:
// When we delete pods off a node, if the node was not empty at the time we then
// queue an eviction watcher. If we hit an error, retry deletion.
go wait.Until(nc.doEvictionPass, scheduler.NodeEvictionPeriod, stopCh)
}
// 6.一直监听node状态是否健康
// Incorporate the results of node health signal pushed from kubelet to master.
go wait.Until(func() {
if err := nc.monitorNodeHealth(); err != nil {
klog.Errorf("Error monitoring node health: %v", err)
}
}, nc.nodeMonitorPeriod, stopCh)
<-stopCh
}
MonitorNodeHealth
此部分有如下几个作用
-
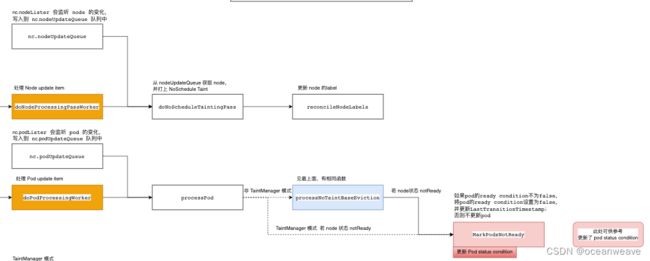
读取 Node 的 Label,用于确定 Node 属于哪个 zone;若该 zone 是新增的,就注册到 zonePodEvictor 或 zoneNoExecuteTainter (TaintManager 模式)
-
zonePodEvictor 后续用于该 zone 中失联的 Node,用于 Node 级别驱逐(就是驱逐 Node 上所有 Pod,并设置为 evicted 状态,此部分参见)
-
// pkg/controller/nodelifecycle/node_lifecycle_controller.go // addPodEvictorForNewZone checks if new zone appeared, and if so add new evictor. // dfy: 若出现新的 zone ,初始化 zonePodEvictor 或 zoneNoExecuteTainter func (nc *Controller) addPodEvictorForNewZone(node *v1.Node) { nc.evictorLock.Lock() defer nc.evictorLock.Unlock() zone := utilnode.GetZoneKey(node) // dfy: 若出现新的 zone ,初始化 zonePodEvictor 或 zoneNoExecuteTainter if _, found := nc.zoneStates[zone]; !found { // dfy: 没有找到 zone value,设置为 Initial nc.zoneStates[zone] = stateInitial // dfy: 没有 TaintManager,创建一个 限速队列,不太清楚有什么作用??? if !nc.runTaintManager { // dfy: zonePodEvictor 负责将 pod 从无响应的节点驱逐出去 nc.zonePodEvictor[zone] = scheduler.NewRateLimitedTimedQueue( flowcontrol.NewTokenBucketRateLimiter(nc.evictionLimiterQPS, scheduler.EvictionRateLimiterBurst)) } else { // dfy: zoneNoExecuteTainter 负责为 node 打上污点 taint nc.zoneNoExecuteTainter[zone] = scheduler.NewRateLimitedTimedQueue( flowcontrol.NewTokenBucketRateLimiter(nc.evictionLimiterQPS, scheduler.EvictionRateLimiterBurst)) } // Init the metric for the new zone. klog.Infof("Initializing eviction metric for zone: %v", zone) evictionsNumber.WithLabelValues(zone).Add(0) } } func (nc *Controller) doEvictionPass() { nc.evictorLock.Lock() defer nc.evictorLock.Unlock() for k := range nc.zonePodEvictor { // Function should return 'false' and a time after which it should be retried, or 'true' if it shouldn't (it succeeded). nc.zonePodEvictor[k].Try(func(value scheduler.TimedValue) (bool, time.Duration) { // dfy: 此处 value.Value 存储的是 Cluster Name node, err := nc.nodeLister.Get(value.Value) if apierrors.IsNotFound(err) { klog.Warningf("Node %v no longer present in nodeLister!", value.Value) } else if err != nil { klog.Warningf("Failed to get Node %v from the nodeLister: %v", value.Value, err) } nodeUID, _ := value.UID.(string) // dfy: 获得分配到该节点上的 Pod pods, err := nc.getPodsAssignedToNode(value.Value) if err != nil { utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("unable to list pods from node %q: %v", value.Value, err)) return false, 0 } // dfy: 删除 Pod remaining, err := nodeutil.DeletePods(nc.kubeClient, pods, nc.recorder, value.Value, nodeUID, nc.daemonSetStore) if err != nil { // We are not setting eviction status here. // New pods will be handled by zonePodEvictor retry // instead of immediate pod eviction. utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("unable to evict node %q: %v", value.Value, err)) return false, 0 } // dfy: 在nodeEvictionMap设置node的状态为evicted if !nc.nodeEvictionMap.setStatus(value.Value, evicted) { klog.V(2).Infof("node %v was unregistered in the meantime - skipping setting status", value.Value) } if remaining { klog.Infof("Pods awaiting deletion due to Controller eviction") } if node != nil { zone := utilnode.GetZoneKey(node) evictionsNumber.WithLabelValues(zone).Inc() } return true, 0 }) } }
-
-
监听 Node 健康状态(通过监听 Node Lease 进行判别)
-
若 Lease 不更新,且超过了容忍时间 gracePeriod,认为该 Node 失联(更新 Status Ready Condition 为 Unknown)
-
// tryUpdateNodeHealth checks a given node's conditions and tries to update it. Returns grace period to // which given node is entitled, state of current and last observed Ready Condition, and an error if it occurred. func (nc *Controller) tryUpdateNodeHealth(node *v1.Node) (time.Duration, v1.NodeCondition, *v1.NodeCondition, error) { // 省略一大部分 probeTimestamp 更新逻辑 // dfy: 通过 lease 更新,来更新 probeTimestamp observedLease, _ := nc.leaseLister.Leases(v1.NamespaceNodeLease).Get(node.Name) if observedLease != nil && (savedLease == nil || savedLease.Spec.RenewTime.Before(observedLease.Spec.RenewTime)) { nodeHealth.lease = observedLease nodeHealth.probeTimestamp = nc.now() } // dfy: 注意此处, Lease 没更新,导致 probeTimestamp 没变动,因此 现在时间超过了容忍时间,将此 Node 视作失联 Node if nc.now().After(nodeHealth.probeTimestamp.Add(gracePeriod)) { // NodeReady condition or lease was last set longer ago than gracePeriod, so // update it to Unknown (regardless of its current value) in the master. nodeConditionTypes := []v1.NodeConditionType{ v1.NodeReady, v1.NodeMemoryPressure, v1.NodeDiskPressure, v1.NodePIDPressure, // We don't change 'NodeNetworkUnavailable' condition, as it's managed on a control plane level. // v1.NodeNetworkUnavailable, } nowTimestamp := nc.now() // dfy: 寻找 node 是否有上面几个异常状态 for _, nodeConditionType := range nodeConditionTypes { // dfy: 具有异常状态,就进行记录 _, currentCondition := nodeutil.GetNodeCondition(&node.Status, nodeConditionType) if currentCondition == nil { klog.V(2).Infof("Condition %v of node %v was never updated by kubelet", nodeConditionType, node.Name) node.Status.Conditions = append(node.Status.Conditions, v1.NodeCondition{ Type: nodeConditionType, Status: v1.ConditionUnknown, Reason: "NodeStatusNeverUpdated", Message: "Kubelet never posted node status.", LastHeartbeatTime: node.CreationTimestamp, LastTransitionTime: nowTimestamp, }) } else { klog.V(2).Infof("node %v hasn't been updated for %+v. Last %v is: %+v", node.Name, nc.now().Time.Sub(nodeHealth.probeTimestamp.Time), nodeConditionType, currentCondition) if currentCondition.Status != v1.ConditionUnknown { currentCondition.Status = v1.ConditionUnknown currentCondition.Reason = "NodeStatusUnknown" currentCondition.Message = "Kubelet stopped posting node status." currentCondition.LastTransitionTime = nowTimestamp } } } // We need to update currentReadyCondition due to its value potentially changed. _, currentReadyCondition = nodeutil.GetNodeCondition(&node.Status, v1.NodeReady) if !apiequality.Semantic.DeepEqual(currentReadyCondition, &observedReadyCondition) { if _, err := nc.kubeClient.CoreV1().Nodes().UpdateStatus(context.TODO(), node, metav1.UpdateOptions{}); err != nil { klog.Errorf("Error updating node %s: %v", node.Name, err) return gracePeriod, observedReadyCondition, currentReadyCondition, err } nodeHealth = &nodeHealthData{ status: &node.Status, probeTimestamp: nodeHealth.probeTimestamp, readyTransitionTimestamp: nc.now(), lease: observedLease, } return gracePeriod, observedReadyCondition, currentReadyCondition, nil } } return gracePeriod, observedReadyCondition, currentReadyCondition, nil }
-
-
根据 zone 设置驱逐速率
-
每个 zone 有不同数量的 Node,根据该 zone 中 Node 失联数量的占比,设置不同的驱逐速率
-
// dfy: 1. 计算 zone 不健康程度; 2. 根据 zone 不健康程度设置不同的驱逐速率 func (nc *Controller) handleDisruption(zoneToNodeConditions map[string][]*v1.NodeCondition, nodes []*v1.Node) { newZoneStates := map[string]ZoneState{} allAreFullyDisrupted := true for k, v := range zoneToNodeConditions { zoneSize.WithLabelValues(k).Set(float64(len(v))) // dfy: 计算该 zone 的不健康程度(就是失联 node 的占比) // nc.computeZoneStateFunc = nc.ComputeZoneState unhealthy, newState := nc.computeZoneStateFunc(v) zoneHealth.WithLabelValues(k).Set(float64(100*(len(v)-unhealthy)) / float64(len(v))) unhealthyNodes.WithLabelValues(k).Set(float64(unhealthy)) if newState != stateFullDisruption { allAreFullyDisrupted = false } newZoneStates[k] = newState if _, had := nc.zoneStates[k]; !had { klog.Errorf("Setting initial state for unseen zone: %v", k) nc.zoneStates[k] = stateInitial } } allWasFullyDisrupted := true for k, v := range nc.zoneStates { if _, have := zoneToNodeConditions[k]; !have { zoneSize.WithLabelValues(k).Set(0) zoneHealth.WithLabelValues(k).Set(100) unhealthyNodes.WithLabelValues(k).Set(0) delete(nc.zoneStates, k) continue } if v != stateFullDisruption { allWasFullyDisrupted = false break } } // At least one node was responding in previous pass or in the current pass. Semantics is as follows: // - if the new state is "partialDisruption" we call a user defined function that returns a new limiter to use, // - if the new state is "normal" we resume normal operation (go back to default limiter settings), // - if new state is "fullDisruption" we restore normal eviction rate, // - unless all zones in the cluster are in "fullDisruption" - in that case we stop all evictions. if !allAreFullyDisrupted || !allWasFullyDisrupted { // We're switching to full disruption mode if allAreFullyDisrupted { klog.V(0).Info("Controller detected that all Nodes are not-Ready. Entering master disruption mode.") for i := range nodes { if nc.runTaintManager { _, err := nc.markNodeAsReachable(nodes[i]) if err != nil { klog.Errorf("Failed to remove taints from Node %v", nodes[i].Name) } } else { nc.cancelPodEviction(nodes[i]) } } // We stop all evictions. for k := range nc.zoneStates { if nc.runTaintManager { nc.zoneNoExecuteTainter[k].SwapLimiter(0) } else { nc.zonePodEvictor[k].SwapLimiter(0) } } for k := range nc.zoneStates { nc.zoneStates[k] = stateFullDisruption } // All rate limiters are updated, so we can return early here. return } // We're exiting full disruption mode if allWasFullyDisrupted { klog.V(0).Info("Controller detected that some Nodes are Ready. Exiting master disruption mode.") // When exiting disruption mode update probe timestamps on all Nodes. now := nc.now() for i := range nodes { v := nc.nodeHealthMap.getDeepCopy(nodes[i].Name) v.probeTimestamp = now v.readyTransitionTimestamp = now nc.nodeHealthMap.set(nodes[i].Name, v) } // We reset all rate limiters to settings appropriate for the given state. for k := range nc.zoneStates { // dfy: 设置 zone 的驱逐速率 nc.setLimiterInZone(k, len(zoneToNodeConditions[k]), newZoneStates[k]) nc.zoneStates[k] = newZoneStates[k] } return } // We know that there's at least one not-fully disrupted so, // we can use default behavior for rate limiters for k, v := range nc.zoneStates { newState := newZoneStates[k] if v == newState { continue } klog.V(0).Infof("Controller detected that zone %v is now in state %v.", k, newState // dfy: 设置 zone 的驱逐速率 nc.setLimiterInZone(k, len(zoneToNodeConditions[k]), newState) nc.zoneStates[k] = newState } } } // ComputeZoneState returns a slice of NodeReadyConditions for all Nodes in a given zone. // The zone is considered: // - fullyDisrupted if there're no Ready Nodes, // - partiallyDisrupted if at least than nc.unhealthyZoneThreshold percent of Nodes are not Ready, // - normal otherwise func (nc *Controller) ComputeZoneState(nodeReadyConditions []*v1.NodeCondition) (int, ZoneState) { readyNodes := 0 notReadyNodes := 0 for i := range nodeReadyConditions { if nodeReadyConditions[i] != nil && nodeReadyConditions[i].Status == v1.ConditionTrue { readyNodes++ } else { notReadyNodes++ } } switch { case readyNodes == 0 && notReadyNodes > 0: return notReadyNodes, stateFullDisruption case notReadyNodes > 2 && float32(notReadyNodes)/float32(notReadyNodes+readyNodes) >= nc.unhealthyZoneThreshold: return notReadyNodes, statePartialDisruption default: return notReadyNodes, stateNormal } } // dfy: 根据该 zone 健康状态(也就是健康比例),设置驱逐效率(频率) func (nc *Controller) setLimiterInZone(zone string, zoneSize int, state ZoneState) { switch state { case stateNormal: if nc.runTaintManager { nc.zoneNoExecuteTainter[zone].SwapLimiter(nc.evictionLimiterQPS) } else { nc.zonePodEvictor[zone].SwapLimiter(nc.evictionLimiterQPS) } case statePartialDisruption: if nc.runTaintManager { nc.zoneNoExecuteTainter[zone].SwapLimiter( nc.enterPartialDisruptionFunc(zoneSize)) } else { nc.zonePodEvictor[zone].SwapLimiter( nc.enterPartialDisruptionFunc(zoneSize)) } case stateFullDisruption: if nc.runTaintManager { nc.zoneNoExecuteTainter[zone].SwapLimiter( nc.enterFullDisruptionFunc(zoneSize)) } else { nc.zonePodEvictor[zone].SwapLimiter( nc.enterFullDisruptionFunc(zoneSize)) } } }
-
-
进行 Pod 驱逐的处理 proceeNoTaintBaseEviction
TaintManger.Run
-
TainManager 的驱逐逻辑,看代码不难理解,大概说明
-
若开启 TaintManager 模式,所有 Pod、Node 的改变都会被放入,nc.tc.podUpdateQueue 和 nc.tc.nodeUpdateQueue 中
-
当 Node 失联时,会被打上 NoExecute Effect Taint(不在此处,在 main Controller.Run 函数中)
-
此处会先处理 nc.tc.nodeUpdateQueue 的驱逐
-
首先会检查 Node 是否有 NoExecute Effect Taint;没有就取消驱逐
-
有的话,进行 Pod 的逐个驱逐,检查 Pod 是否有该 Taint 的 toleration,有的话,就根据 toleration 设置 pod 的定时删除;没有 Toleration,就立即删除
-
-
接下来处理 nc.tc.podUpdateQueue 的驱逐
- 进行 Pod 的逐个驱逐,检查 Pod 是否有该 Taint 的 toleration,有的话,就根据 toleration 设置 pod 的定时删除;没有 Toleration,就立即删除
-
Node Pod 的处理
- 此处就是 nc.podUpdateQueue 和 nc.NodeUpdateQueue 的一些驱逐逻辑
- 比如给 Node 打上 NoSchedule Taint
- 检测到 Node 不健康,给 Pod 打上 Ready Condition = False 的 Status Condition
- 进行 Pod 驱逐的处理 proceeNoTaintBaseEviction
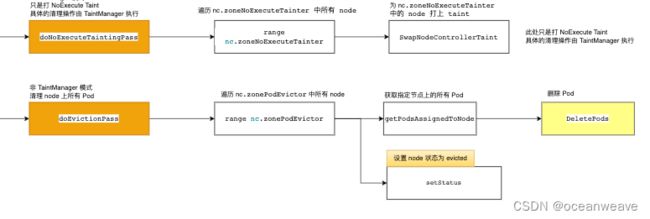
驱逐
- 此处 TaintManager 模式,只是打上 NoExecute Effect Taint —— doNoExecuteTaintingPass 函数
- 非 TaintManager 模式,会清理 zonePodEvicotr 记录的 Node 上的所有 Pod( Node 级别驱逐)